linux之目录结构介绍(二)
解析映射文件
/etc/hosts

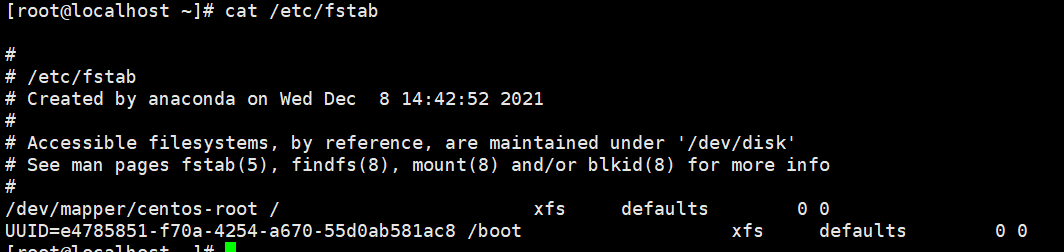
磁盘挂载文件
/etc/fstab
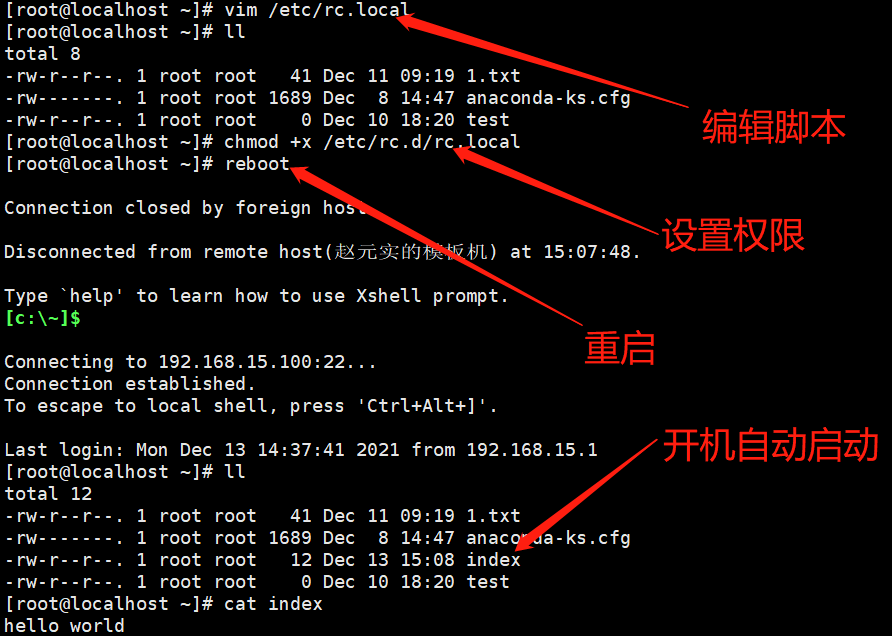
开机加载脚本
/etc/rc.local
设置开机自启动脚本
1 1、编辑开机自启动脚本 2 vim /etc/rc.local 3 2、设置开机自启动权限 4 chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local 5 3、重启系统
系统启动级别
1、系统启动级别
0、关机 1、单用户模式(无法通过xshell的方式使用) 2、多用户无网络模式 3、完全多用户模式 4、待定 5、桌面模式 6、重启
2、格式
init [编号] 临时设置
systemctl set-default [系统启动级别]
3、通过单用户模式修改root用户密码
1、重启 2、在启动选择系统内核界面,按 e 键进入单用户模式 3、找到 linux16 开头行,删除 ro , 并且在 ro 处添加 rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh 4、按 ctrl + x 进行系统重新引导 5、执行 chroot /sysroot 6、执行 passwd root 7、执行 touch /.autorelabel 8、执行 Ctrl + D 重启系统 注:selinux必须是永久关闭
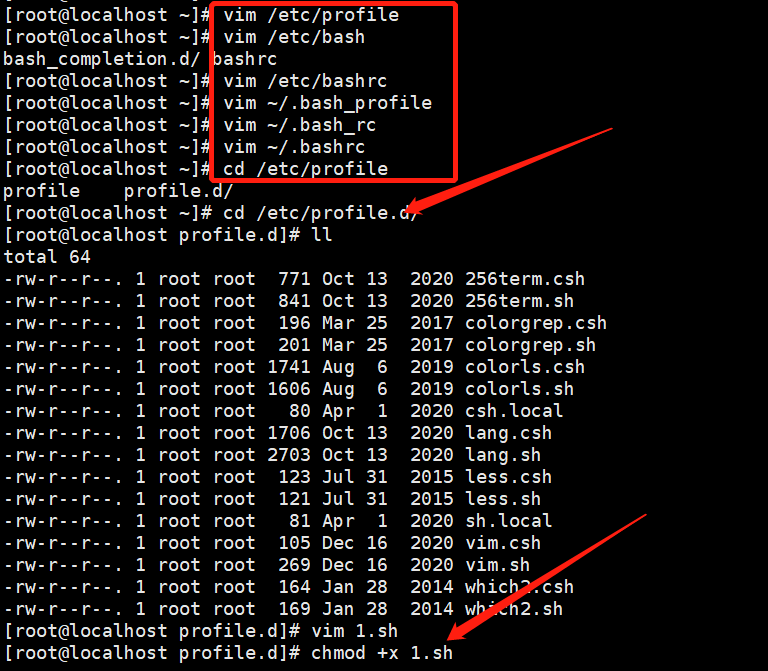
变量加载文件
1、文件
/etc/profile /etc/bashrc ~/.bash_profile ~/.bashrc
2、文件夹
/etc/profile.d/
3、添加环境变量的方式
临时添加和永久添加
4、增加环境变量的格式
export 环境变量名='变量路径'
5、查看本机的环境变量
echo $环境变量名 : 查看某一个环境变量 printenv : 查看所有的环境变量
6、读取环境变量的几种情况以及读取文件的先后顺序
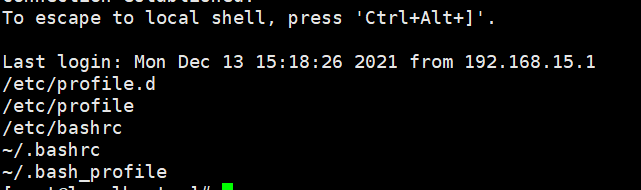
1、设置环境变量
2、重启
