Spring事物控制
事物控制:
事物控制分为:
声明式事务控制
基于 XML 的声明式事务控制
基于注解的声明式事务控制
编程式事物控制与声明式事物控制的区别:
编程式事物控制:就是我们通过写代码来控制的
声明式事物控制:基于xml配置, 好处:我们通过配置xml来实现,这样可以解耦合,在不写代码情况下对业务层进行控制,简化开发
你的业务代码就是你的业务代码,你的事物控制就是你的控制事物
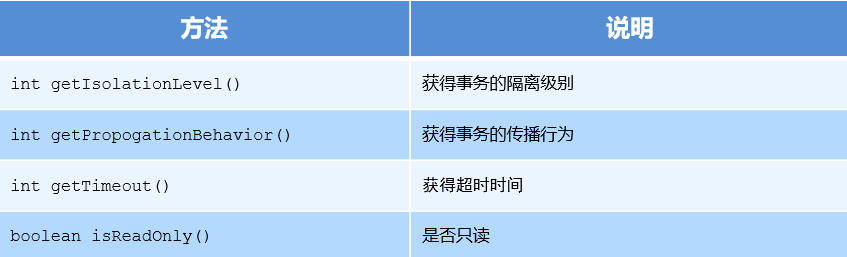
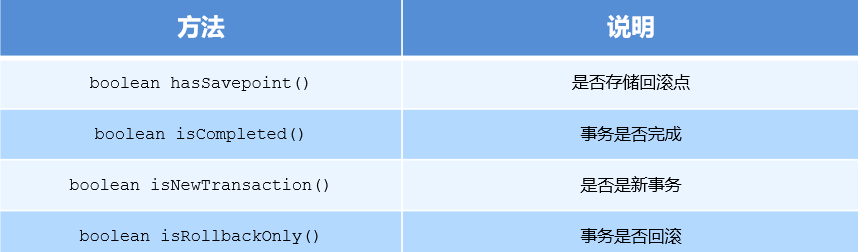
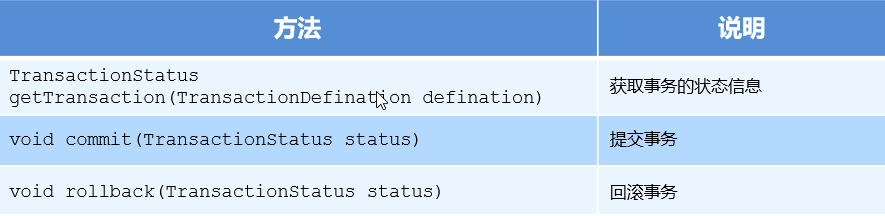
编程式事务控制相关对象
注意:
PlatformTransactionManager 是接口类型,不同的 Dao 层技术则有不同的实现类,例如:Dao 层技术是jdbc 或 mybatis 时:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
Dao 层技术是hibernate时:org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager
- ISOLATION_DEFAULT - ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED - ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED - ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ - ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE
- **REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)** - **SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)** - MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常 - REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。 - NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起 - NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常 - NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行 REQUIRED 类似的操作 - 超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置 - 是否只读:建议查询时设置为只读
- PlatformTransactionManager - TransactionDefinition - TransactionStatus
- 事务管理不侵入开发的组件。具体来说,业务逻辑对象就不会意识到正在事务管理之中,事实上也应该如此,因为事务管理是属于系统层面的服务,而不是业务逻辑的一部分,如果想要改变事务管理策划的话,也只需要在定义文件中重新配置即可
- 在不需要事务管理的时候,只要在设定文件上修改一下,即可移去事务管理服务,无需改变代码重新编译,这样维护起来极其方便
注意:Spring 声明式事务控制底层就是AOP。
声明式事务控制明确事项:
-
谁是切点?
-
谁是通知?
-
配置切面?
