Java注解定义
Java注解又称Java标注,是在 JDK5 时引入的新特性,注解(也被称为元数据)。
Java注解它提供了一种安全的类似注释的机制,用来将任何的信息或元数据(metadata)与程序元素(类、方法、成员变量等)进行关联。
Java注解是附加在代码中的一些元信息,用于一些工具在编译、运行时进行解析和使用,起到说明、配置的功能。
Java注解应用
1.生成文档这是最常见的,也是java 最早提供的注解;
2.在编译时进行格式检查,如@Override放在方法前,如果你这个方法并不是覆盖了超类方法,则编译时就能检查出;
3.跟踪代码依赖性,实现替代配置文件功能,比较常见的是spring 2.5 开始的基于注解配置,作用就是减少配置;
4.在反射的 Class, Method, Field 等函数中,有许多于 Annotation 相关的接口,可以在反射中解析并使用 Annotation。
Java注解分类
1、Java自带的标准注解
包括@Override、@Deprecated、@SuppressWarnings等,使用这些注解后编译器就会进行检查。
2、元注解
元注解是用于定义注解的注解,包括@Retention、@Target、@Inherited、@Documented、@Repeatable 等。
元注解也是Java自带的标准注解,只不过用于修饰注解,比较特殊。
3、自定义注解
用户可以根据自己的需求定义注解。
Java标准注解
JDK 中内置了以下注解:
1.@Override
class Parent { public void test() { } } class Child extends Parent { /** * 放开下面的注释,编译时会告警 */ /* @Override public void test() { } */ }
2.Deprecated
@Deprecated 用于标明被修饰的类或类成员、类方法已经废弃、过时,不建议使用。
@Deprecated class TestClass { // do something }
3.@SuppressWarnings
@SuppressWarnings 用于关闭对类、方法、成员编译时产生的特定警告。
1)抑制单类型的警告
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void addItems(String item){ @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") List items = new ArrayList(); items.add(item); }
2)抑制多类型的警告
@SuppressWarnings(value={"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public void addItems(String item){
List items = new ArrayList();
items.add(item);
}
3)抑制所有类型的警告
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public void addItems(String item){
List items = new ArrayList();
items.add(item);
}
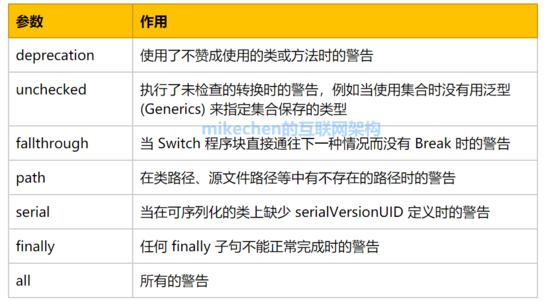
@SuppressWarnings 注解的常见参数值的简单说明:
4.@FunctionalInterface
@FunctionalInterface 用于指示被修饰的接口是函数式接口,在 JDK8 引入。
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface UserService { void getUser(Long userId); // 默认方法,可以用多个默认方法 public default void setUser() { } // 静态方法 public static void saveUser() { } // 覆盖Object中的equals方法 public boolean equals(Object obj);}
函数式接口(Functional Interface)就是一个有且仅有一个抽象方法,但是可以有多个非抽象方法的接口。
Java元注解
元注解是java API提供的,是用于修饰注解的注解,通常用在注解的定义上:
1.@Retention
@ Retention用来定义该注解在哪一个级别可用,在源代码中(SOURCE)、类文件中(CLASS)或者运行时(RUNTIME)。
@Retention 源码:
@Documented@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Retention { RetentionPolicy value(); } public enum RetentionPolicy { //此注解类型的信息只会记录在源文件中,编译时将被编译器丢弃,也就是说 //不会保存在编译好的类信息中 SOURCE, //编译器将注解记录在类文件中,但不会加载到JVM中。如果一个注解声明没指定范围,则系统 //默认值就是Class CLASS, //注解信息会保留在源文件、类文件中,在执行的时也加载到Java的JVM中,因此可以反射性的读取。 RUNTIME }
2.@Documented
@Documented:生成文档信息的时候保留注解,对类作辅助说明
@Documented 示例
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Column { public String name() default "fieldName"; public String setFuncName() default "setField"; public String getFuncName() default "getField"; public boolean defaultDBValue() default false; }
3.@Target
@Target:用于描述注解的使用范围(即:被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)
@Target源码:
@Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Target { ElementType[] value(); }
ElementType 是一个枚举类型,它定义了被 @Target 修饰的注解可以应用的范围:
4.@Inherited
@Inherited:说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解
表示自动继承注解类型。 如果注解类型声明中存在 @Inherited 元注解,则注解所修饰类的所有子类都将会继承此注解。
@Inherited public @interface Greeting { public enum FontColor{ BULE,RED,GREEN}; String name(); FontColor fontColor() default FontColor.GREEN; }
5.@Repeatable
@Repeatable 表示注解可以重复使用。
当我们需要重复使用某个注解时,希望利用相同的注解来表现所有的形式时,我们可以借助@Repeatable注解。
以 Spring @Scheduled 为例:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Schedules { Scheduled[] value(); } @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Repeatable(Schedules.class) public @interface Scheduled { // ... }
自定义注解
当我们理解了内置注解, 元注解和获取注解的反射接口后,我们便可以开始自定义注解了。
创建自定义注解和创建一个接口相似,但是注解的interface关键字需要以@符号开头,我们可以为注解声明方法。
自定义注解格式:
// 元注解
public @interface 注解名称{
// 属性列表
}
我们先来看看注解的例子:
1.创建自定义注解
/** * 自定义注解例子 * * @author mikechen */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Inherited public @interface HelloAnnotation { String value(); } ————————————————
2.使用自定义注解
/** * 使用自定义注解 * * @author mikechen */ public class HelloAnnotationClient { @HelloAnnotation(value="Simple custom Annotation example") public void sayHello(){ System.out.println("Inside sayHello method.."); } }
3.测试自定义注解
/** * 自定义注解测试 * * @author mikechen */ public class HelloAnnotationTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { HelloAnnotationClient helloAnnotationClient=new HelloAnnotationClient(); Method method=helloAnnotationClient.getClass().getMethod("sayHello"); if(method.isAnnotationPresent(HelloAnnotation.class)){ HelloAnnotation helloAnnotation=method.getAnnotation(HelloAnnotation.class); //Get value of custom annotation System.out.println("Value : "+helloAnnotation.value()); //Invoke sayHello method method.invoke(helloAnnotationClient); } } }



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)