06-NIN 图像分类
NIN网络中,主要提及两点:
1. )多层感知机
2.)global average pooling
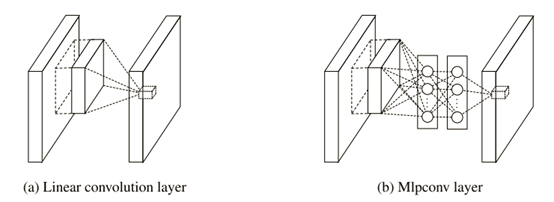
图1 线性卷积层和mlpconv层的区别
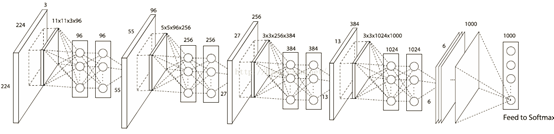
图2 NIN网络架构
第一个卷积核是11x11x3x96,因此在一个patch块上卷积的输出是1x1x96的feature map(一个96维的向量).在其后又接了一个MLP层,输出仍然是96.因此这个MLP层就等价于一个1 x 1 的卷积层,这样工程上任然按照之前的方式实现,不需要额外工作.
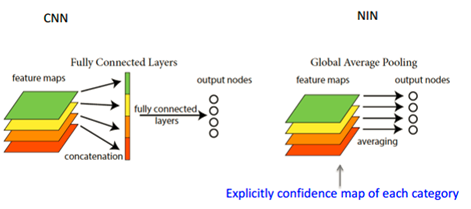
图3 全连接层FC和global average pooling的区别
传统的cnn是在较低层使用卷积,如分类任务中,最后的卷积层所得feature map被矢量化进行全连接层,然后使用softmax 回归进行分类。一般来说,在卷积的末端完成的卷积与传统分类器的桥接。全连接阶段易于过拟合,妨碍整个网络的泛化能力,一般应有一些规则方法来处理过拟合。
在传统CNN中很难解释最后的全连接层输出的类别信息的误差怎么传递给前边的卷积层.而global average pooling更容易解释.另外,全连接层容易过拟合,往往依赖于dropout等正则化手段.
global average pooling的概念非常简单,分类任务有多少个类别,就控制最终产生多少个feature map.对每个feature map的数值求平均作为某类别的置信度,类似FC层输出的特征向量,再经过softmax分类.其优点有:
1.)参数数量减少,减轻过拟合(应用于AlexNet,模型230MB->29MB);
2.)更符合卷积网络的结构,使feature map和类别信息直接映射;
3.)求和取平均操作综合了空间信息,使得对输入的空间变换更鲁棒(与卷积层相连的FC按顺序对特征进行了重新编排(flatten),可能破坏了特征的位置信息).
4.)FC层输入的大小须固定,这限制了网络输入的图像大小.
NIN的pytorch实现:

1 import torch.nn as nn 2 3 4 #定义模型 5 class NIN_Net(nn.Module):#继承父类nn.Module 6 def __init__(self): 7 super(NIN_Net, self).__init__()#super可以指代父类而不需要显式的声明,这对更改基类(此处为__init__())的时候是有帮助的,使得代码更容易维护 8 self.classifier = nn.Sequential( 9 nn.Conv2d(3, 192, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2), 10 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 11 nn.Conv2d(192, 160, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 12 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 13 nn.Conv2d(160, 96, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 14 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 15 nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1), 16 nn.Dropout(0.5), 17 18 nn.Conv2d(96, 192, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2), 19 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 20 nn.Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 21 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 22 nn.Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 23 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 24 nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1), 25 nn.Dropout(0.5), 26 27 nn.Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1), 28 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 29 nn.Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 30 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 31 nn.Conv2d(192, 10, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0), 32 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 33 nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=8, stride=1, padding=0), 34 35 ) 36 37 def forward(self, x): 38 x = self.classifier(x) 39 40 #将得到的数据平展 41 x = x.view(x.size(0), 10) 42 return x
classfyNet_main.py

1 import torch 2 from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 3 from torch import nn, optim 4 from torchvision import datasets, transforms 5 from torchvision.transforms.functional import InterpolationMode 6 7 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 8 9 10 import time 11 12 from Lenet5 import Lenet5_new 13 from Resnet18 import ResNet18,ResNet18_new 14 from AlexNet import AlexNet 15 from Vgg16 import VGGNet16 16 from Densenet import DenseNet121, DenseNet169, DenseNet201, DenseNet264 17 18 from NIN import NIN_Net 19 from GoogleNet import GoogLeNet 20 21 def main(): 22 23 print("Load datasets...") 24 25 # transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5)---以0.5的概率对图片做水平横向翻转 26 # transforms.ToTensor()---shape从(H,W,C)->(C,H,W), 每个像素点从(0-255)映射到(0-1):直接除以255 27 # transforms.Normalize---先将输入归一化到(0,1),像素点通过"(x-mean)/std",将每个元素分布到(-1,1) 28 transform_train = transforms.Compose([ 29 transforms.Resize((224, 224), interpolation=InterpolationMode.BICUBIC), 30 # transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4), # 先四周填充0,在吧图像随机裁剪成32*32 31 transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5), 32 transforms.ToTensor(), 33 transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)) 34 ]) 35 36 transform_test = transforms.Compose([ 37 transforms.Resize((224, 224), interpolation=InterpolationMode.BICUBIC), 38 # transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4), # 先四周填充0,在吧图像随机裁剪成32*32 39 transforms.ToTensor(), 40 transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)) 41 ]) 42 43 # 内置函数下载数据集 44 