数据库连接池
我们在使用数据库连接的时候一般是不会让我们去手动实现jdbc去连接数据库的,不,是一定。因为jdbc不停的去创建关闭连接是很耗费资源的,所以就有了数据库连接池
数据库连接池
概念:其实就是一个容器(集合),存放数据库连接的容器。
当系统初始化好后,容器被创建,容器中会申请一些连接对象,当用户来访问数据库时,从容器中获取连接对象,用户访问完之后,会将连接对象归还给容器。
资源池的优点:
1. 节约资源 2. 用户访问高效
数据库连接池分类:
有很多种 我们来举例两个 免费的: C3P0:数据库连接池技术 --- 可以省略一本不会去使用 Druid:数据库连接池实现技术,由阿里巴巴提供的 ---主要使用这个
Druid(数据库连接池 ) :使用步骤
1: 首先导入 Druid的jar包 :druid-1.0.9.jar 2. 定义配置文件: * 是properties形式的 * 可以叫任意名称,可以放在任意目录下 3. 加载配置文件。Properties 4. 获取数据库连接池对象:通过工厂来来获取 DruidDataSourceFactory 5. 获取连接:getConnection
数据库连接池的close()
数据库连接池的close()是归还连接,将从数据库连接池获取的连接归还到池内不是关闭数据库连接
eg:
配置文件.properties
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql:///girls username=zhao password=123456 # 初始化连接数量 initialSize=5 # 最大连接数 maxActive=10 # 最大等待时间 maxWait=3000
定义工具类获取配置文件建立连接
JdbcUtils.class
package com.atguigu.utils;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static DruidDataSource dataSource;
static {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 读取 jdbc.properties属性配置文件
InputStream inputStream = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
// 从流中加载数据
properties.load(inputStream);
// 创建 数据库连接 池
dataSource = (DruidDataSource) DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取数据库连接池中的连接
* @return 如果返回null,说明获取连接失败<br/>有值就是获取连接成功
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
/**
* 关闭连接,放回数据库连接池
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(Connection conn){
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
使用
public void Update(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement state = null; try { conn = JdbcPool.getConnectionOne(); -- 使用数据库连接池获取连接 String sql = "update admin set username =? where password =?"; state = conn.prepareStatement(sql); state.setObject(1,"AugustFive"); state.setObject(2,"500"); state.execute(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(state != null){ try { state.close(); 释放连接 将连接归还到数据库连接池内 } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
上面已经学习了我们经常使用的druid的数据库连接池,那么我们来学习一个简化增删改操作的类
commons-dbutils 是 Apache 组织提供的一个开源 JDBC工具类库,它是对JDBC的简单封装,学习成本极低,并且使用dbutils能极大简化jdbc编码的工作量,同时也不会影响程序的性能。
使用:
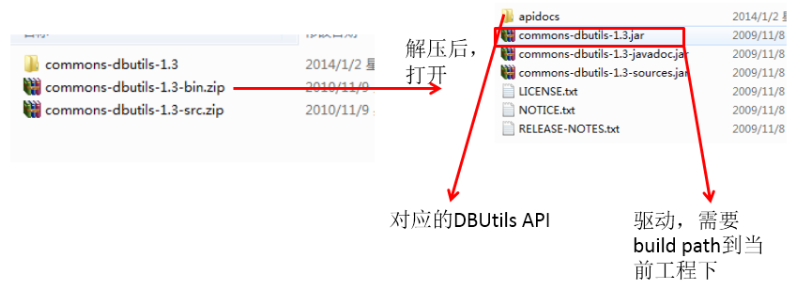
先将 commons-dbutils-1.3.jar jar包导入libs下的然后加入本模块下就可以使用
DbUtils :提供如关闭连接、装载JDBC驱动程序等常规工作的工具类,里面的所有方法都是静态的。主要方法如下: - public static void close(…) throws java.sql.SQLException: DbUtils类提供了三个重载的关闭方法。这些方法检查所提供的参数是不是NULL,如果不是的话,它们就关闭Connection、Statement和ResultSet。 - public static void closeQuietly(…): 这一类方法不仅能在Connection、Statement和ResultSet为NULL情况下避免关闭,还能隐藏一些在程序中抛出的SQLEeception。 - public static void commitAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException: 用来提交连接的事务,然后关闭连接 - public static void commitAndCloseQuietly(Connection conn): 用来提交连接,然后关闭连接,并且在关闭连接时不抛出SQL异常。 - public static void rollback(Connection conn)throws SQLException:允许conn为null,因为方法内部做了判断 - public static void rollbackAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException - rollbackAndCloseQuietly(Connection) - public static boolean loadDriver(java.lang.String driverClassName):这一方装载并注册JDBC驱动程序,如果成功就返回true。使用该方法,你不需要捕捉这个异常ClassNotFoundException。
该类简单化了SQL查询,它与ResultSetHandler组合在一起使用可以完成大部分的数据库操作,能够大大减少编码量
QueryRunner类提供了两个构造器: - 默认的构造器 - 需要一个 javax.sql.DataSource 来作参数的构造器
