Redis实战2 - 使用Redis构建支持程序
使用Redis构建支持程序
构建的不是应用程序,而是记录应用程序信息、记录访客信息、为应用程序提供配置信息等手段来帮助和支持应用程序。
使用Redis记录日志
如何用Redis存储与世界紧密相关的日志
最新日志
将最新消息以列表形式存储在Redis中
查看代码
def log_recent(conn, name, message, level, pipe=None):
dest = 'rescent:%s:%s'%(name, level)
message = time.asctime() + ' ' + message
pipe = pipe or conn.pipeline()
pipe.lpush(dest, message)
pipe.ltrim(dest, 0, 99)
pipe.execute()最常见日志
查看代码
def log_common(conn:redis.Redis, name, msg, level, timeout=5):
dest = 'common:%s:%s'%(name, level) # 存储近期常见日志消息的键
start_key = dest + ':start' # 统计的是每小时内最常见日志,故使用一个键保存当前小时数
pipe = conn.pipeline()
end = time.time() + timeout
while time.time() < end:
try:
pipe.watch(start_key) # 监视当前小时数,确保轮换操作可正确执行
hour_start = datetime.datetime.now().hour
existing = int(str(pipe.get(start_key)))
pipe.multi()
if existing and existing < hour_start: # 将前一个小时的日志归档
pipe.rename(dest, dest+':last')
pipe.rename(start_key, dest + ':pstart')
pipe.set(start_key, hour_start)
elif not existing:
pipe.set(start_key, hour_start)
pipe.zincrby(dest, 1, msg) # 更新日志出现次数
log_recent(pipe, name, msg, level, pipe)
return
except redis.exceptions.WatchError:
continue使用Redis实现计数器并进行数据统计
将计数器存储到Redis
计数器:
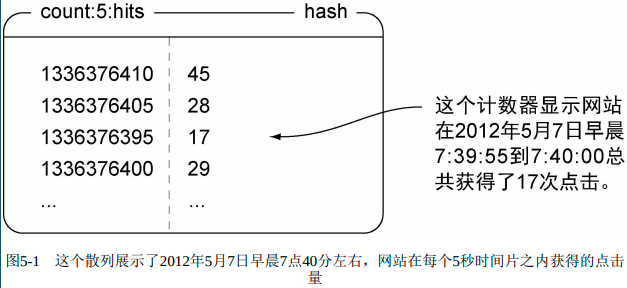
已有计数器:

查看代码
PERCISION = [1, 5, 60, 300, 3600, 18000, 86400]
def update_counter(conn:redis.Redis, name, count=1, now=None):
now = now or time.time()
pipe = conn.pipeline()
for prec in PERCISION:
pnow = int(now / prec) * prec # 获取时间片的开始
hash = '%s:%s'%(prec, name)
pipe.zadd('known:', {hash: 0}) # 添加到已知计数器
pipe.hincrby('count:' + hash, str(pnow), count) # 对指定名字和精度的计数器进行更新
pipe.execute()
def get_counter(conn:redis.Redis, name, precision):
hash = '%s:%s'%(precision, name)
data = conn.hgetall('count:' + hash)
to_return = []
for key, value in data.items():
to_return.append((int(key), int(value)))
to_return.sort()
return to_return
# 60秒一次遍历有序集合中的计数器,只清理应该清理的计数器
def clean_counters(conn:redis.Redis):
'''
任何时候都可能有新计数器加入
同一时间可能有多个不同清理操作在执行
对于一个每天只更新一次的计数器,每分钟尝试清理一次是浪费资源
计数器不包含数据,那么久不应该清理
'''
pipe = conn.pipeline(True)
passes = 0 # 记录清理操作次数
while not QUIT:
start = time.time()
index = 0
while index < conn.zcard('known:'): # 遍历所有已知计数器
hash = conn.zrange('known:', index, index) # 取得被检查计数器
index += 1
if not hash:
break
hash = hash[0]
prec = int(hash.partition(':')[0]) # 计数器精度
bprec = int(prec // 60) or 1 # 每60秒循环一次,判断本次计算是否要进行清理
if passes % bprec:
continue
hkey = 'count:' + hash
cutoff = time.time() - SAMPLE_COUNT * prec # 根据给定精度与要保留的样本数量,计算出要保留什么时间点前的样本
samples = map(int, conn.hkeys(hkey))
sorted(samples)
remove = bisect.bisect_right(samples, cutoff) # 计算要移除的样本数量
if remove:
conn.hdel(hkey, *samples[:remove])