/etc/profile.d --> /etc/profile --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc --> ~/.bash_profile
3、切换用户
/etc/profile.d --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc 知识储备: useradd [用户名] su [用户名]
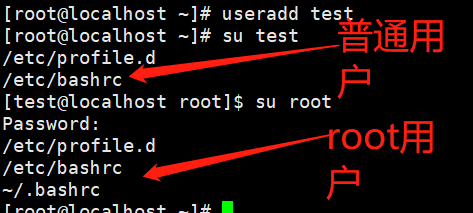
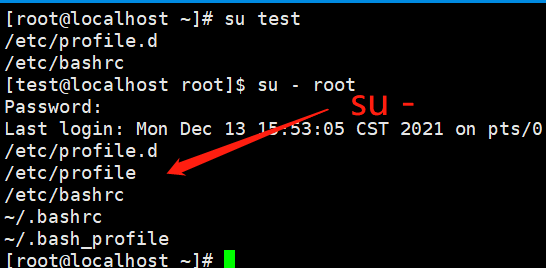
4、重新登录用户
1、su - [用户名] /etc/profile.d --> /etc/profile --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc --> ~/.bash_profile 2、ssh root@192.168.15.101 /etc/profile.d --> /etc/profile --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc --> ~/.bash_profile
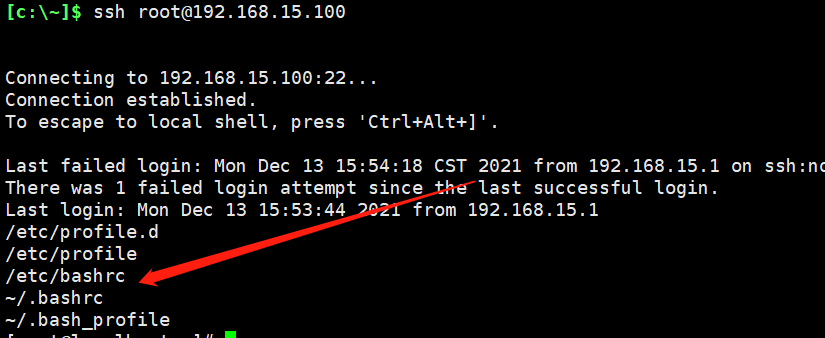
登录提示文件
1、登录成功之后的显示信息
/etc/motd
2、登录之前显示的信息
/etc/issue
编译安装目录
安装第三方软件的目录
/user/local
系统日志目录
/var
保持系统运行状态的目录
1、保存cpu运行状态
文件:/proc/cpuinfo
命令:lscpu
2、保存内存状态
文件:/proc/meminfo
命令:free
3、保存系统负载
文件:/proc/loadavg
命令:w
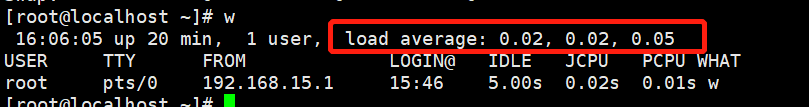
0.02 : 1分钟内的CPU负载 0.02 : 5分钟内的CPU负载 0.05 :15分钟内的CPU负载
负载:当前系统的所有进程占用cpu的时间比
4、保存系统挂载信息的
文件:/proc/mounts
命令:mount / umount






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构