Spring Boot集成MyBatis开发Web项目
1、Maven构建Spring Boot
创建Maven Web工程,引入spring-boot-starter-parent依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>xyz.ibenben</groupId>
<artifactId>zhongdian</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>zhongdian Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<!-- Inherit defaults from Spring Boot -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<!-- Add typical dependencies for a web application -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- Package as an executable jar -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<!-- Add Spring repositories -->
<!-- (you don't need this if you are using a .RELEASE version) -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<url>http://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<url>http://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<url>http://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<url>http://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>
使用spring-boot-starter-parent来构建Spring Boot项目是一个非常好的方法,但非常多项目本身就是依赖其他的父模块的,再或者spring-boot-starter-parent默认提供的那么多配置和功能我们用不到。
我们也能够使用其他的依赖方式来引入Spring Boot。
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<!-- Import dependency management from Spring Boot -->
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>这是Spring官网给的demo配置,有兴趣的能够直接跳过去查看:http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.4.0.RC1/reference/htmlsingle/#getting-started-maven-installation
2、Spring Boot项目的代码结构
Spring Boot项目与一般的Java Web项目的代码结构没有太大的差别或要求,但为了降低配置的数量(无配置),Spring Boot也有一些比較好的建议。
com
+- example
+- myproject
+- Application.java
|
+- domain
| +- Customer.java
| +- CustomerRepository.java
|
+- service
| +- CustomerService.java
|
+- web
+- CustomerController.java2.1 不要使用默认的包路径
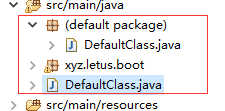
我们交由Spring管理的类,须要放入一个包下。例如以下图中的DefaultClass.java是不行的。由于Spring Boot对带注解的类进行扫描的时候,这些默认包路径下的类会出问题。
当然。基于代码规范的要求。一般的程序猿都不会这样子构建自己的代码。这里说明是为了真的遇到这样的情况出问题时。能够高速地解决这个问题。
2.2 Spring Boot应用入口
package com.example.myproject;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}入口类Application带main方法,我们直接执行main方法就能启动Spring Boot项目了,这样极大程序地方便了我们调试程序和项目。
Application类说明自己是Spring Boot的入口类,那么须要增加@Configuration注解。
@EnableAutoConfiguration习惯放在主方法类Application上。当项目执行时,Spring容器去自己主动查找带特定注解的类,如:带@Entity、@Service等类。
@ComponentScan假设不带basePackage 属性的话。它会自己主动扫描以入口类所在的包为父节点下全部子包下的类。这也是Spring Boot会提议我们把Application类放于根包路径下。
假设我们的项目和Spring Boot建议的代码结构一样。Application类放在根包路径下。
那么我们能够使用@SpringBootApplication来取代上面三个注解。
package com.example.myproject;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}3、Spring Boot的Web项目实现
3.1 Application类支持Web应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}入口类Application继承SpringBootServletInitializer并重写configure方法。执行主方法后,会将我们的web项目打包成war,并默认启动一个端口为8080的tomcat容器来执行我们的Web项目。
3.2 其他server软件支持
假设我们不想使用tomcat,而是其他的server软件。如Jetty。
你须要移除tomcat的依赖,并增加Jetty的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>3.3 server端口更改
增加application.yml配置文件。
# Server settings
server:
port: 80
address: 127.0.0.1这里须要注意。yml配置文件是的值属性前面必须有一个空格。假设没有空格,Spring的解析器会忽略此配置项。
3.4 Controller
Spring支持Spring MVC的Controler的使用方式。
请參考:http://blog.csdn.net/p_3er/article/category/2868979
Spring Boot应用中@RestController的Controller带有默认基于Jackson2的对象转JSON功能。如:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("/thing")
public MyThing thing() {
return new MyThing();
}
}3.5 配置编码及JSP支持
# SPRING PROFILES
spring:
# HTTP ENCODING
http:
encoding.charset: UTF-8
encoding.enable: true
encoding.force: true
mvc:
view.prefix: /WEB-INF/jsp/
view.suffix: .jsp增加以上配置后,还须要引入用于编译jsp的jasper包依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>增加JSP支持配置后,以下a方法和b方法者是跳转到/WEB-INF/jsp/regiester.jsp页面。
package xyz.letus.boot.controller;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/page")
public class PageController {
@RequestMapping("/a")
public String b(Map<String, Object> model){
model.put("msg", "张三");
return "regiester";
}
@RequestMapping("/b")
public ModelAndView b(HttpServletRequest request){
ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView();
view.setViewName("regiester");
request.setAttribute("msg", "Davie");
return view;
}
}
3.6 Spring Boot应用实现热部署
在插件管理中增加springloaded依赖就能够。
<!-- Package as an executable jar -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- spring热部署-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>springloaded</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>当系统通过 mvn spring-boot:run启动或者 右键application debug 启动java文件时,系统会监视classes文件,当有classes文件被修改时,系统会又一次载入类文件,不用重新启动启动服务。