if remove == len(samples):
try:
pipe.watch(hkey)
if not pipe.hlen(hkey):
pipe.multi()
pipe.zrem('know:', hash)
pipe.execute()
index -= 1
else:
pipe.unwatch()
except redis.exceptions.WatchError:
pass
passes += 1
duration = min(int(time.time() - start) + 1, 60)
time.sleep(max(60 - duration, 1))使用Redis存储统计数据
使用有序集合进行保存,方便交并集运算
查看代码
def update_status(conn:redis.Redis, context, type, value, timeout=5):
dest = 'status:%s:%s'%(context, type) # 负责存储统计数据的键
start_key = dest + ':start'
pipe = conn.pipeline(True)
end = time.time() + timeout
while time.time() < end:
try:
pipe.watch(start_key)
hour_start = datetime.datetime.now().hour
existing = int(str(pipe.get(start_key)))
pipe.multi()
if existing and existing < hour_start: # 每一个小时数据备份一份
pipe.rename(dest, dest+':last')
pipe.rename(start_key, dest + ':pstart')
pipe.set(start_key, hour_start)
# 创建两个临时有序集合,然后聚合,再删除
tkey1 = str(uuid.uuid4())
tkey2 = str(uuid.uuid4())
pipe.zadd(tkey1, {'min': value})
pipe.zadd(tkey2, {'max': value})
pipe.zunionstore(dest, [dest, tkey1], aggregate='MIN')
pipe.zunionstore(dest, [dest, tkey2], aggregate='MAX')
pipe.delete(tkey1, tkey2)
pipe.zincrby(dest, 1, 'count')
pipe.zincrby(dest, value, 'sum')
pipe.zincrby(dest, value*value, 'sumsq')
return pipe.execute()[-3:]
except redis.exceptions.WatchError:
continue
def get_status(conn:redis.Redis, context, type):
key = 'status:%s:%s'%(context, type)
data = dict(conn.zrange(key, 0, -1, withscores=True))
data['average'] = data['sum'] / data['count']
numerator = data['numsq'] - data['num'] ** 2 / data['count']
data['stddev'] = (numerator / (data['count'] -1 or 1)) ** .5
return data简化统计数据的记录与发现
查看代码
@contextlib.contextmanager # 将这个生成器用在上下文管理器
def access_time(conn, context):
start = time.time() # 记录代码执行前的时间
yield # 运行被包裹的代码
delta = time.time() - start # 计算执行时长
stats = update_stats(conn, context, 'AccessTime', delta)#
average = stats[1] / stats[0] # 计算平均时长
pipe = conn.pipeline(True)
pipe.zadd('slowest:AccessTime', context, average) #
pipe.zremrangebyrank('slowest:AccessTime', 0, -101) #
pipe.execute()
def process_view(conn, callback):
with access_time(conn, request.path): # 打开上下文并计算时间
return callback()查询IP地址所属的城市和国家
将一个IP所属城市载入Redis中,然后通过搜索数据库发现玩家位置。
一个表记录IP地址段和城市ID zset实现 ;另一个表保存城市ID和城市信息 hash 存储
查看代码
def ip_to_score(ip_address):
score = 0
for v in ip_address.split('.'):
score = score * 256 + int(v, 10)
return score
def import_ips_to_redis(conn, filename): #A
csv_file = csv.reader(open(filename, 'rb'))
for count, row in enumerate(csv_file):
start_ip = row[0] if row else '' #B
if 'i' in start_ip.lower():
continue
if '.' in start_ip: #B
start_ip = ip_to_score(start_ip) #B
elif start_ip.isdigit(): #B
