Scalable packet classification using a compound algorithm
ABSTRACT
Cross-producting+PTSS
RELATED WORK
- 决策树和cross-producting搜索速度快,PTSS和独立集(?Independent Stes)内存需求少(tradeoff)
- all not scale well
ALGORITHM:two categories
- 两种搜索/储存方法并行:cross-producting table储存一定数量filter,tuple储存剩余filter

- filter set
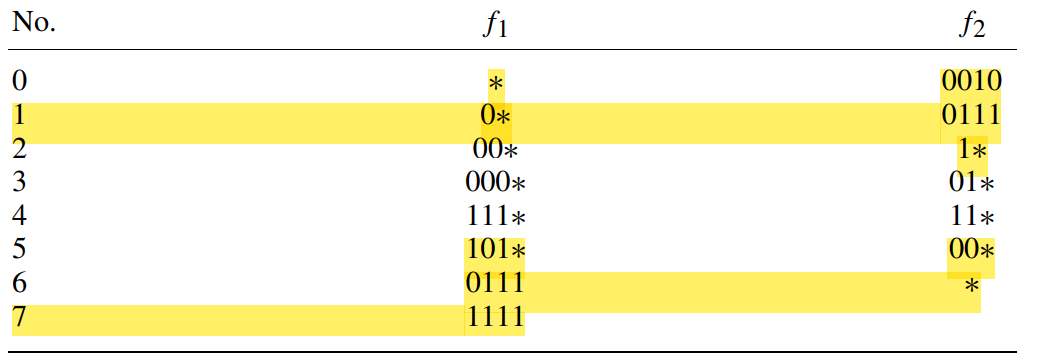
- 单个维度prefix种类(f1=8,f2=7)
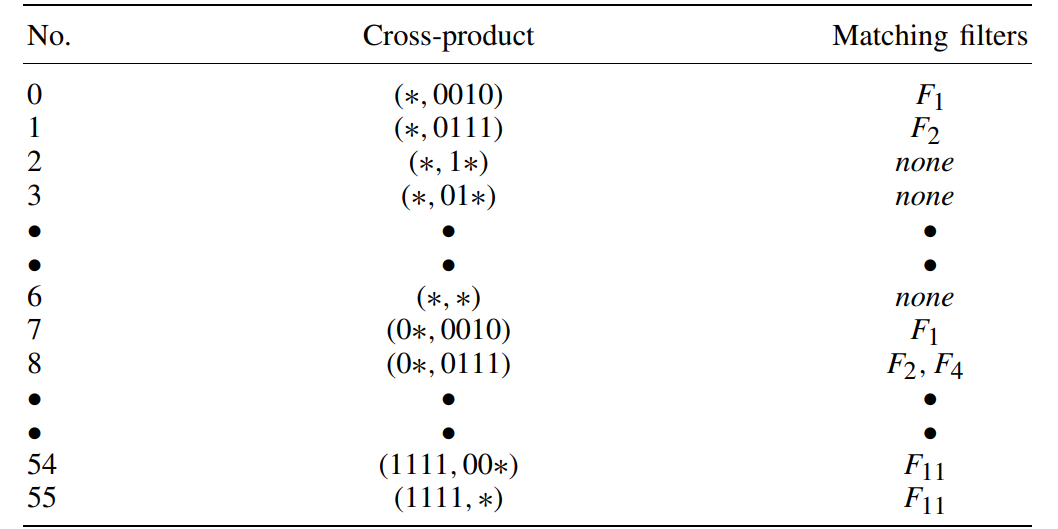
- 仅用cross-product需要占用大量内存(entries=7*8=56)
tuple selection:选择用于TSS的元组
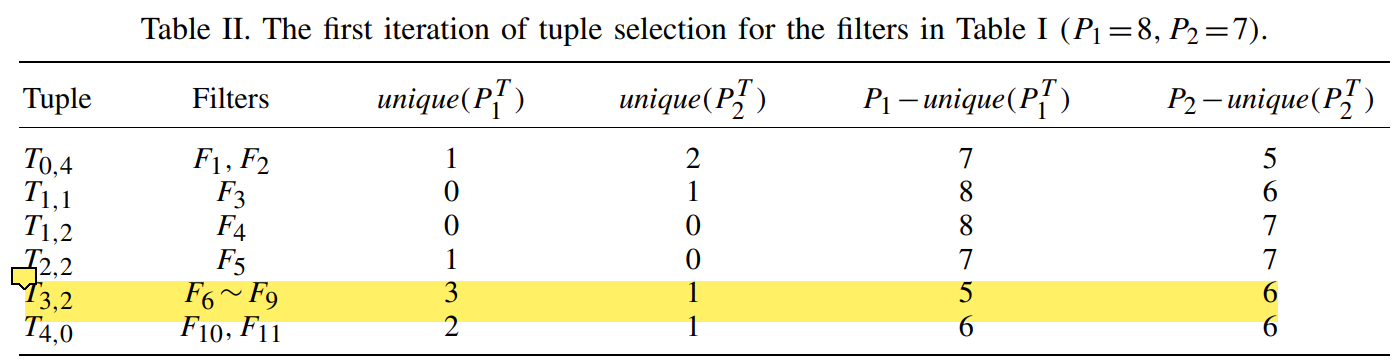


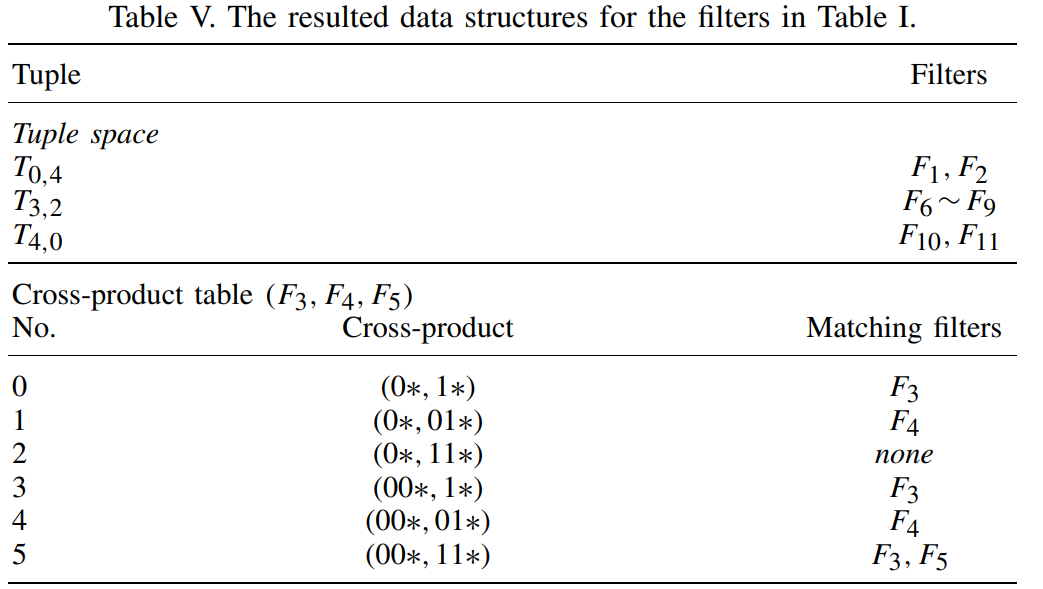
- tuple selection:选择用于TSS的元组,并在下一个interation将已提取的元组前缀删除选择下一个用于TSS的元组,直到有一组(p1-unique(p1))*(p1-unique(p2))<=C (p1、p2为当前interation的前缀数,unique是元组中独特前缀(只出现在这个元组的前缀)的数量,C是词条数,两个的乘积就是当前cross-product table词条数)。由于cross-product table需要大量储存空间,所以要限制其数目
- 筛选的目的是把有独特前缀多的元组提取出来,在形成tuple list的时候每个list中元组数量少,取交集时精确性更高,所花时间更少(用trie树匹配前缀最多只要O(W),每个tuple list数量少意味着取交集时匹配少)
- 元组剪枝就是在取交集时,将不会出现匹配过滤器的元组削减
- 将部分filter用于TSS,减少cross-product的压力
