今天再来总结关于如何实现WebApi的身份验证,以完成该系列所有文章,WebApi常见的实现方式有:FORM身份验证、集成WINDOWS验证、Basic基础认证、Digest摘要认证
第一种:FORM身份验证(若在ASP.NET应用程序使用,则该验证方式不支持跨域,因为cookie无法跨域访问)
1.定义一个FormAuthenticationFilterAttribute,该类继承自AuthorizationFilterAttribute,并重写其OnAuthorization,在该方法中添加从请求头中获取有无登录的Cookie,若有则表示登录成功,否则失败,代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Http; using System.Web.Http.Filters; using System.Web.Security; using System.Net.Http; using System.Collections.ObjectModel; using System.Net.Http.Headers; using System.Threading; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Net; using System.Text; namespace WebApplication1.Models { public class FormAuthenticationFilterAttribute : AuthorizationFilterAttribute { private const string UnauthorizedMessage = "请求未授权,拒绝访问。"; public override void OnAuthorization(System.Web.Http.Controllers.HttpActionContext actionContext) { if (actionContext.ActionDescriptor.GetCustomAttributes<AllowAnonymousAttribute>().Count > 0) { base.OnAuthorization(actionContext); return; } if (HttpContext.Current.User != null && HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated) { base.OnAuthorization(actionContext); return; } var cookies = actionContext.Request.Headers.GetCookies(); if (cookies == null || cookies.Count < 1) { actionContext.Response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized) { Content = new StringContent(UnauthorizedMessage, Encoding.UTF8) }; return; } FormsAuthenticationTicket ticket = GetTicket(cookies); if (ticket == null) { actionContext.Response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized) { Content = new StringContent(UnauthorizedMessage, Encoding.UTF8) }; return; } //这里可以对FormsAuthenticationTicket对象进行进一步验证 var principal = new GenericPrincipal(new FormsIdentity(ticket), null); HttpContext.Current.User = principal; Thread.CurrentPrincipal = principal; base.OnAuthorization(actionContext); } private FormsAuthenticationTicket GetTicket(Collection<CookieHeaderValue> cookies) { FormsAuthenticationTicket ticket = null; foreach (var item in cookies) { var cookie = item.Cookies.SingleOrDefault(c => c.Name == FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName); if (cookie != null) { ticket = FormsAuthentication.Decrypt(cookie.Value); break; } } return ticket; } } }
2.在需要认证授权后才能访问的Controller中类或ACTION方法上添加上述授权过滤器FormAuthenticationFilterAttribute,也可在global文件中将该类添加到全局过滤器中,同时定义一个登录ACTION,用于登录入口,示例代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Net; using System.Net.Http; using System.Web; using System.Web.Http; using System.Web.Security; using WebApplication1.Models; namespace WebApplication1.Controllers { [FormAuthenticationFilter] public class TestController : ApiController { [AllowAnonymous] [AcceptVerbs("Get")] [Route("Api/Test/Login")] public HttpResponseMessage Login(string uname, string pwd) { if ("admin".Equals(uname, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) && "api.admin".Equals(pwd)) { //创建票据 FormsAuthenticationTicket ticket = new FormsAuthenticationTicket(1, uname, DateTime.Now, DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(30), false, string.Empty); //加密票据 string authTicket = FormsAuthentication.Encrypt(ticket); //存储为cookie HttpCookie cookie = new HttpCookie(FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName, authTicket); cookie.Path = FormsAuthentication.FormsCookiePath; HttpContext.Current.Response.AppendCookie(cookie); //或者 //FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(uname, false, "/"); return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, "登录成功!"); } else { HttpContext.Current.Response.AppendCookie(new HttpCookie(FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName) { Expires = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-10) });//测试用:当登录失败时,清除可能存在的身份验证Cookie return Request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, "登录失败,无效的用户名或密码!"); } } // GET api/test public IEnumerable<string> GetValues() { return new string[] { "value1", "value2" }; } // GET api/test/5 public string GetValue(int id) { return "value"; } } }
