使用PowerShell/CMD自动化安装并配置MySQL数据库
最近在给同事的项目打包时,需要自动化安装MySQL及配置。
以前我们的上位机项目首选SQLite数据库,这样省去了安装配置及运行时的问题,但这次项目是另外一位同事负责的,我只是帮忙解决一些技术问题。
他使用了MySQL数据库,所以这里总结了一下在Windows环境下,如何自动化安装及配置MySQL。
由于该项目是内网环境使用,所以省去了一些安全设置及开启MySQL网络访问,这一块可以查阅相关资料解决。
1、下载MySQL
打开MySQL官网,下载Windows安装包
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/installer/
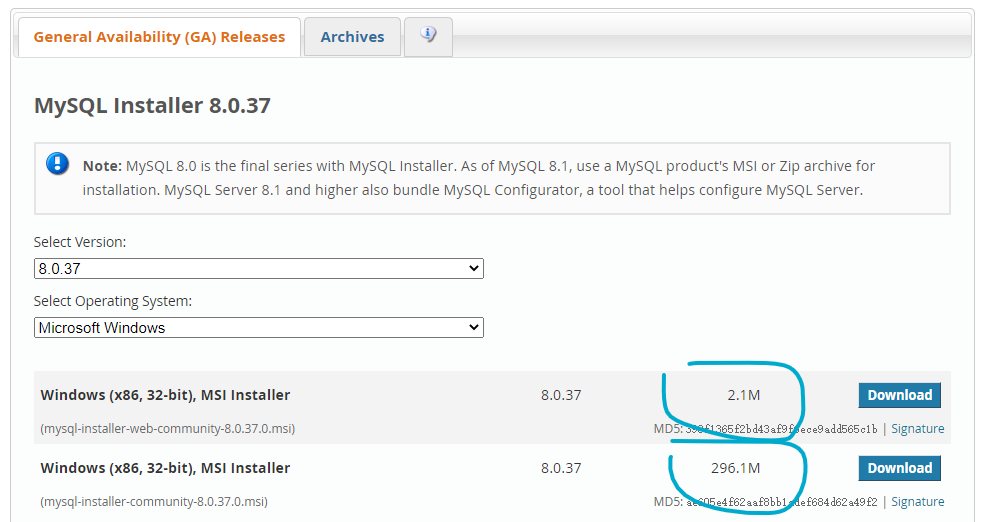
上面的是在线安装包,下面是离线安装包,建议选择离线安装包。
2、安装MySQL
在前面的文章中,介绍了如何使用msiexec安装.msi安装包,这里不再介绍,可以参考前面的文章。
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaotianff/p/11558602.html
自动化安装的命令是:
1 msiexec /i mysql-installer-community-8.0.37.0.msi /qn
3、配置MySQL
在安装完成MySQL后,MySQL安装程序会默认钩选打开配置程序(mysql_configurator.exe),这个程序会引导我们对MySQL进行配置。
在手动安装时可以借助这个程序进行配置
自动化安装时,需要创建配置文件,并通过MySQL安装目录下的bin/mysqld.exe加载配置文件来进行配置。
配置步骤如下:
1、首先我们创建一个my.ini的配置文件,文件内容如下:
这里为了方便大家理解,我先用mysql_configurator.exe生成了一个my.ini,然后全部贴在了这里

1 # Other default tuning values 2 # MySQL Server Instance Configuration File 3 # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 4 # Generated by the MySQL Server Instance Configuration Wizard 5 # 6 # 7 # Installation Instructions 8 # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 9 # 10 # On Linux you can copy this file to /etc/my.cnf to set global options, 11 # mysql-data-dir/my.cnf to set server-specific options 12 # (@localstatedir@ for this installation) or to 13 # ~/.my.cnf to set user-specific options. 14 # 15 # On Windows, when MySQL has been installed using MySQL Installer you 16 # should keep this file in the ProgramData directory of your server 17 # (e.g. C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y). To make sure the server 18 # reads the config file, use the startup option "--defaults-file". 19 # 20 # To run the server from the command line, execute this in a 21 # command line shell, e.g. 22 # mysqld --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini" 23 # 24 # To install the server as a Windows service manually, execute this in a 25 # command line shell, e.g. 26 # mysqld --install MySQLXY --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini" 27 # 28 # And then execute this in a command line shell to start the server, e.g. 29 # net start MySQLXY 30 # 31 # 32 # Guidelines for editing this file 33 # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 34 # 35 # In this file, you can use all long options that the program supports. 36 # If you want to know the options a program supports, start the program 37 # with the "--help" option. 38 # 39 # More detailed information about the individual options can also be 40 # found in the manual. 41 # 42 # For advice on how to change settings please see 43 # https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/server-configuration-defaults.html 44 # 45 # 46 # CLIENT SECTION 47 # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 48 # 49 # The following options will be read by MySQL client applications. 50 # Note that only client applications shipped by MySQL are guaranteed 51 # to read this section. If you want your own MySQL client program to 52 # honor these values, you need to specify it as an option during the 53 # MySQL client library initialization. 54 # 55 [client] 56 57 # pipe= 58 59 # socket=MYSQL 60 61 port=3306 62 63 [mysql] 64 no-beep 65 66 # default-character-set= 67 68 # SERVER SECTION 69 # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 70 # 71 # The following options will be read by the MySQL Server. Make sure that 72 # you have installed the server correctly (see above) so it reads this 73 # file. 74 # 75 # server_type=2 76 [mysqld] 77 78 # The next three options are mutually exclusive to SERVER_PORT below. 79 # skip-networking 80 # enable-named-pipe 81 # shared-memory 82 83 # shared-memory-base-name=MYSQL 84 85 # The Pipe the MySQL Server will use. 86 # socket=MYSQL 87 88 # The access control granted to clients on the named pipe created by the MySQL Server. 