IO模型
IO模型简介
IO模型研究的主要是网络IO(linux系统)
基本关键字
同步(synchronous) 大部分情况下会采用缩写的形式 sync
异步(asynchronous) async
阻塞(blocking)
非阻塞(non-blocking)
五种IO
blocking IO 阻塞IO
nonblocking IO 非阻塞IO
IO multiplexing IO多路复用
signal driven IO 信号驱动IO
asynchronous IO 异步IO
由signal driven IO(信号驱动IO)在实际中并不常用,所以主要介绍其余四种IO Model。
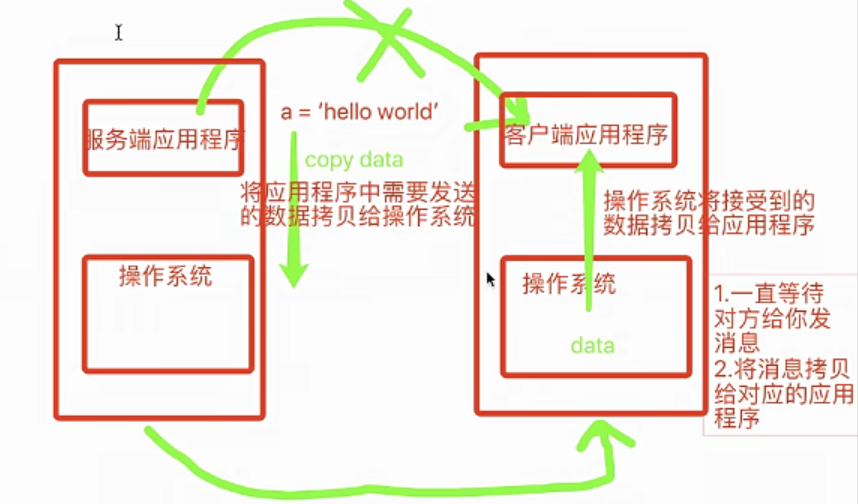
再说一下IO发生时涉及的对象和步骤。对于一个network IO (这里我们以read举例),它会涉及到两个系统对象,一个是调用这个IO的process (or thread),另一个就是系统内核(kernel)。当一个read操作发生时,该操作会经历两个阶段:
1、等待数据准备 (Waiting for the data to be ready)
2、将数据从内核拷贝到进程中(Copying the data from the kernel to the process)
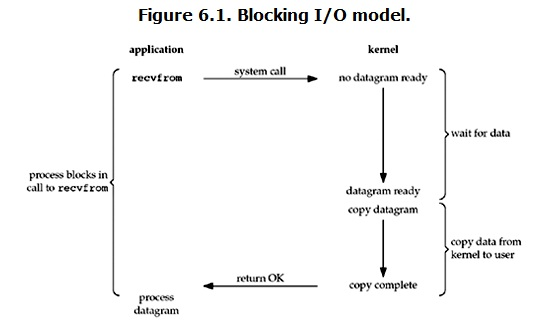
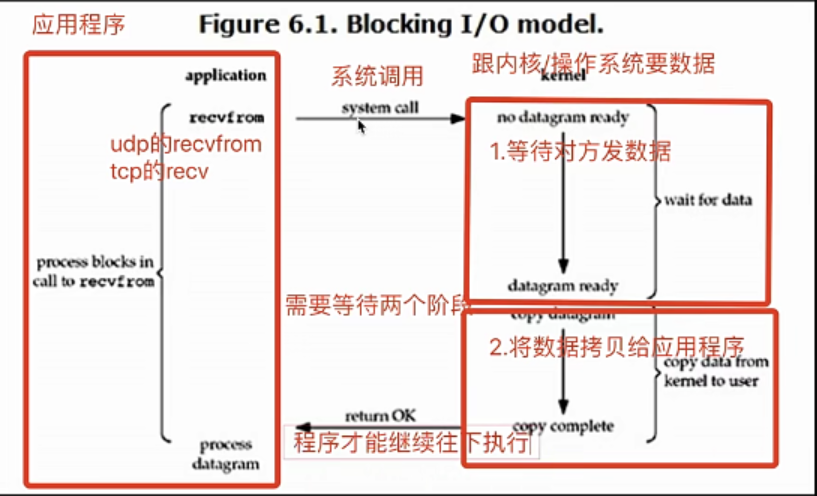
常见的网络阻塞状态:
accept recv recvfrom
阻塞IO模型
读操作流程大概是这样:
在服务端开设多进程或者多线程 进程池线程池 其实还是没有解决IO问题,该等的地方还是得等 没有规避,只不过多个人等待的彼此互不干扰
非阻塞IO模型
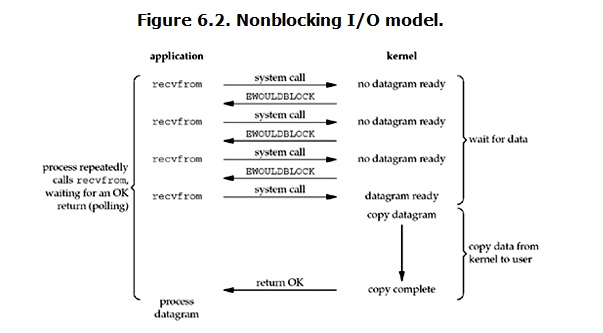
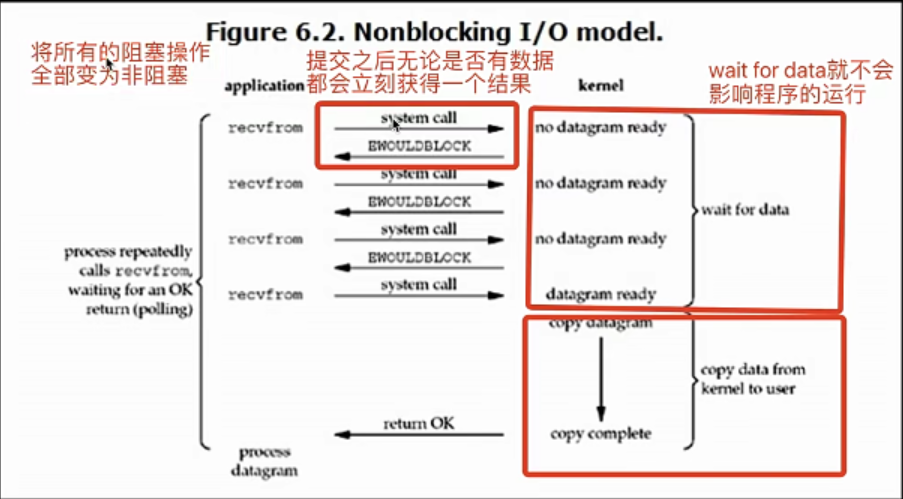
服务端
import socket import time server = socket.socket() server.bind(('127.0.0.1', 8081)) server.listen(5) server.setblocking(False) # 将所有的网络阻塞变为非阻塞 r_list = [] del_list = [] while True: try: conn, addr = server.accept() r_list.append(conn) except BlockingIOError: # time.sleep(0.1) # print('列表的长度:',len(r_list)) # print('做其他事') for conn in r_list: try: data = conn.recv(1024) # 没有消息 报错 if len(data) == 0: # 客户端断开链接 conn.close() # 关闭conn # 将无用的conn从r_list删除 del_list.append(conn) continue conn.send(data.upper()) except BlockingIOError: continue except ConnectionResetError: conn.close() del_list.append(conn) # 挥手无用的链接 for conn in del_list: r_list.remove(conn) del_list.clear()
客户端