注:使用application run(非debug模式下),热部署功能会失效。
4、Spring Boot集成MyBatis
4.1 增加基础依赖
MyBatis:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0</version>
</dependency>
mybatis-spring-boot-starter:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>MySQL:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>4.2 数据库配置
# SPRING PROFILES
spring:
# DATASOURCE
datasource:
driverClass: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/hire?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: test 4.3 引入通用Mapper
- 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper</artifactId>
<version>3.3.7</version>
</dependency>- 配置通用Mapper
package xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.common.configure;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureAfter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import tk.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer;
import java.util.Properties;
@Configuration
public class MyBatisMapperScannerConfig {
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() {
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
mapperScannerConfigurer.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName("sqlSessionFactory");
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.*.dao");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("mappers", "xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.common.BaseDao");
properties.setProperty("notEmpty", "false");
properties.setProperty("IDENTITY", "MYSQL");
mapperScannerConfigurer.setProperties(properties);
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}
}
事实上MyBatisMapperScannerConfig 是一个MyBatis扫描Mapper接口扫描。
MapperScannerConfigurer依据指定的创建接口或注解创建映射器。我们这里映射了xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.*.dao包下的接口。
使用MapperScannerConfigurer。没有必要去指定SqlSessionFactory或SqlSessionTemplate,由于MapperScannerConfigurer将会创建MapperFactoryBean,之后自己主动装配。可是,假设你使用了一个以上的DataSource(因此,也是多个的SqlSessionFactory),那么自己主动装配可能会失效。这样的情况下,你能够使用sqlSessionFactory或sqlSessionTemplate属性来设置正确的工厂/模板。
注意的是网络上有些文章中在MapperScannerConfigurer之前还配置了 MyBatisConfig。由于MapperScannerConfigurer会创建MapperFactoryBean,所以我的项目中没有再配置MyBatisConfig。经使用没有出现不论什么问题。
4.4 通用Mapper的使用(Dao层)
BaseDao:
package xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.common;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.MySqlMapper;
public interface BaseDao<T> extends Mapper<T>,MySqlMapper<T>{
}
*Dao:
package xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.common.BaseDao;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.entity.User;
public interface UserDao extends BaseDao<User>{
@Select("select * from user where state = #{state}")
public List<User> selectByState(Integer state);
}
MyBatis的Dao与其他的ORM框架不一样的是,MyBatis的Dao事实上就是Mapper,是一个接口。是通过MapperScannerConfigurer扫描后生成实现的,我们不须要再写Dao接口的实现。
4.5 业务处理及事务(Service层)
package xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.service;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.entity.User;
public interface UserService {
public void saveUser(User user);
}
package xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.service.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.dao.TaskDao;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.dao.UserDao;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.entity.Task;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.entity.User;
import xyz.ibenben.zhongdian.system.service.UserService;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
private TaskDao taskDao;
@Transactional
public void saveUser(User user){
user = userDao.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
user.setUsername("5566");
userDao.updateByPrimaryKey(user);
// int i = 10/0;
Task task = new Task();
task.setName("task 100");
task.setDescript("task100 descriot");
task.setState(1);
taskDao.insert(task);
Task temp = new Task();
task.setState(1);
List<Task> list = taskDao.selectByRowBounds(temp, new RowBounds(2, 12));
System.out.println(list.size());
for(Task t : list){
System.out.println(t.getName());
}
List<User> users = userDao.selectByState(1);
for(User u : users){
System.out.println(u.getUsername());
}
}
}
Spring Boot集成MyBatis后,实现事物管理的方法非常easy,仅仅须要在业务方法前面加上@Transactional注解就能够了。
上面方法中用了一个被除数为0的表达式来进行測试事务。