start_ip = int(start_ip, 10) #B
else:
continue #C
city_id = row[2] + '_' + str(count) #D
conn.zadd('ip2cityid:', city_id, start_ip) #E
def import_cities_to_redis(conn, filename): #A
for row in csv.reader(open(filename, 'rb')):
if len(row) < 4 or not row[0].isdigit():
continue
row = [i.decode('latin-1') for i in row]
city_id = row[0] #B
country = row[1] #B
region = row[2] #B
city = row[3] #B
conn.hset('cityid2city:', city_id, #C
json.dumps([city, region, country])) #查找IP所属城市
查看代码
def find_city_by_ip(conn, ip_address):
if isinstance(ip_address, str): #A
ip_address = ip_to_score(ip_address) #A
city_id = conn.zrevrangebyscore( #B
'ip2cityid:', ip_address, 0, start=0, num=1) #B
if not city_id:
return None
city_id = city_id[0].partition('_')[0] #C
return json.loads(conn.hget('cityid2city:', city_id)) #D
服务的发现和配置
存储配置信息
将配置写入redis,应用程序获取这些信息,这样就不用推送
查看代码
LAST_CHECKED = None
IS_UNDER_MAINTENANCE = False
def is_under_maintenance(conn):
'''
在redis中检测键的值并返回
'''
global LAST_CHECKED, IS_UNDER_MAINTENANCE #A
if LAST_CHECKED < time.time() - 1: # 为了降低负载,控制访问频率
LAST_CHECKED = time.time() #C
IS_UNDER_MAINTENANCE = bool(conn.get('is-under-maintenance')) #D
return IS_UNDER_MAINTENANCE #E为每个应用程序组件分别配置一个Redis服务器
构建一个函数,可以从一个键中取出一个json编码的配置值,键由服务类型、应用程序名等命名,如:config:redis:statistics
查看代码
def set_config(conn, type, component, config):
conn.set('config:%s:%s'%(type, component),json.dumps(config))
CONFIGS = {}
CHECKED = {}
def get_config(conn, type, component, wait=1):
key = 'config:%s:%s'%(type, component)
# 检查是否要对配置信息更新
if CHECKED.get(key) < time.time() - wait: #A
# 记录最后一次更新时间
CHECKED[key] = time.time() #B
# 获取redis存储的配置
config = json.loads(conn.get(key) or '{}') #C
config = dict((str(k), config[k]) for k in config)#G
# 取得正在使用的配置
old_config = CONFIGS.get(key) #D
# 不同时合并
if config != old_config: #E
CONFIGS[key] = config #F
return CONFIGS.get(key)自动Redis连接管理
编写一个装饰器,自动连接除配置服务以外的所有其他Redis服务
查看代码
REDIS_CONNECTIONS = {}
def redis_connection(component, wait=1): #A
key = 'config:redis:' + component #B
def wrapper(function): #C
# 将被包裹函数的一些有用元数据复制给配置处理器
@functools.wraps(function) #D
def call(*args, **kwargs): #E
# 获取新旧配置
old_config = CONFIGS.get(key, object()) #F
_config = get_config(config_connection, 'redis', component, wait) #G
config = {}
for k, v in _config.iteritems(): #L
config[k.encode('utf-8')] = v #L
# 配置不同则创建新连接
if config != old_config: #H
REDIS_CONNECTIONS[key] = redis.Redis(**config) #H
return function( #I
REDIS_CONNECTIONS.get(key), *args, **kwargs) #I
return call #J
return wrapper #K
@redis_connection('logs')
def log_recent(conn, app, message):
pass
log_recent('main', 'User 235 logged in')


