实验三
task1:
button.hpp:
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
// 按钮类
class Button {
public:
Button(const string &text);
string get_label() const;
void click();
private:
string label;
};
Button::Button(const string &text): label{text} {
}
inline string Button::get_label() const {
return label;
}
void Button::click() {
cout << "Button '" << label << "' clicked\n";
}
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include "button.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// 窗口类
class Window{
public:
Window(const string &win_title);
void display() const;
void close();
void add_button(const string &label);
private:
string title;
vector<Button> buttons;
};
Window::Window(const string &win_title): title{win_title} {
buttons.push_back(Button("close"));
}
inline void Window::display() const {
string s(40, '*');
cout << s << endl;
cout << "window title: " << title << endl;
cout << "It has " << buttons.size() << " buttons: " << endl;
for(const auto &i: buttons)
cout << i.get_label() << " button" << endl;
cout << s << endl;
}
void Window::close() {
cout << "close window '" << title << "'" << endl;
buttons.at(0).click();
}
void Window::add_button(const string &label) {
buttons.push_back(Button(label));
}
点击查看代码
#include "window.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
void test() {
Window w1("new window");
w1.add_button("maximize");
w1.display();
w1.close();
}
int main() {
cout << "用组合类模拟简单GUI:\n";
test();
}

自定义了Button类、Window类
使用了string和vector
task2:
task2.cpp
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void output1(const vector<int> &v) {
for(auto &i: v)
cout << i << ", ";
cout << "\b\b \n";
}
void output2(const vector<vector<int>> v) {
for(auto &i: v) {
for(auto &j: i)
cout << j << ", ";
cout << "\b\b \n";
}
}
void test1() {
vector<int> v1(5, 42);
const vector<int> v2(v1);
v1.at(0) = -999;
cout << "v1: "; output1(v1);
cout << "v2: "; output1(v2);
cout << "v1.at(0) = " << v1.at(0) << endl;
cout << "v2.at(0) = " << v2.at(0) << endl;
}
void test2() {
vector<vector<int>> v1{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6, 7}};
const vector<vector<int>> v2(v1);
v1.at(0).push_back(-999);
cout << "v1: \n"; output2(v1);
cout << "v2: \n"; output2(v2);
vector<int> t1 = v1.at(0);
cout << t1.at(t1.size()-1) << endl;
const vector<int> t2 = v2.at(0);
cout << t2.at(t2.size()-1) << endl;
}
int main() {
cout << "测试1:\n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2:\n";
test2();
}

第一行定义一个长度为5值全为42的整形vector对象v1,第二行使用v1复制构造了一个vector对象v2,第三行对v1的第一个值进行修改
task3:
vectorInt.hpp
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// 动态int数组对象类
class vectorInt{
public:
vectorInt(int n);
vectorInt(int n, int value);
vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi);
~vectorInt();
int& at(int index);
const int& at(int index) const;
vectorInt& assign(const vectorInt &v);
int get_size() const;
private:
int size;
int *ptr; // ptr指向包含size个int的数组
};
vectorInt::vectorInt(int n): size{n}, ptr{new int[size]} {
}
vectorInt::vectorInt(int n, int value): size{n}, ptr{new int[size]} {
for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i)
ptr[i] = value;
}
vectorInt::vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi): size{vi.size}, ptr{new int[size]}
{
for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i)
ptr[i] = vi.ptr[i];
}
vectorInt::~vectorInt() {
delete [] ptr;
}
const int& vectorInt::at(int index) const {
assert(index >= 0 && index < size);
return ptr[index];
}
int& vectorInt::at(int index) {
assert(index >= 0 && index < size);
return ptr[index];
}
vectorInt& vectorInt::assign(const vectorInt &v) {
delete[] ptr; // 释放对象中ptr原来指向的资源
size = v.size;
ptr = new int[size];
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
ptr[i] = v.ptr[i];
return *this;
}
int vectorInt::get_size() const {
return size;
}
int vectorInt::get_size() const {