查找:两个表都查,按优先级选择filter
REFINEMENTS
Multiple cross-product tables
- 给元组数量设置界限Ct,当词条数目小于界限Ce时,若元组数量大于Ct,则将之前选出的元组再进行新一轮tuple selection,当词条数目小于界限Ce时剩余的filter被放进一个新的cross-product table
- 目的:减少TSS元组数量
Nested level tuple space
- 原先元组分类根据字段长度,现在根据前缀级别
- 当新filter加入时,前缀级别有可能改变
Adaptive implementation of cross-product table
- 储存cross-product table有两种数据结构:direct-access array or hash table
- 两种混用
UPDATES
Deletion
- both:不删除前缀,ation置空
Insertion
- TSS(NLTs):不改变原有结构,新开元组集,用字段长度表示
- cross-product table:加到TSS里
EVALUATION
- 多种结合:Cross-producting+PTSS,PLTs+NLTs(TSS),direct-access array+hash table(cross-product table)
- tradeoff between storage and search:内存占用比较,但是查询速度相对快,Cross-producting+PTSS结合适用大型数据库
看不懂的
- 储存cross-product table有两种数据结构:direct-access array or hash table
- The time complexity of Cross-producting is O(dlogN+Wd ) and that of Pruned Tuple Space Search is O(dlogN), where W is the maximum prefix length and Wd denotes the maximum number of tuples.



