linux之find
作用
根据文件的名称或属性查找文件
格式
find [查找范围] [参数]
参数
1、按照文件的名字查找
-name
-iname (忽略大小写)
可配合的
* :通配符
1、[root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -name 'hosts' /etc/hosts
2、find /etc/ -name '*hosts*'
2、按照文件的大小查询文件
-size
可以配合的
+ 表示大于
- 表示小于
没有符号 就是等于
1、[root@localhost ~]# find /root -size +1M 2、[root@localhost ~]# find /root -size -1M 3、[root@localhost ~]# find /root -size 1000M
扩展:快速生成一个指定大小的文件
[root@localhost ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=4.txt bs=10M count=100
dd : 生成文件 if :从什么地方读 of : 写入到什么文件 bs : 每次写入多少内容 count : 写入多少次
3、按照时间来查找
-mtime :按照修改文件的时间来查找
-ctime :按照文件创建的时间来查找
-atime :按照访问时间来查找
可配合的:
+:查询某个时间段之前的数据
-:查询某个时间段之内的数据
1、[root@localhost ~]# find /root -mtime +2 2、[root@localhost ~]# find /root -mtime -1
4、按照文件的权限位来查找
-user :按照用户的属主来查找
-group :按照用户的属组来查找
1、[root@localhost ~]# find /root -user root 2、[root@localhost ~]# find /root -group test01
5、按照文件的类型查询
-type
文件类型有
d : 文件夹
l : 链接文件
s : 套接字文件
p : 管道文件
c : 字符文件
b :磁盘文件
f : 普通文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /root -type f
6、按照文件的权限查找
-perm(权限是按照数字来查找的)
[root@localhost ~]# find /root -perm 644
7、按照index node号码来查询
-inum
[root@localhost ~]# find /root -inum 134946661
8、配合参数(不可以单独使用)
-a :并且
-o :或许
-maxdepth :查询的目录深度(必须放置与第一个参数位)
-exec : 将find处理好的结果交给其他命令继续处理。

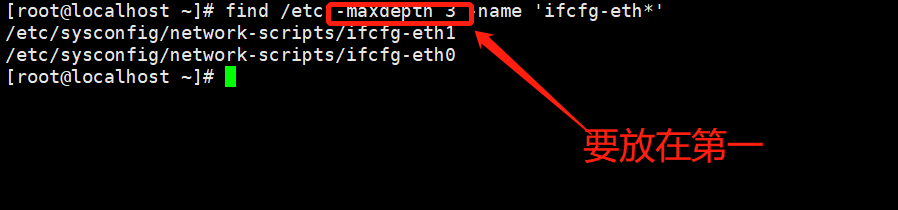
案例
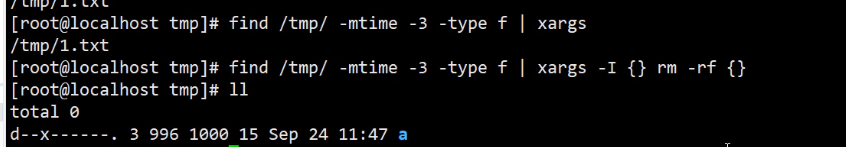
要求把/etc目录下,所有的普通文件打包压缩到/tmp目录 [root@localhost /tmp]# tar -czPf /tmp/etcv2.tar.gz `find /etc/ -type f | xargs`
知识扩展
| :前面一个命令的结果交给后面一个命令处理
xargs :把处理的文本变成以空格分割的一行
` ` :提前执行命令,然后讲结果交给其他命令来处理





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构