return size;
}
点击查看代码
#include "vectorInt.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
void output(const vectorInt &vi) {
for(auto i = 0; i < vi.get_size(); ++i)
cout << vi.at(i) << ", ";
cout << "\b\b \n";
}
void test1() {
int n;
cout << "Enter n: ";
cin >> n;
vectorInt x1(n);
for(auto i = 0; i < n; ++i) x1.at(i) = i*i;
cout << "x1: "; output(x1);
vectorInt x2(n, 42);
vectorInt x3(x2);
x2.at(0) = -999;
cout << "x2: "; output(x2);
cout << "x3: "; output(x3);
}
void test2() {
const vectorInt x(5, 42);
vectorInt y(10, 0);
cout << "y: "; output(y);
y.assign(x);
cout << "y: "; output(y);
cout << "x.at(0) = " << x.at(0) << endl;
cout << "y.at(0) = " << y.at(0) << endl;
}
int main() {
cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
}
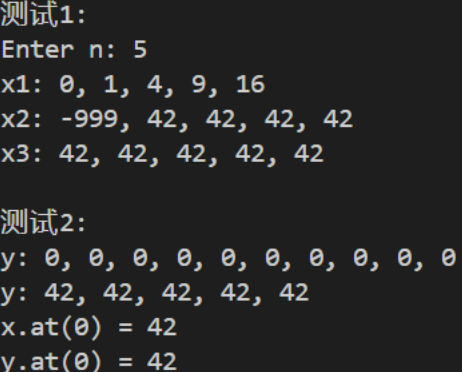
深复制
task4
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Matrix {
private:
int lines; // 矩阵对象内元素行数
int cols; // 矩阵对象内元素列数
double *ptr;
class Matrix {
public:
Matrix(int n, int m); // 构造函数,构造一个n*m的矩阵, 初始值为value
Matrix(int n); // 构造函数,构造一个n*n的矩阵, 初始值为value
Matrix(const Matrix &x); // 复制构造函数, 使用已有的矩阵X构造
~Matrix();
void set(const double *pvalue); // 用pvalue指向的连续内存块数据按行为
矩阵赋值
void clear(); // 把矩阵对象的值置0
const double& at(int i, int j) const; // 返回矩阵对象索引(i,j)的元素const引用
double& at(int i, int j); // 返回矩阵对象索引(i,j)的元素引用
int get_lines() const; // 返回矩阵对象行数
int get_cols() const; // 返回矩阵对象列数
void display() const;
};
// 析构函数
~Matrix() {
for (int i = 0; i < lines; ++i) delete[] ptr[i];
delete[] ptr;
}
点击查看代码
#include "matrix.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
const int N = 1000;
// 输出矩阵对象索引为index所在行的所有元素
void output(const Matrix &m, int index) {
assert(index >= 0 && index < m.get_lines());
for(auto j = 0; j < m.get_cols(); ++j)
cout << m.at(index, j) << ", ";
cout << "\b\b \n";
}
void test1() {
double x[1000] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int n, m;
cout << "Enter n and m: ";
cin >> n >> m;
Matrix m1(n, m); // 创建矩阵对象m1, 大小n×m
m1.set(x); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m1赋值
Matrix m2(m, n); // 创建矩阵对象m1, 大小m×n
m2.set(x); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m1赋值
Matrix m3(2); // 创建一个2×2矩阵对象
m3.set(x); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m4赋值
cout << "矩阵对象m1: \n"; m1.display(); cout << endl;
cout << "矩阵对象m2: \n"; m2.display(); cout << endl;
cout << "矩阵对象m3: \n"; m3.display(); cout << endl;
}
void test2() { Matrix m1(2, 3);
m1.clear();
const Matrix m2(m1);
m1.at(0, 0) = -999;
cout << "m1.at(0, 0) = " << m1.at(0, 0) << endl;
cout << "m2.at(0, 0) = " << m2.at(0, 0) << endl;
cout << "矩阵对象m1第0行: "; output(m1, 0);
cout << "矩阵对象m2第0行: "; output(m2, 0);
}
int main() {
cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
cout << "测试2: \n";
test2();
}
点击查看代码
#ifndef USER_HPP
#define USER_HPP
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class User {
private:
std::string name;
std::string password;
std::string email;
public:
// 单参数构造函数,默认密码和邮箱
User(const std::string& name)
: name(name), password("123456"), email("") {}
// 三参数构造函数
User(const std::string& name, const std::string& password, const std::string& email)
: name(name), password(password), email(email) {}
// 设置邮箱
void set_email();
// 修改密码
void change_password();
// 显示用户信息
void display() const;
};
#endif // USER_HPP
点击查看代码
#include "user.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;
void test() {
vector<User> user_lst;
User u1("Alice", "2024113", "Alice@hotmail.com");
user_lst.push_back(u1);
cout << endl;
User u2("Bob");
u2.set_email();
u2.change_password();
user_lst.push_back(u2);
cout << endl;
User u3("Hellen");
u3.set_email();
u3.change_password();
user_lst.push_back(u3); cout << endl;
cout << "There are " << user_lst.size() << " users. they are: " << endl;
for(auto &i: user_lst) {
i.display();
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
test();
}



