3、Struts2的API访问和数据封装
一、API的访问
在使用Struts2的框架的过程中,发现Struts2和Servlet的API是解耦合的。在实际开发中,经常使用到Servlet的API,比如进行登录,将用户的信息保存到Session中,
有的时候需要向页面输出一些内容,用到response对象。涉及到Servlet的API的访问。
1、完全解耦合的方式,通过ActionContext类访问[推荐]
Struts2框架提供了ActionContext类来访问Servlet API,ActionContext是Action执行的上下文对象。在ActionContext中保存了Action执行所需要的所有对象,
包括parameters,request,session,application等。
// 将key-value键值对放入ActionContext中,模拟Servlet API中的HTTPServletRequest 的setAttribute()方法 void put(String key,Object value) // 通过参数Key来查找当前ActionContext中的值 Object get(String key) // 返回一个Application级的对象 Map<String,Object> getApplication() // 获取当前线程的ActionContext对象 static ActionContext getContext() // 返回一个包含所有HttpServletRequest参数信息 Map<String,Object> getParameters() // 返回一个Map类型的HttpSession对象 Map<String,Object> getSession() // 设置Application上下文 void SetApplication(Map<String,Object> application) // 设置一个Map类型的Session值 void setSession(Map<String,Object> session)
注意:这种方式只能获得代表request、session、application的数据的Map集合,不能操作这些对象的本身的方法。
案例:
Action类
package com.turtle.demo4.action; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import java.util.Map; public class Demo4Action extends ActionSupport { public String save(){ // 从前端返回来的参数中取值 // 通过ActionContext来取得ActionContext对象 ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext(); // actionContext.getParameters()可以取到map值的对象 Map<String, Object> contextParameters = actionContext.getParameters(); // 遍历输出值 for (Map.Entry<String,Object> entry : contextParameters.entrySet()){ String key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue().toString(); } // 向返回前端的参数中设置值 // 把值设置到session中 actionContext.getSession().put("name1","session"); // request.setAttribute("","") actionContext.put("name2","request"); // application.setAttribute("","") actionContext.getApplication().put("name3", "application"); return SUCCESS; } }
Jsp页面
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: 22274 Date: 2019/10/27 Time: 23:52 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1>使用ServletContext</h1> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo4Action.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="name" value=""/><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="password" value=""/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: 22274 Date: 2019/10/27 Time: 23:52 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%> <html> <head> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1>使用ServletContext</h1> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo4Action.action" method="post"> Session :<input type="text" name="name1" value="${name1}"/><br/> Request :<input type="text" name="name2" value="${name2}"/><br/> Application:<input type="text" name="name3" value="${name3}"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <package name="demo4" extends="struts-default" namespace="/"> <action name="demo4Action" class="com.turtle.demo4.action.Demo4Action" method="save"> <result name="success">/demo4/success.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
结果:
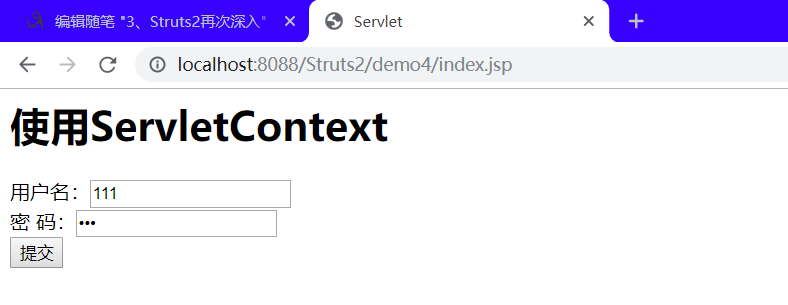
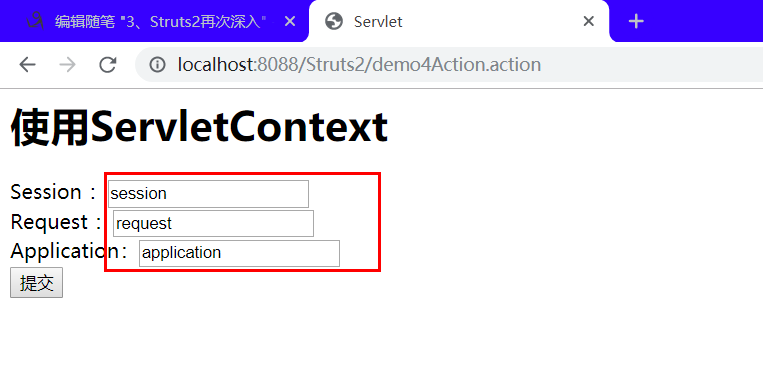
2、使用Servlet的API的原生方式
该方法可以直接访问Servle API,提供了ServletActionContext类,该类包含了我么所需要的几个方法
// 获取web应用中的HttpServletRequest对象 static HttpServletRequest() // 获取web应用中的HttpServletResponse对象 static HttpServletResponse getResponse() // 获取web应用中的ServletContext对象 static ServletContext getServletContext() // 获取WEb应用中的PageContext对象 static PageContext getPageContext()
Action类:
