Java Web之会话技术
客户端与服务器通信过程中,会产生一些数据。比如,A和B分别登陆了某宝购物网站,A买了一个Android手机,B买了一个iPhone手机,当结账时,web服务器需要分别对用户A和B的信息分别保存。根据Java Web之Servlet技术中所说,HttpServletRequest对象和ServletContext对象都可以保存数据,但是这二者在该情形下是不适合使用的。
- 客户端的每次请求,服务器都会产生一个HttpServletRequest对象,该对象只保存本次请求所传递的数据。由于购买和结账是两个不同的请求,所以使用HttpServletRequest对象保存信息会造成丢失。
- 同一个Web应用共享一个ServletContext对象,所以当多个用户结账时无法区分哪个商品是哪个用户购买的,这显然是不可行的。
1、Cookie对象
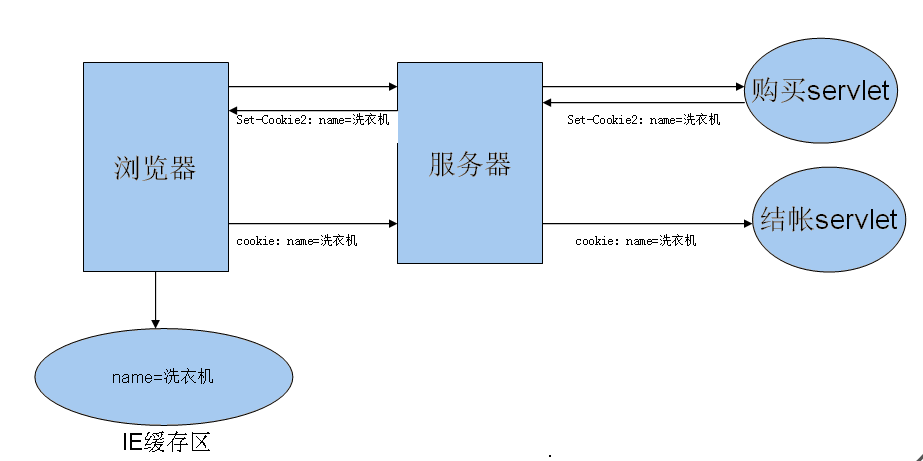
Cookie是一种会话技术,它用于将会话过程中的数据保存在用户的浏览器中,从而使浏览器和服务器更好的交互。服务器向客户端发送Cookie时,会在HTTP响应头字段增加Set-Cookie字段,该字段设置的Cookie遵循一定规则,比如以键值对形式保存,Cookie属性值可以有多个,但是这些属性之间必须以分号和空格分隔。以下是一个Cookie示例:
Set-Cookie:"lastTime="2016-05-21 12:03:10"; Version=1"
Cookie使用
为了封装Cookie信息,Servlet API中提供了一个javax.servlet.http.Cookie类,该类包含了生成Cookie信息和提取Cookie信息各个属性的方法,Cookie唯一的构造方法下:
public Cookie(java.lang.String name, java.lang.String value)
构造方法中,name用于指定Cookie名称,value指定Cookie的值,注意,Cookie一旦创建后,其名称就不允许更改了,Cookie值是可以更改的。Cookie类常用的方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
| String getName() | 返回Cookie名称 |
| void setValue(String newValue)/String getValue() | 设置/获取Cookie值 |
| void setMaxAge(int expiry)/int getMaxAge() | 设置/获取Cookie在浏览中保存有效的秒数 |
| void setPath(String uri)/public String getPath() | 设置/获取Cookie向有效目录路径 |
| void setDomain(String pattern)/String getDomain() | 设置/获取Cookie的有效域 |
| void setSecure(boolean flag)/boolean getSecure() | 设置/获取Cookie是否只能使用安全的协议传送 |
Cookie示例
利用Cookie技术实现提示上次访问时间功能。
package zzz;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet(name="CookieTest", urlPatterns={"/CookieTest"})
public class CookieTest extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 指定响应编码方式
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String lastTime = null;
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for (int i = 0; cookies != null && i < cookies.length; i++) {
if (cookies[i].getName().equals("lastTime")) {
lastTime = cookies[i].getValue();
}
}
if (lastTime == null) {
out.println("你好,这是你首次访问网站");
}
else {
out.println("你好,你上次访问该网站时间为:" + lastTime);
}
// 创建cookie,将当前时间记录到cookie中并返回
String time = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss").format(new Date());
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("lastTime", time);
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
@Override
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
2、Session技术
Cookie技术可以将用户信息保存在浏览器中,并且可在多次请求中共享数据,但是如果传递的信息比较多, 使用Cookie技术明显加大服务端程序的处理难度。此时,可以使用Session技术来实现,其通过将会话数据保存在服务端。注意:Session对象对应着一个ID,所以一般是需要客户端记录该对象的ID,通常情况下,Session是通过Cookie技术来传递Session对象ID的。
Session对象是与每个请求紧密相关的,HttpServletRequest定义了用于获取Session对象的getSession()方法,如下所示:
public HttpSession getSession(boolean create); public HttpSession getSession();
第一个getSession()根据参数值决定是否创建新的Session对象,如果参数为true,则相关的HttpSession对象不存在时创建新的HttpSession对象,如果参数为false,则不会创建新的HttpSession对象。第二个getSession()方法则相当于第一个方法参数为true的情况。HttpSession常用方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
| String getId() | 返回该HttpSession对象关联的会话标识号 |
| int getMaxInactiveInterval() | 返回当前HttpSession对象最大生存周期,单位为s |
| void invalidate() | 强制使HttpSession对象失效 |
| void setAttribute(String name, Object value) | 将一个对象与一个名称关联后存储到HttpSession对象中 |
| Object getAttribute(String name) | 返回当前HttpSession对象中指定名称的属性对象 |
| void removeAttribute(String name) | 从当前HttpSession对象中删除指定名称属性对象 |
Web服务器管理HttpSession对象时,会采用超时管理机制判断客户单是否还在继续访问。一定时间内,某个客户一直没有访问,Web服务器就会认为该客户端已经结束请求,将与该客户会话所关联的HttpSession对象给垃圾回收掉。如果之后该客户端再次访问,则重新创建一个新的HttpSession对象。会话的有效时间可以再web.xml中设置,默认值有Servlet容器定义,在tomcat的安装目录中的web.xml中有如下配置,就是设置Session超时时间的,单位为分钟。
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
Session示例
利用Session技术实现提示上次访问时间功能。
package zzz;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
@WebServlet(name="SessionTest", urlPatterns={"/SessionTest"})
public class SessionTest extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 指定响应编码方式
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String user = null;
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for (int i = 0; cookies != null && i < cookies.length; i++) {
if (cookies[i].getName().equals("user")) {
user = cookies[i].getValue();
}
}
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if (user == null) {
out.println("你好,这是你首次访问网站");
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("user", "luoxn28");
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
else {
String time = (String) session.getAttribute("lastTime");
out.println("你好,你上次访问该网站时间为:" + time);
}
String lastTime = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss").format(new Date());
session.setAttribute("lastTime", lastTime);
}
@Override
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}