一、二叉树的遍历
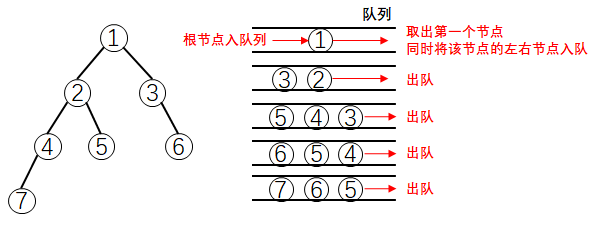
1.1 二叉树的层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return {};
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
vector<int> ret;
while(!que.empty()){
auto tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
ret.push_back(tmp->val);
if(tmp->left) que.push(tmp->left);
if(tmp->right) que.push(tmp->right);
}
return ret;
}
1.2 前序,中序,后序遍历(递归)
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res){
if(root==nullptr) return;
dfs(root->left, res);
dfs(root->right, res);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
dfs(root, res);
return res;
}
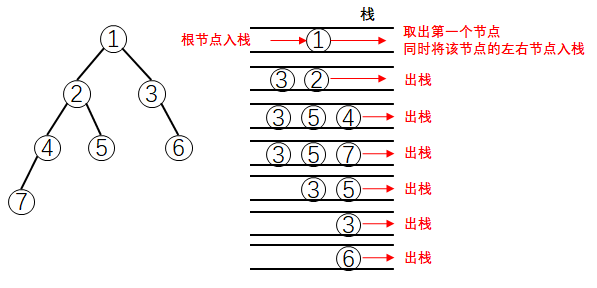
1.3 前序,中序,后序遍历(迭代)
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root == nullptr) return {};
stack<TreeNode*>stk;
stk.push(root);
while(!stk.empty()){
TreeNode* tmp = stk.top();
stk.pop();
res.push_back(tmp->val);
if(tmp->right) stk.push(tmp->right);
if(tmp->left) stk.push(tmp->left);
}
return res;
}
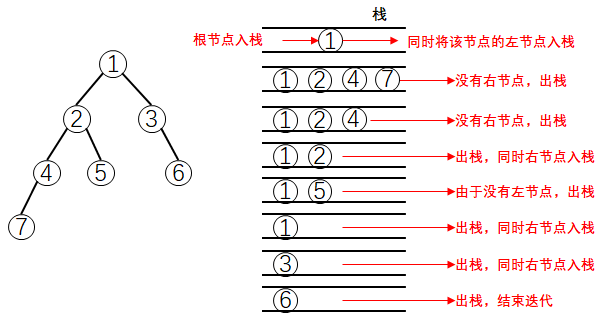
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>res;
if(root == nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
stk.push(root);
while(!stk.empty()){
while(stk.top()->left != nullptr) stk.push(stk.top()->left);
while(!stk.empty()){
TreeNode* tmp = stk.top(); stk.pop();
res.push_back(tmp->val);
if(tmp->right){
stk.push(tmp->right);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root == nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
stk.push(root);
TreeNode* lastnode = nullptr;
while(!stk.empty()){
while(stk.top()->left != nullptr) stk.push(stk.top()->left);
while(!stk.empty()){
if(lastnode == stk.top()->right || stk.top()->right == nullptr){
TreeNode* node = stk.top(); stk.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
lastnode = node;
}
else if(stk.top()->right != nullptr){
stk.push(stk.top()->right);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
二、二叉树的其他题目
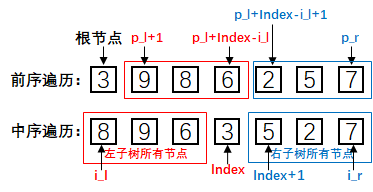
LeetCode 105: 从前序遍历与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
输入:preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
题目分析:
前序遍历中第一个节点就是根节点,第二个节点就是左子树的根节点......
