动手动脑1多层的异常捕获
1.
package text;
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
运行结果:
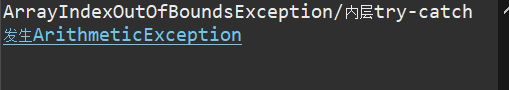
2.
package text; public class text { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
运行结果:
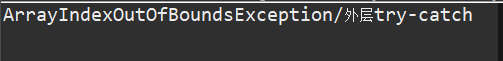
当有多个嵌套的try…catch…finally时,要特别注意finally的执行时机。
3.
package text; public class text { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } // result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } } }
2.运行结果
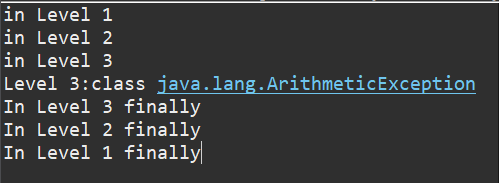
总结:当有多层嵌套的finally时,异常在不同的层次抛出 ,在不同的位置抛出,可能会导致不同的finally语句块执行顺序。
*处理运行异常时,尽量避免,并且尽量用try-catch来辅助。
*在多重catch快后可以加catch(Excetion)来处理遗漏
*对于不确定的也可一加try-catch
*尽量添加finally语句去释放占用的资源,并且finally语句是类似栈来进行释放的。
*还有finally语句不一定执行。
二、throw语句
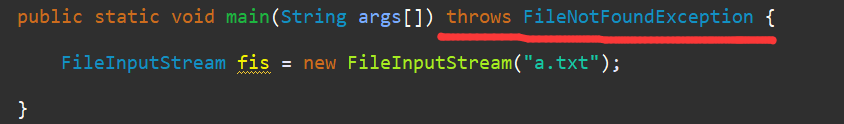
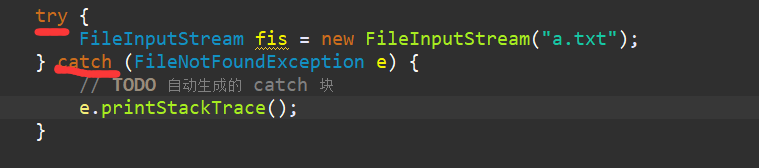
throws语句表明某方法中可能出现某种(或多种)异常,但它自己不能处理这些异常,而需要由调用者来处理。 当一个方法包含throws子句时,需要在调用此方法的代码中使用try/catch/finally进行捕获,或者是重新对其进行声明,否则编译时报错。
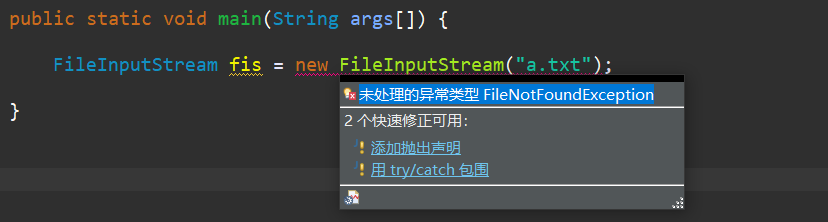
throws语句中声明的异常称为受控(checked)的异常,通常直接派生自Exception类。 RuntimeException(其基类为Exception) 和Error(基类为Throwable)称为非受控的异常。这种异常不用在throws语句中声明。 CheckedExceptionDemo.java示例展示了上述两种异常的特性。
三、以上都是前辈们总结出来的公用的抛出异常,我们在实际应用开发中应该自定义异常与异常处理链。
建议:
* 在中间层组件中抛出异常,在界面层组件中捕获异常在底层组件中捕获JVM抛出的“只有程序员能看懂的”异常,转换为中间层的业务逻辑异常,再由界面层捕获以提供有意义的信息。
* 自身能够处理的异常,不要再向外界抛出。
* 尽可能地在靠近异常发生的地方捕获并处理异常
* 尽可能地捕获最具体的异常类型,不要在中间层用 catch(Exception)“吃掉”所有异常
*在开发阶段捕获并显示所有异常信息,发布阶段要移除部分代码,以避免“过于专业”的异常信息困扰用户,特别地,系统发布之后,不要将服务端异常的详细信息发给客户端,以免被黑客利用


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号