train_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(root="./data/Cifar10/", train=True, 45 transform = transform_train, 46 download=True) 47 test_dataset = datasets.CIFAR10(root = "./data/Cifar10/", 48 train = False, 49 transform = transform_test, 50 download=True) 51 52 print(len(train_dataset), len(test_dataset)) 53 54 Batch_size = 64 55 train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=Batch_size, shuffle = True, num_workers=4) 56 test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size = Batch_size, shuffle = False, num_workers=4) 57 58 # 设置CUDA 59 device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 60 61 # 初始化模型 62 # 直接更换模型就行,其他无需操作 63 # model = Lenet5_new().to(device) 64 # model = ResNet18().to(device) 65 # model = ResNet18_new().to(device) 66 # model = VGGNet16().to(device) 67 # model = DenseNet121().to(device) 68 # model = DenseNet169().to(device) 69 70 # model = NIN_Net().to(device) 71 72 model = GoogLeNet().to(device) 73 74 # model = AlexNet(num_classes=10, init_weights=True).to(device) 75 print(" GoogLeNet train...") 76 77 # 构造损失函数和优化器 78 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 多分类softmax构造损失 79 # opt = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.8, weight_decay=0.001) 80 opt = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0005) 81 82 # 动态更新学习率 ------每隔step_size : lr = lr * gamma 83 schedule = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(opt, step_size=10, gamma=0.6, last_epoch=-1) 84 85 # 开始训练 86 print("Start Train...") 87 88 epochs = 100 89 90 loss_list = [] 91 train_acc_list =[] 92 test_acc_list = [] 93 epochs_list = [] 94 95 for epoch in range(0, epochs): 96 97 start = time.time() 98 99 model.train() 100 101 running_loss = 0.0 102 batch_num = 0 103 104 for i, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(train_loader): 105 106 inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device) 107 108 # 将数据送入模型训练 109 outputs = model(inputs) 110 # 计算损失 111 loss = criterion(outputs, labels).to(device) 112 113 # 重置梯度 114 opt.zero_grad() 115 # 计算梯度,反向传播 116 loss.backward() 117 # 根据反向传播的梯度值优化更新参数 118 opt.step() 119 120 # 100个batch的 loss 之和 121 running_loss += loss.item() 122 # loss_list.append(loss.item()) 123 batch_num+=1 124 125 126 epochs_list.append(epoch) 127 128 # 每一轮结束输出一下当前的学习率 lr 129 lr_1 = opt.param_groups[0]['lr'] 130 print("learn_rate:%.15f" % lr_1) 131 schedule.step() 132 133 end = time.time() 134 print('epoch = %d/100, batch_num = %d, loss = %.6f, time = %.3f' % (epoch+1, batch_num, running_loss/batch_num, end-start)) 135 running_loss=0.0 136 137 # 每个epoch训练结束,都进行一次测试验证 138 model.eval() 139 train_correct = 0.0 140 train_total = 0 141 142 test_correct = 0.0 143 test_total = 0 144 145 # 训练模式不需要反向传播更新梯度 146 with torch.no_grad(): 147 148 # print("=======================train=======================") 149 for inputs, labels in train_loader: 150 inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device) 151 outputs = model(inputs) 152 153 pred = outputs.argmax(dim=1) # 返回每一行中最大值元素索引 154 train_total += inputs.size(0) 155 train_correct += torch.eq(pred, labels).sum().item() 156 157 158 # print("=======================test=======================") 159 for inputs, labels in test_loader: 160 inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device) 161 outputs = model(inputs) 162 163 pred = outputs.argmax(dim=1) # 返回每一行中最大值元素索引 164 test_total += inputs.size(0) 165 test_correct += torch.eq(pred, labels).sum().item() 166 167 print("train_total = %d, Accuracy = %.5f %%, test_total= %d, Accuracy = %.5f %%" %(train_total, 100 * train_correct / train_total, test_total, 100 * test_correct / test_total)) 168 169 train_acc_list.append(100 * train_correct / train_total) 170 test_acc_list.append(100 * test_correct / test_total) 171 172 # print("Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images:%.5f %%" % (100 * test_correct / test_total)) 173 # print("===============================================") 174 175 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4)) 176 177 plt.plot(epochs_list, train_acc_list, label='train_acc_list') 178 plt.plot(epochs_list, test_acc_list, label='test_acc_list') 179 plt.legend() 180 plt.title("train_test_acc") 181 plt.savefig('GoogLeNet_acc_epoch_{:04d}.png'.format(epochs)) 182 plt.close() 183 184 if __name__ == "__main__": 185 186 main()