89 # named-pipe-full-access-group= 90 91 # The TCP/IP Port the MySQL Server will listen on 92 port=3306 93 94 # Path to installation directory. All paths are usually resolved relative to this. 95 # basedir="C:/Program Files/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.3" 96 97 # Path to the database root 98 datadir=C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.3/Data 99 100 # The default character set that will be used when a new schema or table is 101 # created and no character set is defined 102 # character-set-server= 103 104 105 # Administers multifactor authentication (MFA) capabilities. It applies to the authentication 106 # factor-related clauses of CREATE USER and ALTER USER statements used to manage MySQL account 107 # definitions, where "factor" corresponds to an authentication method or plugin associated 108 # with an account. 109 authentication_policy=*,, 110 111 # The default storage engine that will be used when create new tables when 112 default-storage-engine=INNODB 113 114 # The current server SQL mode, which can be set dynamically. 115 # Modes affect the SQL syntax MySQL supports and the data validation checks it performs. This 116 # makes it easier to use MySQL in different environments and to use MySQL together with other 117 # database servers. 118 sql-mode="ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION" 119 120 # General and Slow logging. 121 log-output=FILE 122 123 general-log=0 124 125 general_log_file="DESKTOP-D524565.log" 126 127 slow-query-log=1 128 129 slow_query_log_file="DESKTOP-D524565-slow.log" 130 131 long_query_time=10 132 133 # Error Logging. 134 log-error="DESKTOP-D524565.err" 135 136 # ***** Group Replication Related ***** 137 # Specifies the base name to use for binary log files. With binary logging 138 # enabled, the server logs all statements that change data to the binary 139 # log, which is used for backup and replication. 140 log-bin="DESKTOP-D524565-bin" 141 142 # ***** Group Replication Related ***** 143 # Specifies the server ID. For servers that are used in a replication topology, 144 # you must specify a unique server ID for each replication server, in the 145 # range from 1 to 2^32 − 1. "Unique" means that each ID must be different 146 # from every other ID in use by any other source or replica. 147 server-id=1 148 149 # Indicates how table and database names are stored on disk and used in MySQL. 150 # Value 0 = Table and database names are stored on disk using the lettercase specified in the CREATE 151 # TABLE or CREATE DATABASE statement. Name comparisons are case-sensitive. You should not 152 # set this variable to 0 if you are running MySQL on a system that has case-insensitive file 153 # names (such as Windows or macOS). If you force this variable to 0 with 154 # --lower-case-table-names=0 on a case-insensitive file system and access MyISAM tablenames 155 # using different lettercases, index corruption may result. 156 # Value 1 = Table names are stored in lowercase on disk and name comparisons are not case-sensitive. 157 # MySQL converts all table names to lowercase on storage and lookup. This behavior also applies 158 # to database names and table aliases. 159 # Value 2 = Table and database names are stored on disk using the lettercase specified in the CREATE TABLE 160 # or CREATE DATABASE statement, but MySQL converts them to lowercase on lookup. Name comparisons 161 # are not case-sensitive. This works only on file systems that are not case-sensitive! InnoDB 162 # table names and view names are stored in lowercase, as for lower_case_table_names=1. 163 lower_case_table_names=1 164 165 # This variable is used to limit the effect of data import and export operations, such as 166 # those performed by the LOAD DATA and SELECT ... INTO OUTFILE statements and the 167 # LOAD_FILE() function. These operations are permitted only to users who have the FILE privilege. 168 secure-file-priv="C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.3/Uploads" 169 170 # The maximum amount of concurrent sessions the MySQL server will 171 # allow. One of these connections will be reserved for a user with 172 # SUPER privileges to allow the administrator to login even if the 173 # connection limit has been reached. 