首先我们先建立一个模板用来做事物控制前的准备
流程就是Dao中定义接口用来操作数据 Dao.Impl中定义实现接口的类 都是操作数据库的
Service中定义方法是可以同时操作Dao.Impl的实现的 然后再controller中进行最后的调取
pom.xml

<dependencies> <!-- 导入spring框架包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.0.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- 导入spring的支持切入点表达式的包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.8.6</version> </dependency> <!-- 导入JdbcTemplate连接需要的包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId> <version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- 导入数据库连接池连接需要的包--> <dependency> <groupId>c3p0</groupId> <artifactId>c3p0</artifactId> <version>0.9.1.2</version> </dependency> <!-- 导入数据库连接需要的包--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.32</version> </dependency> <!-- 导入test测试需要的包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
建立数据库中Account表对应的Bean对象

/** * 建立数据库对应的Account表对应的Bean对象 */ public class Account { private Integer id; private String name; private Double price; public Account() { } public Account(Integer id, String name, Double price) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.price = price; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(Double price) { this.price = price; } }
Dao.AccountDao.java
AccountDao接口
public interface AccountDao { /** * 取钱的操作 * @param outMan 取钱的人 * @param money 取出的前 */ public void out(String outMan,double money); /** * 存钱的操作 * @param intMan 存钱的人 * @param money 存进去的钱 */ public void in(String intMan,double money); }
Dao.Impl.AccountDaoImpl.java
/** *实现AccountDao这个接口 */ public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate){ this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } public void out(String outMan, double money) { jdbcTemplate.update("update account set price=price+? where name = ?",money,outMan); } public void in(String intMan, double money) { jdbcTemplate.update("update account set price = price-? where name = ?",money,intMan); } }
Service.AccountService.java
AccountService.java接口用来定义调取Dao的方法
/** * 定义调取Dao实现类的方法 */ public interface AccountService { public void transfer(String outMan,String intMan,double money); }
Service.Impl.AccountServiceImpl.java
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao accountDao; // 从spring容器中获取AccountDao对象 public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao){ this.accountDao = accountDao; } /** * 取钱存钱操作 * @param outMan 取钱人 * @param intMan 存钱人 * @param money 钱数 */ public void transfer(String outMan, String intMan, double money) { accountDao.out(outMan,money); accountDao.in(intMan,money); } }
AccountController.java
public class AccountController { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); AccountService accountService = app.getBean(AccountService.class); accountService.transfer("tom","lucy",500); } }
applicationContext.xml
<!-- 因为在Dao中有操作数据的信息我们需要先配置JdbcTemplate来操作数据库--> <!-- 导入数据库配置信息 --> <context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder> <!-- 配置数据源--> <bean id="dataS" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!-- 建立jdbcTemplate模板对象 然后将配置的数据源放置在jdbcTemplate中--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataS"/> </bean> <!-- 建立AccountDaoImpl类的bean对象然后将jdbcTemplate对象注入其中--> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.spring.Dao.Impl.AccountDaoImpl"> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/> </bean> <!-- 将上面建立的操作数据库的bean注入到AccountServiceImpl类中--> <bean id="accountService" class="com.spring.Service.Impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///test_mybatis
jdbc.username=zhao
jdbc.password=123456
如果上面的我们未配置事物 那么再执行的时候有可能发生一个扣减了一个未增加的情况
public void transfer(String outMan, String intMan, double money) { accountDao.out(outMan,money); int i = 1/0; // 这个是抛出错的 accountDao.in(intMan,money); }
这样就会发生一个扣减一个未增加
增加事物就是让两个一起执行必须两个都同时执行成功才是成功
Spring 的声明式事务顾名思义就是采用声明的方式来处理事务。这里所说的声明,就是指在配置文件中声明,用在 Spring 配置文件中声明式的处理事务来代替代码式的处理事务。
声明式事务处理的作用
声明式事务控制明确事项:
-
谁是切点?
-
谁是通知?
-
配置切面?
