一、环境现状描述:
目前的ElasticSearch集群仅有一个单一节点,且这个集群中已建立有索引,索引已包含业务文档数据(超过200G),该集群已经启用XPACK认证,现希望扩展这个集群,增加复制节点,且复制节点启动后,自动从主节点同步数据到新节点。
目前的ElasticSearch集群节点关键配置情况如下:
Cluster部分配置: cluster.name: prometheus Node部分配置: node.name: node-1 Paths部分配置: path.data: /data/elastic/esdata path.logs: /data/elastic/eslog Network部分配置: #network.host: 192.168.0.1 【注意:由于当前不需要外网访问ES,所以这里没有改成0.0.0.0】 http.port: 19200 Discovery部分配置 discovery.seed_hosts: ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"] Security部分配置: xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.license.self_generated.type: basic xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true
二、扩展集群步骤:
操作概述:
1、关于端口,ES用到的端口主要是2个,默认值分别是9200和9300,9200端口大家很熟悉,用于客户端操作es数据或进行es配置,9300端口是es集群内部通讯用的端口,因此在扩展节点时,新服务器和原服务器之间的9300端口必须互通。如果像上面的配置那样修改了默认端口(出于安全考虑不使用默认端口),则应确保使用的端口未被防火墙拦截。
2、在新节点服务器安装相同的ES版本后,原节点上装了哪些插件,新节点也要安装(将原es的plugin目录复制到新ES目录即可)
3、在原服务器生成p12证书文件,拷贝到新服务器,用于节点的认证。
4、修改两个服务器的配置文件,先启动原服务器,再启动新节点服务器,即可完成扩展。
详细步骤:
1、在新节点安装同版本ES【该步骤不再赘述,就是创建运行es的用户,上传es安装文件解压,修改vm.max_map_count值配置,配置ES_JAVA_HOME就可以了,跟安装单节点的ES一样】
2、修改原服务器和新服务器配置,具体如下:
原服务器调整后的配置文件:

# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: prometheus # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-1 node.data: true node.master: true # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # path.data: /data/elastic/esdata # # Path to log files: # path.logs: /data/elastic/eslog # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different # address here to expose this node on the network: # network.host: 0.0.0.0 network.publish_host: 125.*.*.*【关键:填写当前服务器外网ip】 # # By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it # finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here: # http.port: 19200 transport.tcp.port: 19300 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] #填写当前服务器的ip和9300端口以及新服务器的ip和9300端口,我这里自定义了集群通讯端口是19300 discovery.seed_hosts: ["125.*.*.*:19300", "58.*.*.*:19300"] # # Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes: # cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"] # # For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true # # ---------------------------------- Security ---------------------------------- # # *** WARNING *** # # Elasticsearch security features are not enabled by default. # These features are free, but require configuration changes to enable them. # This means that users don’t have to provide credentials and can get full access # to the cluster. Network connections are also not encrypted. # # To protect your data, we strongly encourage you to enable the Elasticsearch security features. # Refer to the following documentation for instructions. # # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.16/configuring-stack-security.html xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.path: elastic-certificates.p12 xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.path: elastic-certificates.p12