174 max_connections=151 175 176 # The number of open tables for all threads. Increasing this value increases the number 177 # of file descriptors that mysqld requires. 178 table_open_cache=4000 179 180 # Defines the maximum amount of memory that can be occupied by the TempTable 181 # storage engine before it starts storing data on disk. 182 temptable_max_ram=1G 183 184 # Defines the maximum size of internal in-memory temporary tables created 185 # by the MEMORY storage engine and, as of MySQL 8.0.28, the TempTable storage 186 # engine. If an internal in-memory temporary table exceeds this size, it is 187 # automatically converted to an on-disk internal temporary table. 188 tmp_table_size=72M 189 190 # The storage engine for in-memory internal temporary tables (see Section 8.4.4, "Internal 191 # Temporary Table Use in MySQL"). Permitted values are TempTable (the default) and MEMORY. 192 internal_tmp_mem_storage_engine=TempTable 193 194 #*** MyISAM Specific options 195 # The maximum size of the temporary file that MySQL is permitted to use while re-creating a 196 # MyISAM index (during REPAIR TABLE, ALTER TABLE, or LOAD DATA). If the file size would be 197 # larger than this value, the index is created using the key cache instead, which is slower. 198 # The value is given in bytes. 199 myisam_max_sort_file_size=2146435072 200 201 # The size of the buffer that is allocated when sorting MyISAM indexes during a REPAIR TABLE 202 # or when creating indexes with CREATE INDEX or ALTER TABLE. 203 myisam_sort_buffer_size=135M 204 205 # Size of the Key Buffer, used to cache index blocks for MyISAM tables. 206 # Do not set it larger than 30% of your available memory, as some memory 207 # is also required by the OS to cache rows. Even if you're not using 208 # MyISAM tables, you should still set it to 8-64M as it will also be 209 # used for internal temporary disk tables. 210 key_buffer_size=8M 211 212 # Each thread that does a sequential scan for a MyISAM table allocates a buffer 213 # of this size (in bytes) for each table it scans. If you do many sequential 214 # scans, you might want to increase this value, which defaults to 131072. The 215 # value of this variable should be a multiple of 4KB. If it is set to a value 216 # that is not a multiple of 4KB, its value is rounded down to the nearest multiple 217 # of 4KB. 218 read_buffer_size=128K 219 220 # This variable is used for reads from MyISAM tables, and, for any storage engine, 221 # for Multi-Range Read optimization. 222 read_rnd_buffer_size=256K 223 224 #*** INNODB Specific options *** 225 # innodb_data_home_dir= 226 227 # Use this option if you have a MySQL server with InnoDB support enabled 228 # but you do not plan to use it. This will save memory and disk space 229 # and speed up some things. 230 # skip-innodb 231 232 # If set to 1, InnoDB will flush (fsync) the transaction logs to the 233 # disk at each commit, which offers full ACID behavior. If you are 234 # willing to compromise this safety, and you are running small 235 # transactions, you may set this to 0 or 2 to reduce disk I/O to the 236 # logs. Value 0 means that the log is only written to the log file and 237 # the log file flushed to disk approximately once per second. Value 2 238 # means the log is written to the log file at each commit, but the log 239 # file is only flushed to disk approximately once per second. 240 innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1 241 242 # The size in bytes of the buffer that InnoDB uses to write to the log files on 243 # disk. The default value changed from 8MB to 16MB with the introduction of 32KB 244 # and 64KB innodb_page_size values. A large log buffer enables large transactions 245 # to run without the need to write the log to disk before the transactions commit. 