Django contenttypes组件
Django包含一个contenttypes应用程序(app),可以跟踪Django项目中安装的所有模型(Model),提供用于处理模型的高级通用接口。
生成表结构之后有一个表,包含所有其他表
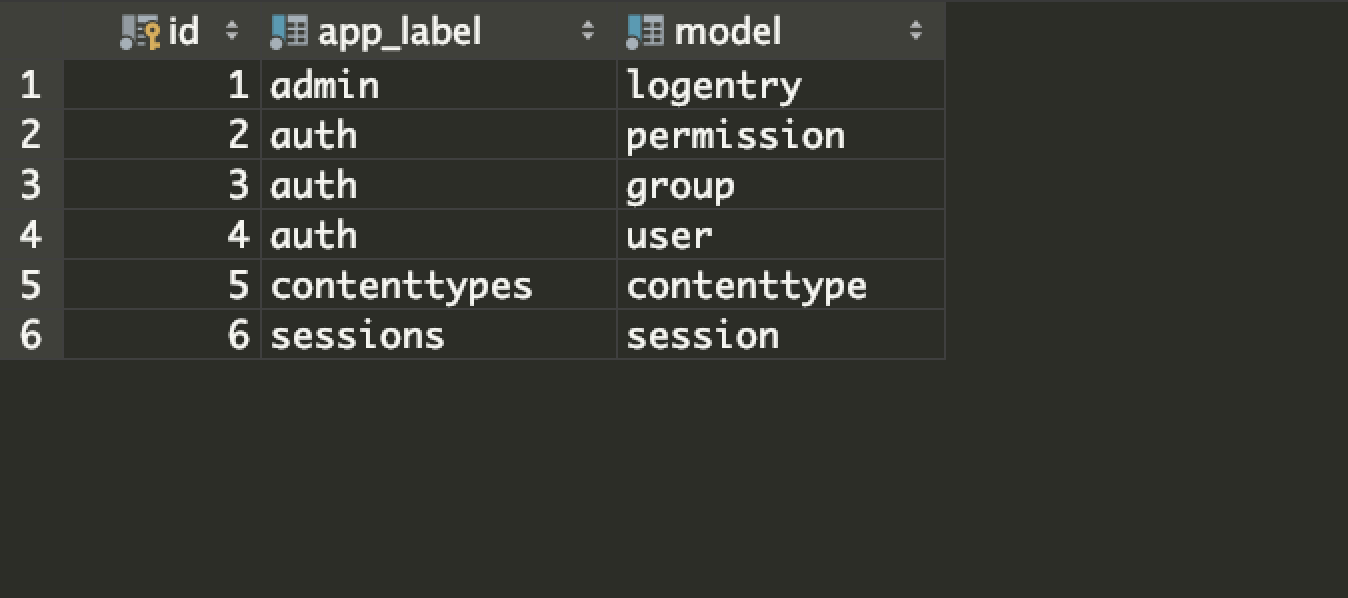
该组件主要应用于像不同的帖子和不同的照片都有评论,但是想只用一张评论表去存储,评论表中应有一个字段说明属于帖子还是照片,有一个字段说明该评论属于具体哪个帖子、哪个照片。

from django.db import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey,GenericRelation,ContentType class Post(models.Model): """帖子表""" title = models.CharField(max_length=72) # 查看一个对象的全部评论用comments,创建时用GenericRelation comments=GenericRelation('Comment') class Picture(models.Model): """图片表""" image = models.ImageField() comments = GenericRelation('Comment') class Comment(models.Model): """评论表""" content = models.TextField() # post = models.ForeignKey(Post, null=True, blank=True, on_delete=models.CASCADE) # picture = models.ForeignKey(Picture, null=True, blank=True, on_delete=models.CASCADE) # 外键关联ContentType(其中有所有的表) content_type=models.ForeignKey(ContentType,on_delete=models.DO_NOTHING) # 关联数据的主键,具体某一行的id(例如具体某一个帖子的id) object_id=models.PositiveSmallIntegerField() # GenericForeignKey字段创建,在数据库中不会存在该字段 content_object=GenericForeignKey('content_type','object_id')

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse from app01 import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import ContentType # Create your views here. def Test(request): # 创建测试数据 方式一 # content_type_pic_obj=ContentType.objects.filter(model='picture').first() # picture_obj=models.Picture.objects.filter(id=1).first() # models.Comment.objects.create(content='图片好看2',content_type=content_type_pic_obj,object_id=picture_obj.id) # models.Comment.objects.create(content='图片好看3',content_type=content_type_pic_obj,object_id=picture_obj.id) # models.Comment.objects.create(content='图片好看4',content_type=content_type_pic_obj,object_id=picture_obj.id) # content_type_post_obj = ContentType.objects.filter(model='post').first() # post_obj_1 = models.Post.objects.filter(title='散文1').first() # post_obj_2 = models.Post.objects.filter(title='散文2').first() # models.Comment.objects.create(content='散文写的好', content_type=content_type_post_obj, object_id=post_obj_1.id) # models.Comment.objects.create(content='散文写的好2', content_type=content_type_post_obj, object_id=post_obj_1.id) # models.Comment.objects.create(content='散文写的好3', content_type=content_type_post_obj, object_id=post_obj_2.id) # 创建测试数据方式二 # picture_obj = models.Picture.objects.filter(image='default_avatar.jpg').first() # models.Comment.objects.create(content_object=picture_obj,content='图片一般般') # post_obj_1 = models.Post.objects.filter(title='散文1').first() # models.Comment.objects.create(content_object=post_obj_1, content='文章一般般') # 查询一个对象的所有评论 comment_list=models.Post.objects.filter(id=1).first().comments.all() print(comment_list) return HttpResponse('...')

"""django_contenttypes编写models URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.urls import include, path 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: path('blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('test/', views.Test), ]
写出漂亮的博客就是为了以后看着更方便的。