新服务的配置文件:

# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: prometheus # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-2 node.data: true node.master: false # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # path.data: /data/elastic/esdata # # Path to log files: # path.logs: /data/elastic/eslogs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different # address here to expose this node on the network: # network.host: 0.0.0.0 # 【该ip填写能被另一台服务器访问到的ip地址】 network.publish_host: *.*.*.* # # By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it # finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here: # http.port: 19200 transport.tcp.port: 19300 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #这里 seed_hosts 只填写原主节点的ip地址和端口,该地址需要能被新节点访问 discovery.seed_hosts: ["*.*.*.*:19300"] # # Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes: # cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"] # # For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true # # ---------------------------------- Security ---------------------------------- # # *** WARNING *** # # Elasticsearch security features are not enabled by default. # These features are free, but require configuration changes to enable them. # This means that users don’t have to provide credentials and can get full access # to the cluster. Network connections are also not encrypted. # # To protect your data, we strongly encourage you to enable the Elasticsearch security features. # Refer to the following documentation for instructions. # # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.16/configuring-stack-security.htmlxpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.path: elastic-certificates.p12 xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.path: elastic-certificates.p12
【注意:如果你的服务器不在一个局域网中或者在不同网段,则network.publish_host这项就必须配置,配置值应为可以被另一台服务器访问的ip(例如公网ip),否则会导致新节点无法加入集群】
3、在原服务器上生成p12证书(如果之前没有生成过)
bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca -out config/elastic-certificates.p12 -pass""
将证书elastic-certificates.p12文件传到新服务器的es安装目录的config目录下(即elasticsearch.yml文件所在目录),chown调整好证书的所有者为elastic用户,且chmod文件权限设置为755。
【注意!!!不要在新服务器上执行bin目录下的elasticsearch-setup-passwords文件来重新配置密码,因为集群中的节点认证信息必须保持一致,上面我们将p12证书拷贝到新服务器就行了,后续访问新服务器节点时,就可以继续使用之前的elastic用户名密码】
4、启动原服务器上的es节点
bin/elasticsearch -d
5、启动新服务器上的es节点
bin/elasticsearch -d
观察两个服务器的日志情况
tail -f /data/elastic/eslogs/prometheus.log
如果有出错的信息,错误信息回显示在这个文件中,按照错误信息调整即可。
【这个日志位于elasticsearch.yml配置文件中的path.logs路径中,文件名就是cluster.name名字】
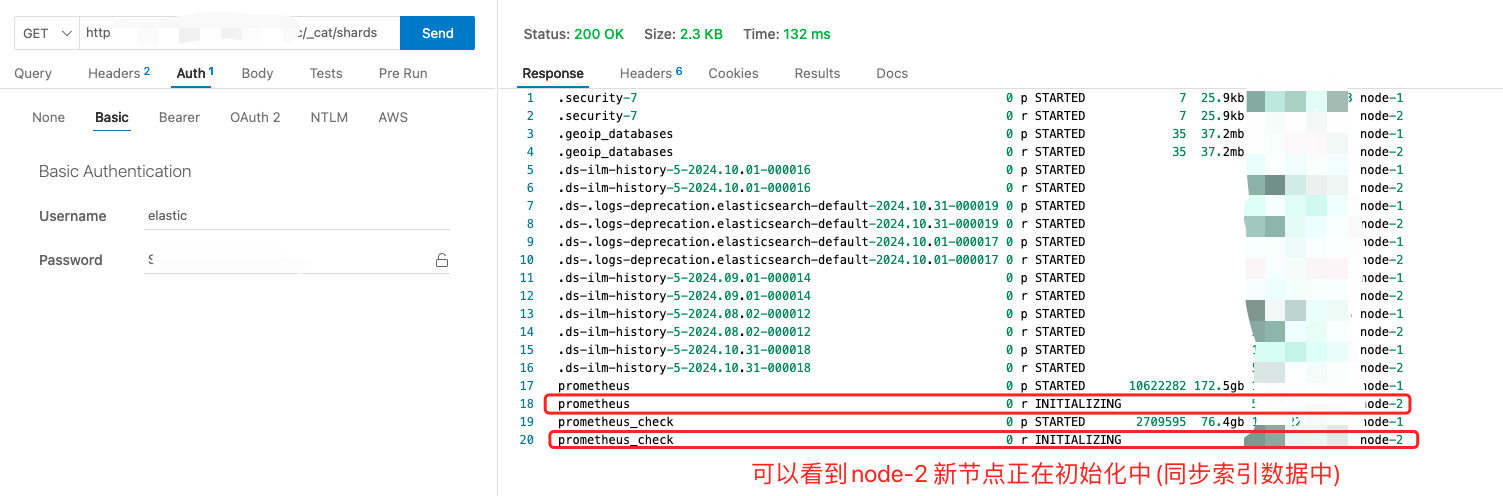
6、至此配置完毕,分别访问原节点和新节点的分片状况:
原服务器节点情况:
新服务器节点情况:
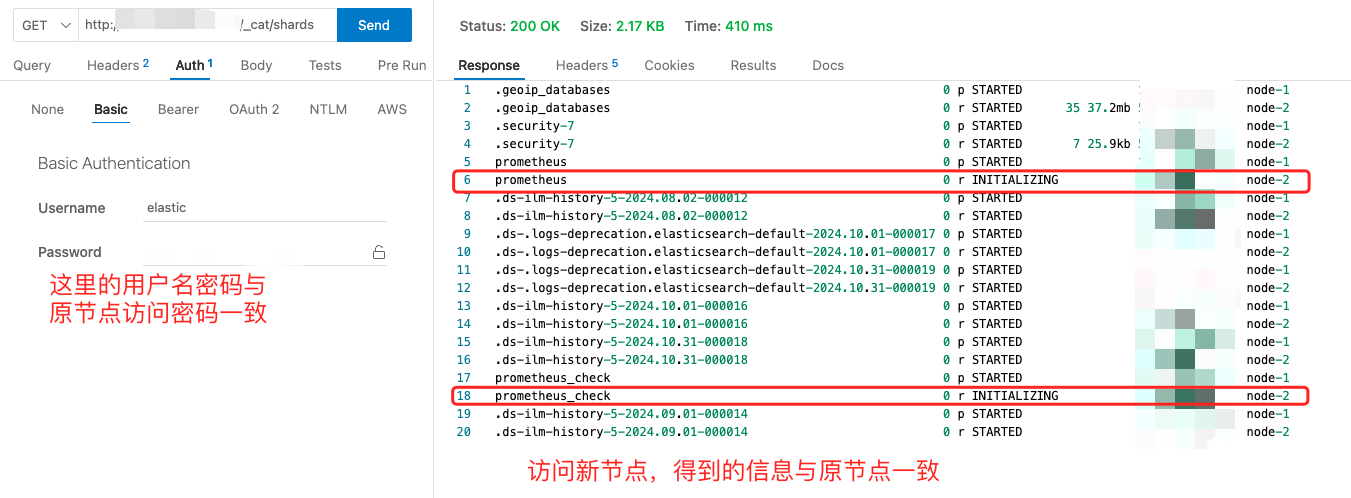
网上的很多教程都是全新安装多个节点的ES集群或者原集群没有做XPACK加密的,在增加节点后,需要执行bin目录下的elasticsearch-setup-passwords来设置密码,这种场景不符合当前的需求(当前环境是单个节点集群已经设置了密码且用于生产,不方便重新设置密码),因此写一下这篇文章记录一下。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号