中序遍历中根节点左边就是左子树
因此,我们通过前序遍历来找到节点,通过在中序遍历中的位置来判断是左子树还是右子树根节点,如下图所示:
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<int, int> index;
public:
TreeNode* myBuildTree(const vector<int>& preorder, const vector<int>& inorder, int preorder_left, int preorder_right, int inorder_left, int inorder_right) {
if (preorder_left > preorder_right) {
return nullptr;
}
int preorder_root = preorder_left;
int inorder_root = index[preorder[preorder_root]];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_root]);
int size_left_subtree = inorder_root - inorder_left;
root->left = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + 1, preorder_left + size_left_subtree, inorder_left, inorder_root - 1);
root->right = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + size_left_subtree + 1, preorder_right, inorder_root + 1, inorder_right);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int n = preorder.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
index[inorder[i]] = i;
}
return myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, 0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
}
};
LeetCode 105: 路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
题目分析:
每个节点不仅有它的 val 值,同时还有一些二叉树的深度,节点数值的和等隐含的属性。在求路径和时,当节点遍历时,将节点与路径和一起作为递归的参数,通过深度优先策略可以判断是否有等于targetSum的路径和。
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return false;
}
if(!root->left && !root->right){
if(root->val == targetSum) return true;
else
return false;
}
bool f1 = hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val);
bool f2 = hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);
return f1 || f2;
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == nullptr) return false;
stack<pair<TreeNode*, int>> stk;
stk.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(root, root->val));
while(!stk.empty()){
pair<TreeNode*, int> cur = stk.top(); stk.pop();
TreeNode* node = cur.first;
int path_value = cur.second;
if(node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr && path_value==targetSum){
return true;
}
if(node->right != nullptr)
stk.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node->right, path_value+node->right->val));
if(node->left != nullptr)
stk.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node->left, path_value+node->left->val));
}
return false;
}
LeetCode 113: 路径总和II
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
题目分析:
这道题跟上题差不多,只不过需要额外定义两个数组,res 和 path。其中 path 记录 dfs 遍历到的节点,当满足条件时就把 path 存入 res, 代替 “return true” 这一步。如果不满足条件,在 dfs 结束时记得弹出 path 的顶端 val, 回退到上一个节点。
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, vector<vector<int>>& res, vector<int>& path){
if (root == nullptr)
return;
path.push_back(root->val);
if(!root->left && !root->right && root->val==targetSum){
res.push_back(path);
}
if(root->left) dfs(root->left, targetSum - root->val, res, path);
if(root->right) dfs(root->right, targetSum - root->val, res, path);
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
dfs(root, targetSum, res, path);
return res;
}
LeetCode 199: 二叉树的右视图
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
题目分析:
这道题采用广度优先的策略会比较好理解,可以参考 `LeetCode 107: 二叉树的层序遍历II`,在层序遍历中,每一个层的最后一个节点就是所要找到的值。如果采用深度优先算法来理解,首先从根节点先访问右子树来确保右边的节点首先出现,然后使用一个 depth 变量来判断该节点是否被挡住。
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return {};
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<int> res;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int cur_size = que.size();
TreeNode* node = nullptr;
for(int i=0; i<cur_size; i++){
node = que.front(); que.pop();
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(node->val);
}
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int depth, vector<int>& res){
if(root == nullptr) return;
if(depth == res.size()){
res.push_back(root->val);
}
dfs(root->right, depth+1, res);
dfs(root->left, depth+1, res);
}
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
dfs(root, 0, res);
return res;
}
LeetCode 113: 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
题目分析:
本题同样可以采取 DFS 和 BFS 的策略。
使用 BFS 进行层序遍历,当碰到第一个节点 node 且 node->left 与 node->right 均为 nullptr 时,该节点的深度就是二叉树的最小深度。
使用 DFS 进行前序遍历,必须要记录每一条路径的深度,然后最小的那个就是结果。
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int res=0;
if(root == nullptr) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int cur_size = que.size();
res++;
for(int i=0; i<cur_size; i++){
TreeNode* node = que.front(); que.pop();
if(node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr)
return res;
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
return 1;
}
int min_depth = INT_MAX;
if (root->left != nullptr) {
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->left), min_depth);
}
if (root->right != nullptr) {
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->right), min_depth);
}
return min_depth + 1;
}







【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步