测试用法一:可直接在浏览器中访问需要授权的方法(即:Login除外),如:http://localhost:11099/api/test/,响应结果如下:
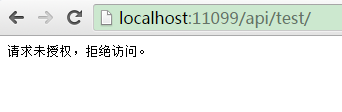
请求头信息如下:
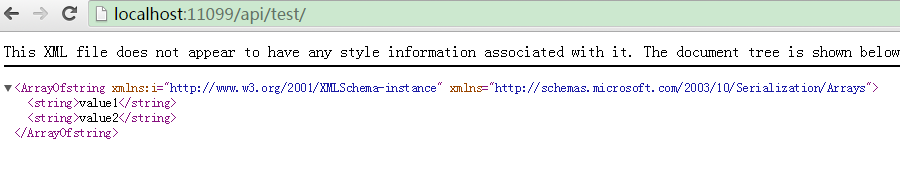
若成功调用Login方法后(http://localhost:11099/api/test/login?uname=admin&pwd=api.admin),再调用上述方法,则可以获得正常的结果,如下图示:
看一下请求时附带的Cookie,如下图示:

测试用法二:采用HttpClient来调用Api的相关方法,示例代码如下:
public async static void TestLoginApi() { HttpClientHandler handler = new HttpClientHandler(); handler.UseCookies = true;//因为采用Form验证,所以需要使用Cookie来记录身份登录信息 HttpClient client = new HttpClient(handler); Console.WriteLine("Login>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"); var response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:11099/api/test/login/?uname=admin&pwd=api.admin"); var r = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<dynamic>(); Console.WriteLine("StatusCode:{0}", response.StatusCode); if (!response.IsSuccessStatusCode) { Console.WriteLine("Msg:{1}", response.StatusCode, r.Message); return; } Console.WriteLine("Msg:{1}", response.StatusCode, r); var getCookies = handler.CookieContainer.GetCookies(new Uri("http://localhost:11099/")); Console.WriteLine("获取到的cookie数量:" + getCookies.Count); Console.WriteLine("获取到的cookie:"); for (int i = 0; i < getCookies.Count; i++) { Console.WriteLine(getCookies[i].Name + ":" + getCookies[i].Value); } Console.WriteLine("GetValues>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"); response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:11099/api/test/"); var r2 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<string>>(); foreach (string item in r2) { Console.WriteLine("GetValues - Item Value:{0}", item); } Console.WriteLine("GetValue>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"); response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:11099/api/test/8"); var r3 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<string>(); Console.WriteLine("GetValue - Item Value:{0}", r3); }
结果如下图示:

如果Web Api作为ASP.NET 或MVC的一部份使用,那么完全可以采用基于默认的FORM身份验证授权特性(Authorize),或采用web.config中配置,这个很简单,就不作说明了,大家可以网上参考关于ASP.NET 或ASP.NET MVC的FORM身份验证。
第二种:集成WINDOWS验证
首先在WEB.CONFIG文件中,增加如下配置,以开启WINDOWS身份验证,配置如下:
<authentication mode="Windows"> </authentication>
然后在需要认证授权后才能访问的Controller中类或ACTION方法上添加Authorize特性,Controller与上文相同不再贴出,当然也可以在WEB.CONFIG中配置:
<authorization> <deny users="?"/> </authorization>
最后将WEB API寄宿到(或者说发布到)IIS,且需要在IIS中启用WINDOWS身份验证,如下图示:
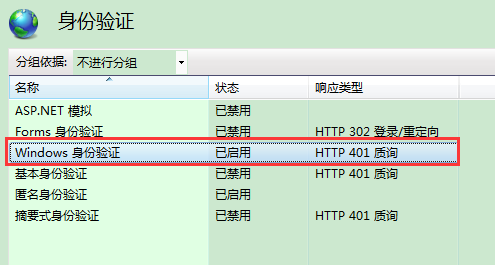
这样就完成了该身份验证模式(理论上WEB服务、WCF若都以IIS为宿主,都可以采用集成WINDOWS身份验证模式),测试方法很简单,第一种直接在浏览器中访问,第二种采用HttpClient来调用WEB API,示例代码如下:
public async static void TestLoginApi2() { HttpClientHandler handler = new HttpClientHandler(); handler.ClientCertificateOptions = ClientCertificateOption.Manual; handler.Credentials = new NetworkCredential("admin", "www.zuowenjun.cn"); HttpClient client = new HttpClient(handler); var response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:8010/api/test/"); var r2 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<string>>(); foreach (string item in r2) { Console.WriteLine("GetValues - Item Value:{0}", item); } response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:8010/api/test/8"); var r3 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<string>(); Console.WriteLine("GetValue - Item Value:{0}", r3); }
第三种:Basic基础认证
1.定义一个继承自AuthorizationFilterAttribute的HttpBasicAuthenticationFilter类,用于实现Basic基础认证,实现代码如下:
using System; using System.Net; using System.Text; using System.Web; using System.Web.Http.Controllers; using System.Web.Http.Filters; using System.Net.Http; using System.Web.Http; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Threading; using System.Net.Http.Headers; namespace WebApplication1.Models { public class HttpBasicAuthenticationFilter : AuthorizationFilterAttribute { public override void OnAuthorization(System.Web.Http.Controllers.HttpActionContext actionContext) { if (actionContext.ActionDescriptor.GetCustomAttributes<AllowAnonymousAttribute>().Count > 0) { base.OnAuthorization(actionContext); return; } if (Thread.CurrentPrincipal != null && Thread.CurrentPrincipal.Identity.IsAuthenticated) { base.OnAuthorization(actionContext); return; } string authParameter = null; var authValue = actionContext.Request.Headers.Authorization; if (authValue != null && authValue.Scheme == "Basic") { authParameter = authValue.Parameter; //authparameter:获取请求中经过Base64编码的(用户:密码) } if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(authParameter)) { Challenge(actionContext); return; } authParameter = Encoding.Default.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(authParameter)); var authToken = authParameter.Split(':'); if (authToken.Length < 2) { Challenge(actionContext); return; } if (!ValidateUser(authToken[0], authToken[1])) { Challenge(actionContext); return; } var principal = new GenericPrincipal(new GenericIdentity(authToken[0]), null); Thread.CurrentPrincipal = principal; if (HttpContext.Current != null) { HttpContext.Current.User = principal; } base.OnAuthorization(actionContext); } private void Challenge(HttpActionContext actionContext) { var host = actionContext.Request.RequestUri.DnsSafeHost; actionContext.Response = actionContext.Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized, "请求未授权,拒绝访问。"); //actionContext.Response.Headers.Add("WWW-Authenticate", string.Format("Basic realm=\"{0}\"", host));//可以使用如下语句 actionContext.Response.Headers.WwwAuthenticate.Add(new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Basic", string.Format("realm=\"{0}\"", host))); } protected virtual bool ValidateUser(string userName, string password) { if (userName.Equals("admin", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) && password.Equals("api.admin")) //判断用户名及密码,实际可从数据库查询验证,可重写 { return true; } return false; } } }
2.在需要认证授权后才能访问的Controller中类或ACTION方法上添加上述定义的类HttpBasicAuthenticationFilter,也可在global文件中将该类添加到全局过滤器中,即可
测试方法很简单,第一种直接在浏览器中访问(同上),第二种采用HttpClient来调用WEB API,示例代码如下:
public async static void TestLoginApi3() { HttpClient client = new HttpClient(); client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = CreateBasicHeader("admin", "api.admin"); var response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:11099/api/test/"); var r2 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<string>>(); foreach (string item in r2) { Console.WriteLine("GetValues - Item Value:{0}", item); } response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:11099/api/test/8"); var r3 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<string>(); Console.WriteLine("GetValue - Item Value:{0}", r3); } public static AuthenticationHeaderValue CreateBasicHeader(string username, string password) { return new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Basic", Convert.ToBase64String(System.Text.ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(string.Format("{0}:{1}", username, password)))); }
实现Basic基础认证,除了通过继承自AuthorizationFilterAttribute来实现自定义的验证授权过滤器外,还可以通过继承自DelegatingHandler来实现自定义的消息处理管道类,具体的实现方式可参见园子里的这篇文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/CreateMyself/p/4857799.html
第四种:Digest摘要认证