246 # Thus, if you have transactions that update, insert, or delete many rows, making 247 # the log buffer larger saves disk I/O. 248 innodb_log_buffer_size=16M 249 250 # The size in bytes of the buffer pool, the memory area where InnoDB caches table 251 # and index data. The default value is 134217728 bytes (128MB). The maximum value 252 # depends on the CPU architecture; the maximum is 4294967295 (232-1) on 32-bit systems 253 # and 18446744073709551615 (264-1) on 64-bit systems. On 32-bit systems, the CPU 254 # architecture and operating system may impose a lower practical maximum size than the 255 # stated maximum. When the size of the buffer pool is greater than 1GB, setting 256 # innodb_buffer_pool_instances to a value greater than 1 can improve the scalability on 257 # a busy server. 258 innodb_buffer_pool_size=128M 259 260 # Defines the amount of disk space occupied by redo log files. This variable supersedes the 261 # innodb_log_files_in_group and innodb_log_file_size variables. 262 innodb_redo_log_capacity=100M 263 264 # Defines the maximum number of threads permitted inside of InnoDB. A value 265 # of 0 (the default) is interpreted as infinite concurrency (no limit). This 266 # variable is intended for performance tuning on high concurrency systems. 267 # InnoDB tries to keep the number of threads inside InnoDB less than or equal to 268 # the innodb_thread_concurrency limit. Once the limit is reached, additional threads 269 # are placed into a "First In, First Out" (FIFO) queue for waiting threads. Threads 270 # waiting for locks are not counted in the number of concurrently executing threads. 271 innodb_thread_concurrency=25 272 273 # The increment size (in MB) for extending the size of an auto-extend InnoDB system tablespace file when it becomes full. 274 innodb_autoextend_increment=64 275 276 # The number of regions that the InnoDB buffer pool is divided into. 277 # For systems with buffer pools in the multi-gigabyte range, dividing the buffer pool into separate instances can improve concurrency, 278 # by reducing contention as different threads read and write to cached pages. 279 innodb_buffer_pool_instances=8 280 281 # Determines the number of threads that can enter InnoDB concurrently. 282 innodb_concurrency_tickets=5000 283 284 # Specifies how long in milliseconds (ms) a block inserted into the old sublist must stay there after its first access before 285 # it can be moved to the new sublist. 286 innodb_old_blocks_time=1000 287 288 # When this variable is enabled, InnoDB updates statistics during metadata statements. 289 innodb_stats_on_metadata=0 290 291 # When innodb_file_per_table is enabled (the default in 5.6.6 and higher), InnoDB stores the data and indexes for each newly created table 292 # in a separate .ibd file, rather than in the system tablespace. 293 innodb_file_per_table=1 294 295 # Use the following list of values: 0 for crc32, 1 for strict_crc32, 2 for innodb, 3 for strict_innodb, 4 for none, 5 for strict_none. 296 innodb_checksum_algorithm=0 297 298 # If this is set to a nonzero value, all tables are closed every flush_time seconds to free up resources and 299 # synchronize unflushed data to disk. 300 # This option is best used only on systems with minimal resources. 301 flush_time=0 302 303 # The minimum size of the buffer that is used for plain index scans, range index scans, and joins that do not use 304 # indexes and thus perform full table scans. 305 join_buffer_size=256K 306 307 # The maximum size of one packet or any generated or intermediate string, or any parameter sent by the 308 # mysql_stmt_send_long_data() C API function. 309 max_allowed_packet=64M 310 311 # If more than this many successive connection requests from a host are interrupted without a successful connection, 312 # the server blocks that host from performing further connections. 313 max_connect_errors=100 314 315 # The number of file descriptors available to mysqld from the operating system 316 # Try increasing the value of this option if mysqld gives the error "Too many open files". 317 open_files_limit=8161 318 319 # If you see many sort_merge_passes per second in SHOW GLOBAL STATUS output, you can consider increasing the 320 # sort_buffer_size value to speed up ORDER BY or GROUP BY operations that cannot be improved with query optimization 321 # or improved indexing. 