05 nfs、rsync、inotify综合案例
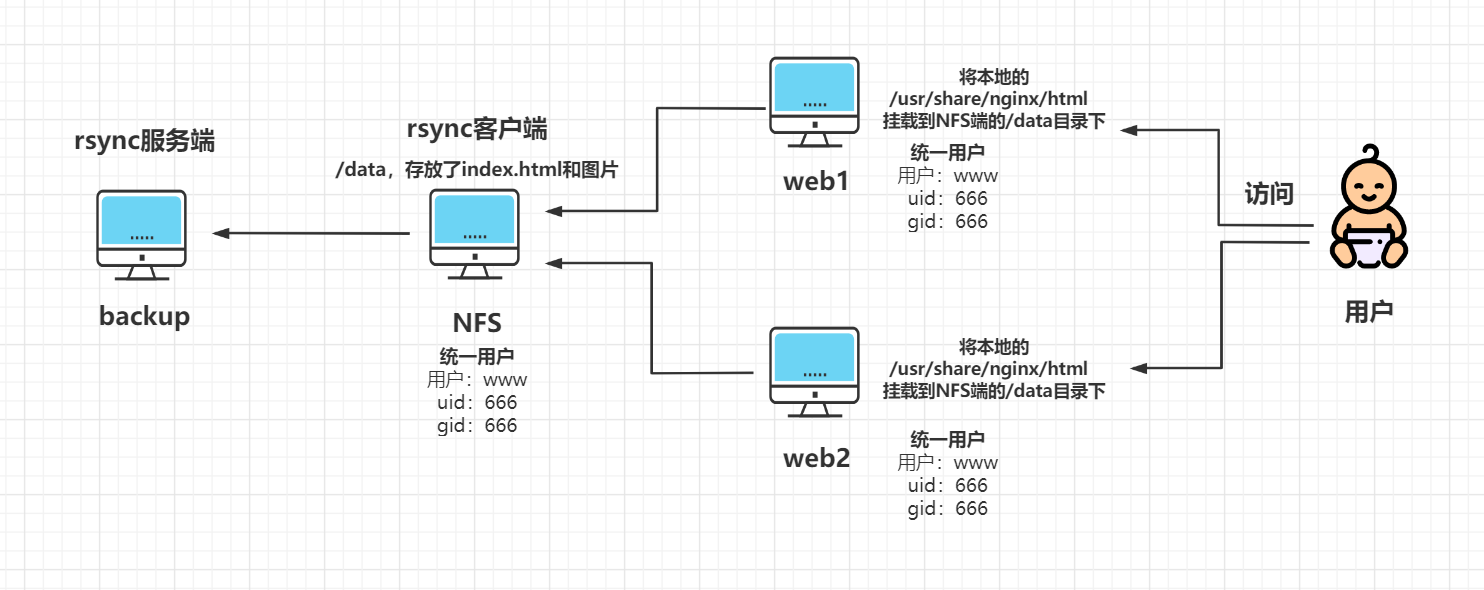
backup
用于备份nfs服务器中的/data目录,是rsync的服务端
#安装rsync
yum install rsync -y
#写配置文件(/etc/rsyncd.conf)
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
uid = rsync
gid = rsync
port = 873
fake super = yes
use chroot = no
max connections = 200
timeout = 600
ignore errors
read only = false
list = false
auth users = baimo
secrets file = /etc/rsync.passwd
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
[backup]
comment = welcome to my backup!
path = /backup
#增加用户
[root@backup ~]# useradd rsync -s /sbin/nologin -M
#创建密码文件并授权
[root@backup ~]# echo "baimo:123" > /etc/rsync.passwd
[root@backup ~]# chmod -R 600 /etc/rsync.passwd
#创建备份目录并授权
[root@backup ~]# mkdir /backup
[root@backup ~]# chown -R rsync.rsync /backup
#启动服务并验证
[root@backup ~]# systemctl start rsyncd
[root@backup ~]# netstat -lntp | grep 873
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1812/rsync
tcp6 0 0 :::873 :::* LISTEN 1812/rsync
nfs
用于存放共享的文件,通过inotify+rsync推送给backup,是rsync的服务端
#安装rsync
yum install rsync nfs-utils rpcbind -y
#编辑密码文件
[root@nfs ~]# echo "export RSYNC_PASSWORD=123" > /etc/profile.d/HJBL.sh
#重启客户端让文件生效
#创建/data目录并统一www用户
[root@nfs ~]# mkdir /data
[root@nfs ~]# groupadd www -g 666
[root@nfs ~]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666
[root@nfs ~]# chown -R www.www /data
#编写inotify脚本
#!/bin/bash
#实时推送备份文件脚本
export RSYNC_PASSWORD=123
dir=/data #监控的文件
inotifywait -mrq --format '%Xe %w %f' -e create,modify,delete,attrib,close_write ${dir} | while read line; do rsync -avz /data baimo@192.168.15.41::backup; done &>/dev/null &
#测试
#nfs端
[root@nfs ~]# bash inotify_rsync.sh
[root@nfs ~]# cd /data && touch a.txt
#backup端
[root@backup ~]# cd /backup/
[root@backup backup]# ll
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 rsync rsync 32 Apr 21 19:37 data
[root@backup backup]# cd data/
[root@backup data]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 rsync rsync 0 Apr 21 19:34 1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 rsync rsync 0 Apr 21 19:37 a.txt
---------------------rsync配置结束,可以同步,下面是NFS---------------------
#编写配置(/etc/exports)
vim /etc/exports
/data 192.168.15.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=666,anongid=666)
#检查配置
[root@nfs ~]# systemctl restart nfs
[root@nfs ~]# cat /var/lib/nfs/etab
/data 192.168.15.0/24(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,nocrossmnt,secure,root_squash,all_squash,no_subtree_check,secure_locks,acl,no_pnfs,anonuid=666,anongid=666,sec=sys,rw,secure,root_squash,all_squash)
web01,web02
服务器,是NFS的客户端,两个操作一样
#配置nginx官方源
[root@web01 ~]# cat >/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo<<EOF
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/\$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
EOF
[root@web01 ~]# yum clean all && yum makecache
#安装nginx和nfs
yum install nginx nfs-utils rpcbind -y
#启动rpcbind和nfs
[root@web02 ~]# systemctl start rpcbind nfs
#查看挂载点
[root@web01 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.15.31
Export list for 192.168.15.31:
/data 192.168.15.0/24
#统一用户权限/
[root@web01 ~]# groupadd www -g 666
[root@web01 ~]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666
[root@web01 ~]# chown -R www.www /usr/share/nginx/html
#挂载
[root@web01 ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.15.31:/data /usr/share/nginx/html
#检查挂载
[root@web02 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 475M 0 475M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 7.6M 479M 2% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 99G 2.6G 97G 3% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 163M 852M 17% /boot
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
192.168.15.31:/data 99G 2.6G 97G 3% /usr/share/nginx/html
#测试权限是否满足
#拉取代码到/usr/share/nginx/html下,并解压
[root@web01 html]# unzip kaoshi.zip
Archive: kaoshi.zip
inflating: index.html
inflating: info.php
inflating: upload_file.php
[root@web01 html]# ll
total 16
-rw-r--r-- 1 www www 2633 May 4 2018 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 www www 52 May 10 2018 info.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www www 2434 Apr 21 17:19 kaoshi.zip
-rw-r--r-- 1 www www 1192 Jan 10 2020 upload_file.php
#web02只需要重复上述步骤到挂载即可
访问并查看两个服务器
[root@web02 ~]# systemctl start nginx