1.定义一个继承自DelegatingHandler的HttpDigestAuthenticationHandler类,用于实现在消息管道中实现Digest摘要认证,同时定义该类所需关联或依赖的其它类,源代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Concurrent; using System.Net; using System.Net.Http; using System.Net.Http.Headers; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Web; namespace WebApplication1.Models { public class HttpDigestAuthenticationHandler : DelegatingHandler { protected async override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken) { try { HttpRequestHeaders headers = request.Headers; if (headers.Authorization != null) { Header header = new Header(request.Headers.Authorization.Parameter, request.Method.Method); if (Nonce.IsValid(header.Nonce, header.NounceCounter)) { string password = "www.zuowenjun.cn";//默认值 //根据用户名获取正确的密码,实际情况应该从数据库查询 if (header.UserName.Equals("admin", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { password = "api.admin";//这里模拟获取到的正确的密码 } #region 计算正确的可授权的Hash值 string ha1 = String.Format("{0}:{1}:{2}", header.UserName, header.Realm, password).ToMD5Hash(); string ha2 = String.Format("{0}:{1}", header.Method, header.Uri).ToMD5Hash(); string computedResponse = String.Format("{0}:{1}:{2}:{3}:{4}:{5}", ha1, header.Nonce, header.NounceCounter, header.Cnonce, "auth", ha2).ToMD5Hash(); #endregion if (String.CompareOrdinal(header.Response, computedResponse) == 0) //比较请求的Hash值与正确的可授权的Hash值是否相同,相则则表示验证通过,否则失败 { // digest computed matches the value sent by client in the response field. // Looks like an authentic client! Create a principal. // var claims = new List<Claim> //{ // new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, header.UserName), // new Claim(ClaimTypes.AuthenticationMethod, AuthenticationMethods.Password) //}; // ClaimsPrincipal principal = new ClaimsPrincipal(new[] { new ClaimsIdentity(claims, "Digest") }); // Thread.CurrentPrincipal = principal; // if (HttpContext.Current != null) // HttpContext.Current.User = principal; var principal = new GenericPrincipal(new GenericIdentity(header.UserName), null); Thread.CurrentPrincipal = principal; if (HttpContext.Current != null) { HttpContext.Current.User = principal; } } } } HttpResponseMessage response = await base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken); if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized) { response.Headers.WwwAuthenticate.Add(new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Digest", Header.GetUnauthorizedResponseHeader(request).ToString())); } return response; } catch (Exception) { var response = request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized); response.Headers.WwwAuthenticate.Add(new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Digest", Header.GetUnauthorizedResponseHeader(request).ToString())); return response; } } } public class Header { public Header() { } public Header(string header, string method) { string keyValuePairs = header.Replace("\"", String.Empty); foreach (string keyValuePair in keyValuePairs.Split(',')) { int index = keyValuePair.IndexOf("=", System.StringComparison.Ordinal); string key = keyValuePair.Substring(0, index).Trim(); string value = keyValuePair.Substring(index + 1).Trim(); switch (key) { case "username": this.UserName = value; break; case "realm": this.Realm = value; break; case "nonce": this.Nonce = value; break; case "uri": this.Uri = value; break; case "nc": this.NounceCounter = value; break; case "cnonce": this.Cnonce = value; break; case "response": this.Response = value; break; case "method": this.Method = value; break; } } if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(this.Method)) this.Method = method; } public string Cnonce { get; private set; } public string Nonce { get; private set; } public string Realm { get; private set; } public string UserName { get; private set; } public string Uri { get; private set; } public string Response { get; private set; } public string Method { get; private set; } public string NounceCounter { get; private set; } // This property is used by the handler to generate a // nonce and get it ready to be packaged in the // WWW-Authenticate header, as part of 401 response public static Header GetUnauthorizedResponseHeader(HttpRequestMessage request) { var host = request.RequestUri.DnsSafeHost; return