322 sort_buffer_size=256K 323 324 # Specify the maximum size of a row-based binary log event, in bytes. 325 # Rows are grouped into events smaller than this size if possible. The value should be a multiple of 256. 326 binlog_row_event_max_size=8K 327 328 329 # If the value of this variable is greater than 0, a replica synchronizes its master.info file to disk. 330 # (using fdatasync()) after every sync_source_info events. 331 sync_source_info=10000 332 333 # If the value of this variable is greater than 0, the MySQL server synchronizes its relay log to disk. 334 # (using fdatasync()) after every sync_relay_log writes to the relay log. 335 sync_relay_log=10000 336 337 # Load mysql plugins at start."plugin_x ; plugin_y". 338 # plugin_load 339 340 # The TCP/IP Port the MySQL Server X Protocol will listen on. 341 loose_mysqlx_port=33060
这里我们注意几条参数即可:
1 # 配置默认编码 2 default-character-set=utf8mb4 3 # 配置端口号 4 port=3306 5 # 配置数据文件路径 6 datadir=C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.3/Data 7 # 默认数据库引擎 8 default-storage-engine=INNODB 9 # 最大连接数 10 max_connections=151 11 # 服务器类型 12 server_type=2
2、将my.ini复制到MySQL安装路径下的bin目录
虽然mysqld可以通过指定参数--defaults-file="xxx\my.ini"的形式来指定配置文件的路径,但还是建议直接将my.ini复制到bin目录下,如C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.3\bin
3、执行以下命令
以管理员运行CMD/PowerShell,
然后切换到MySQL的安装目录(由于MySQL安装后不会自动添加环境变量,所以需要切换到目录下执行命令)
1 C: 2 cd C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.3\bin
然后执行
1 mysqld.exe --initialize-insecure
这一句的作用是设置数据库空密码。
1 mysql --install MySQL_XXXX
这一句的作用是安装Windows服务,服务的名称可以自己定义,如MySQL_XXX
服务安装好后,调用net命令启动服务
1 net start MySQL_XXX
此时安装配置就已经完成了
4、创建数据表
自动化安装的最终目的是自动创建数据库及表,自动化创建步骤如下:
1、创建sql文件,将创建的库及表的脚本写入到sql文件中
假设我们创建一个如下的sql文件,并命名为create.sql
1 CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `mydb` 2 USE `mydb`;
1 CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `patient` ( 2 `PatientId` char(36) NOT NULL, 3 `PatientName` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL 4 PRIMARY KEY (`PatientId`) 5 ) ;
2、将sql文件复制到MySQL安装路径的bin目录下
这里我们是将create.sql复制到C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.3\bin目录下。
3、调用mysql.exe执行sql文件
1 mysql < create.sql -u root
由于默认是没有密码的,所以sql文件直接被执行,创建了mydb的数据库,并创建了patient表。
4、设置密码
之所以最后一步才设置密码,是因为上述操作在使用编程语言调用时会比较方便。
如果先创建了密码,在与控制台程序进行交互时,就需要输入密码,这会增加交互的复杂性。
创建一个set_password.sql文件,内容如下:
1 use mysql; 2 ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '1234'; 3 flush privileges;
然后复制到bin目录下按创建数据库一样的步骤执行即可
1 mysql < set_password.sql -u root
5、在C#中配置MySQL的步骤
1、安装步骤省略,直接调用msiexec执行安装即可
2、将上述中涉及的配置文件及sql文件复制到bin目录下
3、配置MySQL
首先封装一个调用函数
1 private static void Exec(string path,string args) 2 { 3 System.Diagnostics.Process p = new System.Diagnostics.Process(); 4 p.StartInfo.FileName = path; 5 p.StartInfo.Arguments = args; 6 p.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false; 7 p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardError = true; 8 p.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = false; 9 p.Start(); 10 p.BeginErrorReadLine(); 11 p.WaitForExit(); 12 p.Close(); 13 p.Dispose(); 14 }
调用mysqld.exe和mysql.exe进行配置
1 //根据系统安装路径获取 2 //使用msiexec安装时,默认都会安装到这个路径下 3 var mysqlBinPath = "C:\\Program Files\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 8.3\\bin\\"; 4 var mysqldPath = mysqlBinPath + "mysqld.exe"; 5 var mysqlPath = mysqlBinPath + "mysql.exe"; 6 7 var myIniPath = mysqlBinPath + "my.ini"; 8 var createSqlPath = mysqlBinPath + "create.sql"; 9 var setPwdSqlPath = mysqlBinPath + "set_password.sql"; 10 11 Exec(mysqldPath, " --initialize-insecure"); 12 Exec(mysqldPath, $" --install {serviceName}"); 13 var process = System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("net", $" start {serviceName}"); 14 process.WaitForExit(); 15 Exec(mysqlPath, $"< {createSqlPath} -u root"); 16 Exec(mysqlPath, $"< {setPwdSqlPath} -u root");
参考资料:
https://www.cnblogs.com/88223100/p/install-mysql_by_bash.html
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.4/en/windows-installation.html








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
2018-06-24 常用NLog配置