import socket client = socket.socket() client.connect(('127.0.0.1',8081)) while True: client.send(b'hello world') data = client.recv(1024) print(data)
IO多路复用
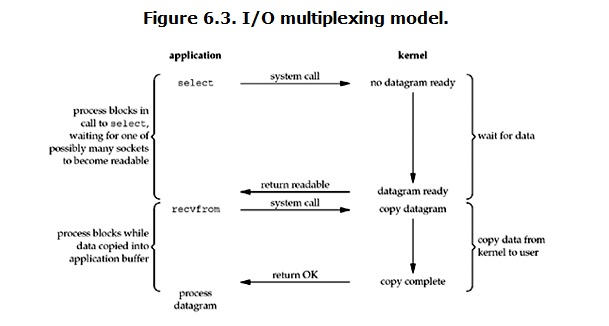
服务端
import socket import select server = socket.socket() server.bind(('127.0.0.1',8080)) server.listen(5) server.setblocking(False) read_list = [server] while True: r_list, w_list, x_list = select.select(read_list, [], []) """ 帮你监管 一旦有人来了 立刻给你返回对应的监管对象 """ # print(res) # ([<socket.socket fd=3, family=AddressFamily.AF_INET, type=SocketKind.SOCK_STREAM, proto=0, laddr=('127.0.0.1', 8080)>], [], []) # print(server) # print(r_list) for i in r_list: # """针对不同的对象做不同的处理""" if i is server: conn, addr = i.accept() # 也应该添加到监管的队列中 read_list.append(conn) else: res = i.recv(1024) if len(res) == 0: i.close() # 将无效的监管对象 移除 read_list.remove(i) continue print(res) i.send(b'heiheiheiheihei')
客户端
import socket client = socket.socket() client.connect(('127.0.0.1',8080)) while True: client.send(b'hello world') data = client.recv(1024) print(data)
异步IO
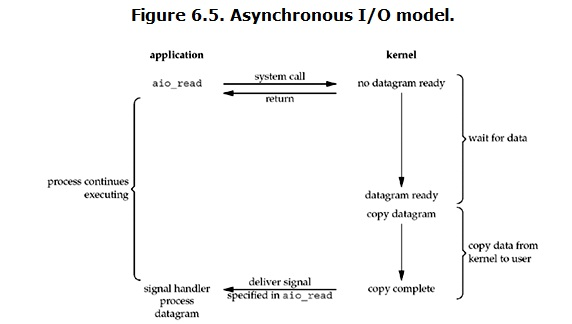
异步IO模型是所有模型中效率最高的 也是使用最广泛的
相关的模块和框架
模块:asyncio模块
异步框架:sanic tronado twisted
import threading import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def hello(): print('hello world %s'%threading.current_thread()) yield from asyncio.sleep(1) # 换成真正的IO操作 print('hello world %s' % threading.current_thread()) loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() tasks = [hello(),hello()] loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks)) loop.close()
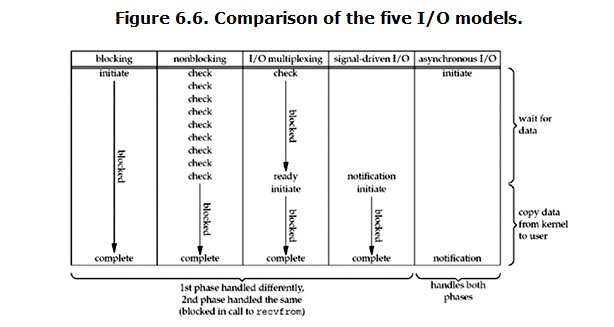
IO模型比较分析





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构