QueryRunner类的主要方法: - 更新 - public int update(Connection conn, String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException:用来执行一个更新(插入、更新或删除)操作。 - ...... - 插入 - public <T> T insert(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler<T> rsh, Object... params) throws SQLException:只支持INSERT语句,其中 rsh - The handler used to create the result object from the ResultSet of auto-generated keys. 返回值: An object generated by the handler.即自动生成的键值 - .... - 批处理 - public int[] batch(Connection conn,String sql,Object params)throws SQLException: INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE语句 - public <T> T insertBatch(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler<T> rsh,Object params)throws SQLException:只支持INSERT语句 - ..... - 查询 - public Object query(Connection conn, String sql, ResultSetHandler rsh,Object... params) throws SQLException:执行一个查询操作,在这个查询中,对象数组中的每个元素值被用来作为查询语句的置换参数。该方法会自行处理 PreparedStatement 和 ResultSet 的创建和关闭。 - ......
修改操作:
@Test public void updateWinter(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JdbcUtilsOne.getConnection(); String sql = " insert into admin(username,password) values(?,?)"; // 插入admin内的一个记录,username是老王password是1000 int insertCount = runner.update(conn,sql,"老王","1000"); // update中填入数据库连接,执行的sql和sql?号的对应的值 System.out.println("添加了"+insertCount+"条记录"); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JdbcUtilsOne.Close(null,conn); } }
查询操作:query()
@Test public void QueryAutumn(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JdbcUtilsOne.getConnection(); String sql = "select id,username,password from admin where id=?"; BeanHandler<Admin> handler = new BeanHandler(Admin.class); // BeanHandler是用来接受单个返回值的 它的泛型是查询的表多对应的类对象 Admin admin = runner.query(conn,sql,handler,1); // 查询使用query() 返回的是对应的表的类 System.out.println(admin); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JdbcUtilsOne.Close(null,conn); } }
API包的说明
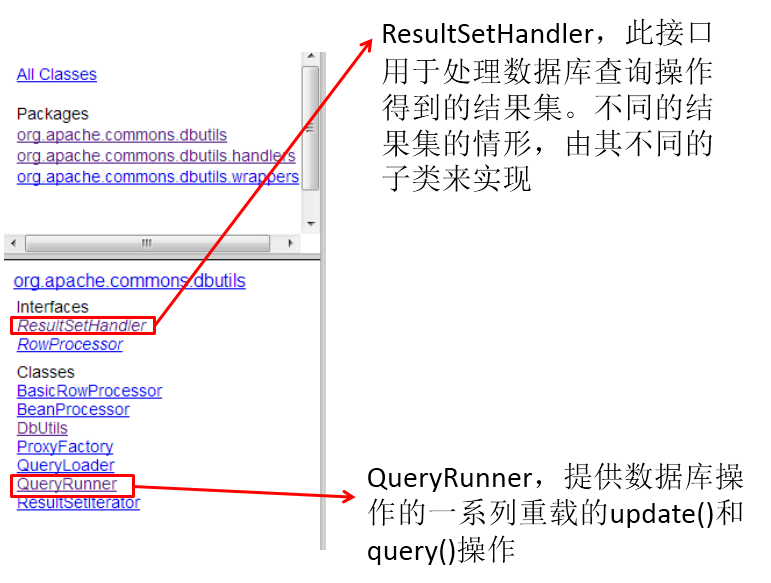
- 该接口用于处理 java.sql.ResultSet,将数据按要求转换为另一种形式。 - ResultSetHandler 接口提供了一个单独的方法:Object handle (java.sql.ResultSet .rs)。 - 接口的主要实现类: - ArrayHandler:把结果集中的第一行数据转成对象数组。 - ArrayListHandler:把结果集中的每一行数据都转成一个数组,再存放到List中。 - BeanHandler:将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中。 - BeanListHandler:将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中,存放到List里。 - ColumnListHandler:将结果集中某一列的数据存放到List中。 - KeyedHandler(name):将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,再把这些map再存到一个map里,其key为指定的key。 - MapHandler:将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个Map里,key是列名,value就是对应的值。 - MapListHandler:将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,然后再存放到List - ScalarHandler:查询单个值对象
查询单条记录使用ResultSetHandler的实现类:BeanHandler
查询多条记录:使用ResultSetHandler的实现类:BeanListHandler
BeanHandler<T> 和BeanListHandler<T>的泛型是查询的表内容所对应的java对象
例如有个表是user表然后要有个java类user.java与之对应 然后BeanHandler和BeanListHandler的泛型就是查询的这个user所对应的user.java类 就是BeanHandler<user> BeanListHandler<User>
查询一个记录:BeanHandler<T>
@Test public void QueryAutumn(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JdbcUtilsOne.getConnection(); String sql = "select id,username,password from admin where id=?"; BeanHandler<Admin> handler = new BeanHandler(Admin.class); // BeanHandler是用来接受单个返回值的 它的泛型是查询的表多对应的类对象 Admin admin = runner.query(conn,sql,handler,1); // 查询使用query() 返回的是对应的表的类 System.out.println(admin); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JdbcUtilsOne.Close(null,conn); } }
查询多个记录BeanListHandler<T>