package com.turtle.demo4.action; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.util.Map; public class Demo4Action extends ActionSupport { public String save(){ // 取从前端页面带过来的数据 HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap(); for(Map.Entry<String,String[]> entry : parameterMap.entrySet()){ String key = entry.getKey(); String[] value = entry.getValue(); } // 往前端传的数据 request.setAttribute("name1","request"); request.getSession().setAttribute ("name2","session"); ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("name3","servletContext"); return SUCCESS; } }
JSP页面和配置文件不做改变,显示的结果也是一样的。
3、接口注入的方式
// 实现该接口可以直接访问WEb应用中的HttpServletRequest实例 ServletRequestAware // 实现该接口可以直接访问WEb应用中的HttpServletResponse实例 ServletResponseAware // 实现该接口可以直接访问WEb应用中的HttpSession实例 SessionAware // 实现该接口可以直接访问WEb应用中的ServletContexte实例 ServletContextAware
Action:
package com.turtle.demo4.action; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletRequestAware; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.util.Map; public class Demo4Action extends ActionSupport implements ServletRequestAware { private HttpServletRequest request; @Override public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) { this.request = httpServletRequest; } public String save(){ // 取从前端页面带过来的数据 Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap(); for(Map.Entry<String,String[]> entry : parameterMap.entrySet()){ String key = entry.getKey(); String[] value = entry.getValue(); } // 往前端传的数据 request.setAttribute("name1","request"); request.getSession().setAttribute ("name2","session"); ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("name3","servletContext"); return SUCCESS; } }
配置文件和结果显示页面与上面的一致。
Servlet是单例的,多个程序访问同一个Servlet只会创建一个Servlet的实例。Action是多例的,一次请求,创建一个Action的实例(不会出现线程安全的问题)。
二、结果页面的配置
1、局部结果页面的配置:
局部结果页面指的是,只能在当前的action中的配置有效。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <package name="demo4" extends="struts-default" namespace="/"> <action name="demo4Action" class="com.turtle.demo4.action.Demo4Action" method="save"> <result name="success">/demo4/success.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
2、全局结果页面的配置:
全局结果页面:全局结果页面指的是,在包中配置一次,其他的在这个包中的所有的action只要返回了这个值,都可以跳转到这个页面。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <package name="demo4" extends="struts-default" namespace="/"> <global-results> <result name="success">/demo4/success.jsp</result> </global-results> <action name="demo4Action" class="com.turtle.demo4.action.Demo4Action" method="save"> <!--<result name="success">/demo4/success.jsp</result>--> </action> </package> </struts>
3、result标签的配置
result标签用于配置页面的跳转。在result标签上有两个属性:
name属性 :逻辑视图的名称。默认值:success
type属性 :页面跳转的类型。
dispatcher :默认值,请求转发。(Action转发JSP)
redirect :重定向。(Action重定向JSP)
chain :转发。(Action转发Action)
redirectAction :重定向。(Action重定向Action)
stream :Struts2中提供文件下载的功能。
三、数据封装:
1、属性驱动:提供属性set方法的方式(不常用)
Action类:
package com.turtle.demo5; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class Demo5Action extends ActionSupport { // 用户名 private String name; // 密码 private String password; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String save() { System.out.println("用户名"+name); System.out.println("密码"+password); return null; } }
前端页面:
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: 22274 Date: 2019/10/27 Time: 23:52 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1>属性驱动第一种方法</h1> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo5Action.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="password"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
2、属性驱动:页面中提供表达式方式
封装的对象
package com.turtle.demo5; public class User { // 名字 private String name; // 密码 private String password; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
Action类
package com.turtle.demo5; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class Demo5Action extends ActionSupport { // 用户对象 private User user; public String save() { System.out.println("用户名"+user.getName()); System.out.println("密码"+user.getPassword()); return null; } public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } }
Jsp页面:
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: 22274 Date: 2019/10/27 Time: 23:52 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1>属性驱动第一种方法</h1> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo5Action.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user.name" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="user.password"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
3、模型驱动,采用模型驱动方式(最常用)
通过实现ModelDriven接口来接收参数,Action类必须实现ModelDerven接口,并且要重写getModel方法,这个方法返回的是Action类所要使用的数据模型对象。
Action类
package com.turtle.demo5; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven; public class Demo5Action extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User> { // 用户对象,需要手动进行实例化 private User user = new User(); /** * 主要就是这个方法 * @return */ @Override public User getModel() { return user; } public String save() { System.out.println("用户名"+user.getName()); System.out.println("密码"+user.getPassword()); return null; } public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } }
jsp页面
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: 22274 Date: 2019/10/27 Time: 23:52 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1>属性驱动第一种方法</h1> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo5Action.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="password"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
汇总:大部分我们会优先使用模型驱动的方式,因为Struts2内部有很多结果都是围绕模型驱动设计的。但如果页面中向
多个对象中封装,那么就要使用属性驱动的方式二了。
4、封装到List集合中
Action类
package com.turtle.demo5; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven; import java.util.List; public class Demo5Action extends ActionSupport { // 用户对象,需要手动进行实例化 // 该变量和jsp中使用的list名字要一致,而且get/set方法也要一致 private List<User> userList; public String save() { for(User user : userList){ System.out.println("用户名"+user.getName()); System.out.println("密码"+user.getPassword()); } return null; } public List<User> getUserList() { return userList; } public void setUserList(List<User> userList) { this.userList = userList; } }
JSp页面:
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: 22274 Date: 2019/10/27 Time: 23:52 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1>属性驱动第一种方法</h1> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo5Action.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="userList[0].name" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="userList[0].password"/><br/> <hr/> 用户名:<input type="text" name="userList[1].name" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="userList[1].password"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
5、封装到Map集合中
Action类
package com.turtle.demo5; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; public class Demo5Action extends ActionSupport { private Map<String,User> userMap; public String save() { for(Map.Entry<String,User> user : userMap.entrySet()){ System.out.println("用户名"+user.getValue().getName()); System.out.println("密码"+user.getValue().getPassword()); } return null; } public Map<String, User> getUserMap() { return userMap; } public void setUserMap(Map<String, User> userMap) { this.userMap = userMap; } }
Jsp页面
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: 22274 Date: 2019/10/27 Time: 23:52 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1>属性驱动第一种方法</h1> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo5Action.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="userMap['0'].name" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="userMap['0'].password"/><br/> <hr/> 用户名:<input type="text" name="userMap['1'].name" /><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="userMap['1'].password"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>