new Header() { Realm = host, Nonce = WebApplication1.Models.Nonce.Generate() }; } public override string ToString() { StringBuilder header = new StringBuilder(); header.AppendFormat("realm=\"{0}\"", Realm); header.AppendFormat(",nonce=\"{0}\"", Nonce); header.AppendFormat(",qop=\"{0}\"", "auth"); return header.ToString(); } } public class Nonce { private static ConcurrentDictionary<string, Tuple<int, DateTime>> nonces = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, Tuple<int, DateTime>>(); public static string Generate() { byte[] bytes = new byte[16]; using (var rngProvider = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider()) { rngProvider.GetBytes(bytes); } string nonce = bytes.ToMD5Hash(); nonces.TryAdd(nonce, new Tuple<int, DateTime>(0, DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(10))); return nonce; } public static bool IsValid(string nonce, string nonceCount) { Tuple<int, DateTime> cachedNonce = null; //nonces.TryGetValue(nonce, out cachedNonce); nonces.TryRemove(nonce, out cachedNonce);//每个nonce只允许使用一次 if (cachedNonce != null) // nonce is found { // nonce count is greater than the one in record if (Int32.Parse(nonceCount) > cachedNonce.Item1) { // nonce has not expired yet if (cachedNonce.Item2 > DateTime.Now) { // update the dictionary to reflect the nonce count just received in this request //nonces[nonce] = new Tuple<int, DateTime>(Int32.Parse(nonceCount), cachedNonce.Item2); // Every thing looks ok - server nonce is fresh and nonce count seems to be // incremented. Does not look like replay. return true; } } } return false; } } }
using System.Linq; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Text; namespace WebApplication1.Models { public static class HashHelper { public static string ToMD5Hash(this byte[] bytes) { StringBuilder hash = new StringBuilder(); MD5 md5 = MD5.Create(); md5.ComputeHash(bytes) .ToList() .ForEach(b => hash.AppendFormat("{0:x2}", b)); return hash.ToString(); } public static string ToMD5Hash(this string inputString) { return Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(inputString).ToMD5Hash(); } } }
2.将上述自定义的HttpDigestAuthenticationHandler类添加到全局消息处理管道中,代码如下:
public static class WebApiConfig { public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config) { config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes(); config.Routes.MapHttpRoute( name: "DefaultApi", routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}", defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional } ); config.MessageHandlers.Add(new HttpDigestAuthenticationHandler());//添加到消息处理管道中 } }
3.在需要认证授权后才能访问的Controller中类或ACTION方法上添加Authorize特性即可。
测试方法很简单,第一种直接在浏览器中访问(同上),第二种采用HttpClient来调用WEB API,示例代码如下:
public async static void TestLoginApi4() { HttpClientHandler handler = new HttpClientHandler(); handler.ClientCertificateOptions = ClientCertificateOption.Manual; handler.Credentials = new NetworkCredential("admin", "api.admin"); HttpClient client = new HttpClient(handler); var response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:11099/api/test/"); var r2 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<string>>(); foreach (string item in r2) { Console.WriteLine("GetValues - Item Value:{0}", item); } response = await client.GetAsync("http://localhost:11099/api/test/8"); var r3 = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<string>(); Console.WriteLine("GetValue - Item Value:{0}", r3); }
该实现方法,参考了该篇文章:http://zrj-software.iteye.com/blog/2163487
实现Digest摘要认证,除了上述通过继承自DelegatingHandler来实现自定义的消息处理管道类外,也可以通过继承自AuthorizationFilterAttribute来实现自定义的验证授权过滤器,Basic基础认证与Digest摘要认证流程基本相同,区别在于:Basic是将密码直接base64编码(明文),而Digest是用MD5进行加密后传输,所以两者实现认证方式上,也基本相同。
最后说明一下,WEB SERVICE、WCF、WEB API实现身份验证的方法有很多,每种方法都有他所适用的场景,我这个系列文章仅是列举一些常见的实见身份验证的方法,一是给自己复习并备忘,二是给大家以参考,文中可能有不足之处,若发现问题,可以在下面评论指出,谢谢!