@Test public void QueryJanuary(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JdbcUtilsOne.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from admin where id < ?"; BeanListHandler<Admin> beanListHandler = new BeanListHandler<>(Admin.class); // 泛型使用admin表多对应的Admin类 List<Admin> admin = runner.query(conn,sql,beanListHandler,23); System.out.println(admin); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JdbcUtilsOne.Close(null,conn); } }
//测试插入 @Test public void testInsert() { Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth)values(?,?,?)"; int insertCount = runner.update(conn, sql, "蔡徐坤","caixukun@126.com","1997-09-08"); System.out.println("添加了" + insertCount + "条记录"); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null); } } //测试查询 /* * BeanHander:是ResultSetHandler接口的实现类,用于封装表中的一条记录。 */ @Test public void testQuery1(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?"; BeanHandler<Customer> handler = new BeanHandler<>(Customer.class); Customer customer = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23); System.out.println(customer); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null); } } /* * BeanListHandler:是ResultSetHandler接口的实现类,用于封装表中的多条记录构成的集合。 */ @Test public void testQuery2() { Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id < ?"; BeanListHandler<Customer> handler = new BeanListHandler<>(Customer.class); List<Customer> list = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23); list.forEach(System.out::println); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null); } } /* * MapHander:是ResultSetHandler接口的实现类,对应表中的一条记录。 * 将字段及相应字段的值作为map中的key和value */ @Test public void testQuery3(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?"; MapHandler handler = new MapHandler(); Map<String, Object> map = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23); System.out.println(map); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null); } } /* * MapListHander:是ResultSetHandler接口的实现类,对应表中的多条记录。 * 将字段及相应字段的值作为map中的key和value。将这些map添加到List中 */ @Test public void testQuery4(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id < ?"; MapListHandler handler = new MapListHandler(); List<Map<String, Object>> list = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23); list.forEach(System.out::println); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null); } } /* * ScalarHandler:用于查询特殊值 */ @Test public void testQuery5(){ Connection conn = null; try { QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3(); String sql = "select count(*) from customers"; ScalarHandler handler = new ScalarHandler(); Long count = (Long) runner.query(conn, sql, handler); System.out.println(count); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null); } }
Spring Jdbc
spring-beans-5.0.0.RELEASE-sources.jar spring-core-5.0.0.RELEASE-sources.jar spring-jdbc-5.0.0.RELEASE-sources.jar spring-tx-5.0.0.RELEASE-sources.jar commons-logging-1.2.jar 这五个jar包的导入
* 步骤: 1. 导入jar包 2. 创建JdbcTemplate对象。依赖于数据源DataSource * JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(ds); 3. 调用JdbcTemplate的方法来完成CRUD的操作 * update():执行DML语句。增、删、改语句 * queryForMap():查询结果将结果集封装为map集合,将列名作为key,将值作为value 将这条记录封装为一个map集合 * 注意:这个方法查询的结果集长度只能是1 * queryForList():查询结果将结果集封装为list集合 * 注意:将每一条记录封装为一个Map集合,再将Map集合装载到List集合中 * query():查询结果,将结果封装为JavaBean对象 * query的参数:RowMapper * 一般我们使用BeanPropertyRowMapper实现类。可以完成数据到JavaBean的自动封装 * new BeanPropertyRowMapper<类型>(类型.class) * queryForObject:查询结果,将结果封装为对象 * 一般用于聚合函数的查询