①引入tx命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
②配置事务增强
<!-- 建立平台事物管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataS"></property> <!--对你的数据源进行管理--> </bean> <!-- 事物增强配置--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="*"/><!--对要增强的类的所有的方法进行增强--> <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="READ_COMMITTED" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <!--仅仅对tracsfer这个方法进行增强--> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice>
③配置事务 AOP 织入
<!-- 配置事物增强--> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="myPoincut" expression="execution(* com.spring.Service.Impl.AccountServiceImpl.transfer(..))"/><!---指定要增强的方法--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPoincut"/> <!-- 配置使用上面的事物增强配置来增强--> </aop:config>
④测试事务控制转账业务代码
@Override public void transfer(String outMan, String inMan, double money) { accountDao.out(outMan,money); int i = 1/0; accountDao.in(inMan,money); }
这个时候我们再进行测试就是两个一起执行成功才会改变结果,只有一个执行是不可以的
也就是我们先配置了数据源之后将数据源交给平台事物管理器,然后将平台事物管理器交给事物增强配置,事物增强配置 选择类的哪些方法,然后配置事物增强的时候为事物增强配置指定具体的类方法
就是数据源先交给平台事物管理器,平台事物管理器再交给事物增强配置,然后再降具体的类方法和事物增强连接在一起
声明式事物的配置
<!-- 建立平台事物管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataS"></property> <!--对你的数据源进行管理--> </bean> <!-- 事物增强配置--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="*"/><!--对要增强的类的所有的方法进行增强--> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置事物增强--> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="myPoincut" expression="execution(* com.spring.Service.Impl.AccountServiceImpl.transfer(..))"/><!---指定要增强的方法--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPoincut"/> <!-- 配置使用上面的事物增强配置来增强--> </aop:config>
声明式事物的配置后就会两个都要执行成功才可以,有一个不成功就不能执行
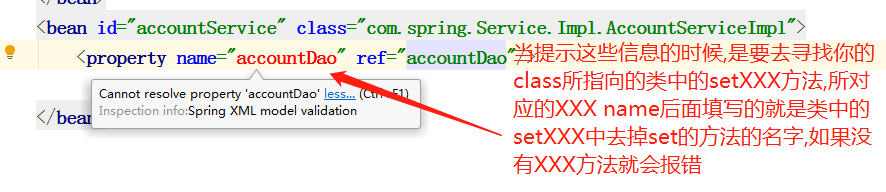
并且你的bean对应的类中的setXXX方法的权限也必须是public的不然也是不可以使用
/** *实现AccountDao这个接口 */ @Repository("accountDao") //添加Dao层类注解,将此类注入到Spring容器中 public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { @Autowired //将JdbcTemplate注入到此类中 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate){ this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } public void out(String outMan, double money) { jdbcTemplate.update("update account set price=price+? where name = ?",money,outMan); } public void in(String intMan, double money) { jdbcTemplate.update("update account set price = price-? where name = ?",money,intMan); } }
编写 AccoutService
@Service("accountService") // 将此类注入到Spring容器中
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) // 写在这里的配置增强代表当前这个类的所有的方法都是可以被增强的
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao; // 从spring容器中获取AccountDao对象
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao){
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
/**
* 取钱存钱操作
* @param outMan 取钱人
* @param intMan 存钱人
* @param money 钱数
*/
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) // 如果上面类也定义了增强而方法也定义那就使用单独的方法自己定义的这个
public void transfer(String outMan, String intMan, double money) {
accountDao.out(outMan,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.in(intMan,money);
}
}
编写 applicationContext.xml 配置文件
<!-- 开启组件扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.spring"></context:component-scan> <!-- 因为在Dao中有操作数据的信息我们需要先配置JdbcTemplate来操作数据库--> <!-- 导入数据库配置信息 --> <context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder> <!-- 配置数据源--> <bean id="dataS" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!-- 建立jdbcTemplate模板对象 然后将配置的数据源放置在jdbcTemplate中--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataS"/> </bean> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataS"/> </bean> <!-- 事物的注解驱动,让@Transactional此注解生效--> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
①使用 @Transactional 在需要进行事务控制的类或是方法上修饰,注解可用的属性同 xml 配置方式,例如隔离级别、传播行为等。
②注解使用在类上,那么该类下的所有方法都使用同一套注解参数配置。
③使用在方法上,不同的方法可以采用不同的事务参数配置。
④Xml配置文件中要开启事务的注解驱动<tx:annotation-driven />
注解声明式事务控制的配置要点
-
平台事务管理器配置(xml方式)
-
事务通知的配置(@Transactional注解配置)
-
事务注解驱动的配置 tx:annotation-driven/
-