Python字典底层实现原理
字典是否是有序
在python3.6之前,字典是无序的,但是python3.7+,字典是有序的
在3.6中,字典有序是一个implementation detail,在3.7才正式成为语言特性,因此3.6中无法确保100%有序
字典的查询、添加、删除的时间复杂度
字典的查询、添加、删除的平均时间复杂度都是O(1),相比列表与元祖,性能更优。
字典的实现原理
python3.6之前的无序字典
字典底层是维护一张哈希表,可以把哈希表堪称一个列表,哈希表中的每一个元素又存储了哈希值(hash)、键(key)、值(value)3个元素
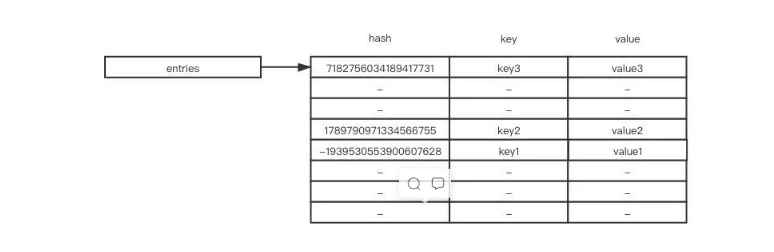
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | enteies = [ ['--', '--', '--'], [hash, key, value], ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], [hash, key, value],] |
带入具体的数值来介绍
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | # 给字典添加一个值,key为hello,value为word# my_dict['hello'] = 'word'# hash表初始如下enteies = [ ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'],]hash_value = hash('hello') # 假设值为 12343543 index = hash_value & ( len(enteies) - 1) # 假设index值计算后等于3# 下面会将值存在enteies中enteies = [ ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], [12343543, 'hello', 'word'], # index=3 ['--', '--', '--'],]# 继续向字典中添加值# my_dict['color'] = 'green'hash_value = hash('color') # 假设值为 同样为12343543index = hash_value & ( len(enteies) - 1) # 假设index值计算后同样等于3# 下面会将值存在enteies中enteies = [ ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], ['--', '--', '--'], [12343543, 'hello', 'word'], # 由于index=3的位置已经被占用,且key不一样,所以判定为hash冲突,继续向下寻找 [12343543, 'color', 'green'], # 找到空余位置,则保存] |
enteies表是稀疏的,随着我们插入的值不同,enteies表会越来越系数(enteies也是一个会动态扩展长度的,每一此扩展长度,都会重新计算所以key的hash值),所以新的字典实现就随之出现
python3.7+后的新的实现方式
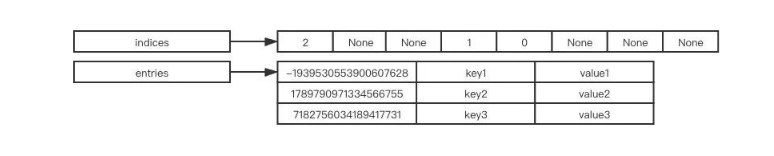
python3.7+带入数据演示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | # 给字典添加一个值,key为hello,value为word# my_dict['hello'] = 'word'# 假设是一个空列表,hash表初始如下indices = [None, None, None, None, None, None]enteies = []hash_value = hash('hello') # 假设值为 12343543index = hash_value & ( len(indices) - 1) # 假设index值计算后等于3# 会找到indices的index为3的位置indices = [None, None, None, 0, None, None]# 此时enteies会插入第一个元素enteies = [ [12343543, 'hello', 'word']]# 我们继续向字典中添加值my_dict['haimeimei'] = 'lihua'hash_value = hash('haimeimei') # 假设值为 34323545index = hash_value & ( len(indices) - 1) # 假设index值计算后等于 0# 会找到indices的index为0的位置indices = [1, None, None, 0, None, None]# 此时enteies会插入第一个元素enteies = [ [12343543, 'hello', 'word'], [34323545, 'haimeimei', 'lihua']] |
查询字典
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | # 下面是一个字典与字典的存储more_dict = {'name': '张三', 'sex': '男', 'age': 10, 'birth': '2019-01-01'}# 数据实际存储indices = [None, 2, None, 0, None, None, 1, None, 3]enteies = [ [34353243, 'name', '张三'], [34354545, 'sex', '男'], [23343199, 'age', 10], [00956542, 'birth', '2019-01-01'],]print(more_dict['age']) # 当我们执行这句时hash_value = hash('age') # 假设值为 23343199index = hash_value & ( len(indices) - 1) # index = 1entey_index = indices[1] # 数据在enteies的位置是2value = enteies[entey_index] # 所以找到值为 enteies[2] |
时间复杂度
字典的平均时间复杂度是O(1),因为字典是通过哈希算法来实现的,哈希算法不可避免的问题就是hash冲突,Python字典发生哈希冲突时,会向下寻找空余位置,直到找到位置。如果在计算key的hash值时,如果一直找不到空余位置,则字典的时间复杂度就变成了O(n)了。
常见的哈希冲突解决方法
开放寻址法(open addressing)
开放寻址法中,所有的元素都存放在散列表里,当产生哈希冲突时,通过一个探测函数计算出下一个候选位置,如果下一个获选位置还是有冲突,那么不断通过探测函数往下找,直到找个一个空槽来存放待插入元素。
再哈希法
这个方法是按顺序规定多个哈希函数,每次查询的时候按顺序调用哈希函数,调用到第一个为空的时候返回不存在,调用到此键的时候返回其值。
链地址法
将所有关键字哈希值相同的记录都存在同一线性链表中,这样不需要占用其他的哈希地址,相同的哈希值在一条链表上,按顺序遍历就可以找到。
公共溢出区
其基本思想是:所有关键字和基本表中关键字为相同哈希值的记录,不管他们由哈希函数得到的哈希地址是什么,一旦发生冲突,都填入溢出表。
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/General_zy/article/details/122038164




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)