// Druid连接池的工具类 private static DataSource source; static { try { Properties pro = new Properties(); InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"); pro.load(is); source = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection conn = source.getConnection(); return conn; } // 获取连接池方法 public static DataSource getSource(){ return source; }

package cn.itcast.jdbctemplate; import cn.itcast.domain.Emp; import cn.itcast.utils.JDBCUtils; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper; import java.sql.Date; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; public class JdbcTemplateDemo2 { //Junit单元测试,可以让方法独立执行 //1. 获取JDBCTemplate对象 private JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource()); /** * 1. 修改1号数据的 salary 为 10000 */ @Test public void test1(){ //2. 定义sql String sql = "update emp set salary = 10000 where id = 1001"; //3. 执行sql int count = template.update(sql); System.out.println(count); } /** * 2. 添加一条记录 */ @Test public void test2(){ String sql = "insert into emp(id,ename,dept_id) values(?,?,?)"; int count = template.update(sql, 1015, "郭靖", 10); System.out.println(count); } /** * 3.删除刚才添加的记录 */ @Test public void test3(){ String sql = "delete from emp where id = ?"; int count = template.update(sql, 1015); System.out.println(count); } /** * 4.查询id为1001的记录,将其封装为Map集合 * 注意:这个方法查询的结果集长度只能是1 */ @Test public void test4(){ String sql = "select * from emp where id = ? or id = ?"; Map<String, Object> map = template.queryForMap(sql, 1001,1002); System.out.println(map); //{id=1001, ename=孙悟空, job_id=4, mgr=1004, joindate=2000-12-17, salary=10000.00, bonus=null, dept_id=20} } /** * 5. 查询所有记录,将其封装为List */ @Test public void test5(){ String sql = "select * from emp"; List<Map<String, Object>> list = template.queryForList(sql); for (Map<String, Object> stringObjectMap : list) { System.out.println(stringObjectMap); } } /** * 6. 查询所有记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合 */ @Test public void test6(){ String sql = "select * from emp"; List<Emp> list = template.query(sql, new RowMapper<Emp>() { @Override public Emp mapRow(ResultSet rs, int i) throws SQLException { Emp emp = new Emp(); int id = rs.getInt("id"); String ename = rs.getString("ename"); int job_id = rs.getInt("job_id"); int mgr = rs.getInt("mgr"); Date joindate = rs.getDate("joindate"); double salary = rs.getDouble("salary"); double bonus = rs.getDouble("bonus"); int dept_id = rs.getInt("dept_id"); emp.setId(id); emp.setEname(ename); emp.setJob_id(job_id); emp.setMgr(mgr); emp.setJoindate(joindate); emp.setSalary(salary); emp.setBonus(bonus); emp.setDept_id(dept_id); return emp; } }); for (Emp emp : list) { System.out.println(emp); } } /** * 6. 查询所有记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合 */ @Test public void test6_2(){ String sql = "select * from emp"; List<Emp> list = template.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Emp>(Emp.class)); for (Emp emp : list) { System.out.println(emp); } } /** * 7. 查询总记录数 */ @Test public void test7(){ String sql = "select count(id) from emp"; Long total = template.queryForObject(sql, Long.class); System.out.println(total); } }
.
一般使用数据库连接池都是先使用 :Druid创建DataSource 然后建立起和数据库连接 然后使用 DbUtils包中的 QueryRunner 类进行增删改查语句的简化操作,



