力扣78题、77题、90题、491题(回溯算法、子集组合)
78、子集
基本思想:
回溯算法
具体实现:
这道题没有if判断递归是否结束
因为这个是每递归一下就加入到结果数组中,
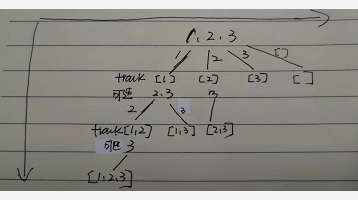
代码:
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { if (nums.length == 0){ result.add(new ArrayList<>()); return result; } subsetsHelper(nums, 0); return result; } private void subsetsHelper(int[] nums, int startIndex){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){ path.add(nums[i]); subsetsHelper(nums,i+1); path.removeLast(); } } }
77、组合
基本思想:
回溯算法
具体实现:
1、组合是不能有重复的
递归函数的参数每次就有起始数,
for循环从start开始递增
上述两个操作保证了不会有重复
2、递归结束条件是到达叶子节点

代码:
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { combineHelper(n, k, 1); return result; } public void combineHelper(int n, int k, int start) { if (path.size() == k) { result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) { path.add(i); combineHelper(n, k, i + 1); path.removeLast(); } } }
剪枝:

具体实现:
k-len(track)是track中还差的元素个数
n-(k-len(track))+1是要达到组合中元素为k,至多开始的位置
比如:n=4,k=3 ,track里面啥也没 4-3+1=2
意思是最多从2开始,组合可以是2,3,4
再循环到3不可能满足组合个数
python写到代码里n-(k-len(track))+2 因为range的第二个参数代表第一个不取的数
代码:
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { combineHelper(n, k, 1); return result; } private void combineHelper(int n, int k, int startIndex){ if (path.size() == k){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for (int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++){ path.add(i); combineHelper(n, k, i + 1); path.removeLast(); } } }
90、子集II
基本思想:
回溯算法
与78题的区别是,子集需要去重
具体实现:

代码:
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();// 存放符合条件结果的集合 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();// 用来存放符合条件结果 public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) { if (nums.length == 0){ result.add(path); return result; } Arrays.sort(nums);//去重需要排序 subsetsWithDupHelper(nums,0); return result; } private void subsetsWithDupHelper(int[] nums, int startIndex){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); if (startIndex >= nums.length){ return; } for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > startIndex && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){ //我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过 continue; } path.add(nums[i]); subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, i + 1); path.removeLast(); } } }
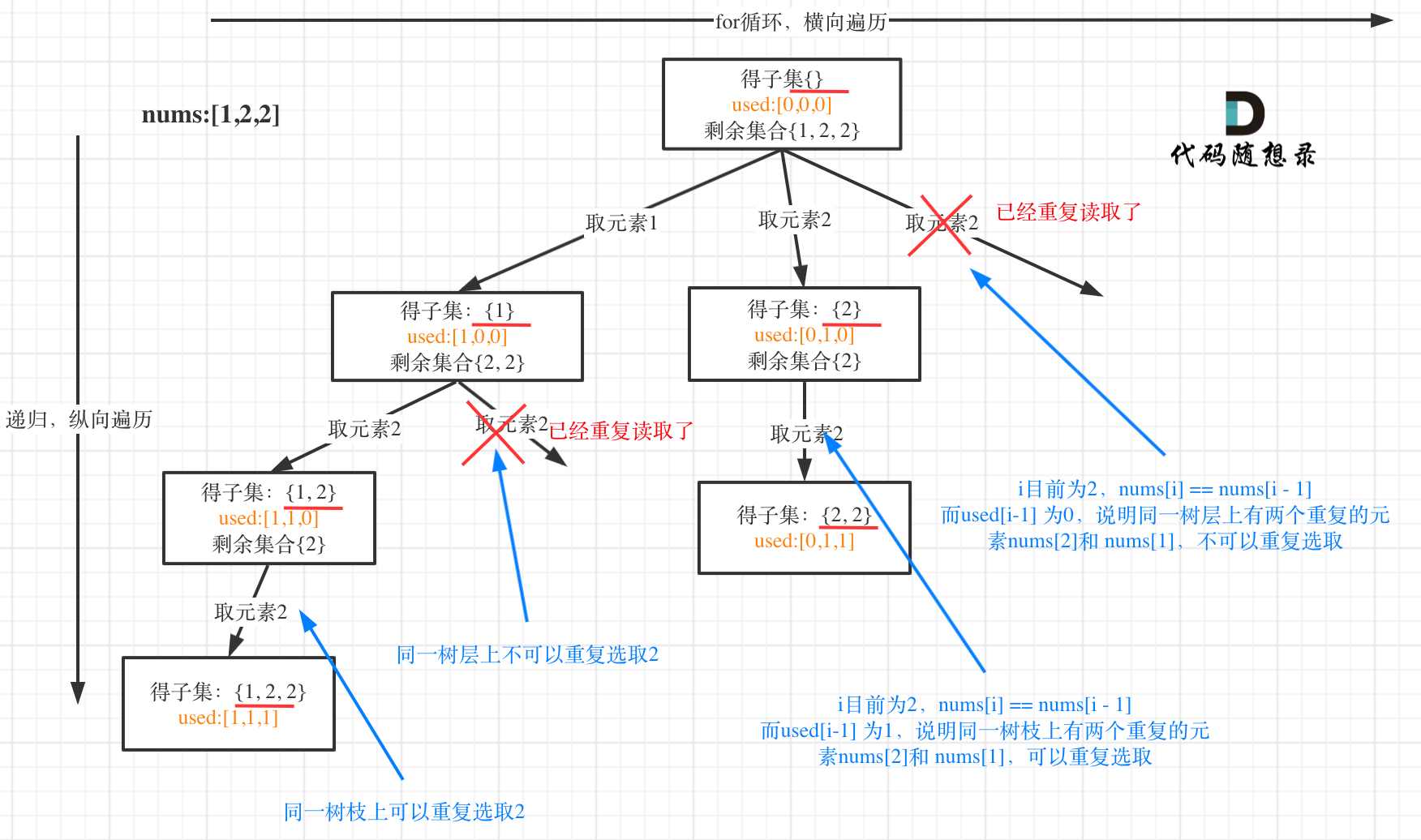
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> track = new LinkedList<>(); boolean[] used; public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); used = new boolean[nums.length]; traversal(nums, 0); return result; } public void traversal(int[] nums, int start) { result.add(new ArrayList<>(track)); for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) continue; //前面有相同的元素并且没有被使用过,那就是同一树层碰到相同元素了 track.add(nums[i]); used[i] = true; traversal(nums, i + 1); track.removeLast(); used[i] = false; } } }
491、递增子序列
基本思想:
回溯算法
与90题不同,90题需要排序,这道题不需要
90题判断是否重复是用nums[i] == nums[i-1],这道题不行
具体实现:
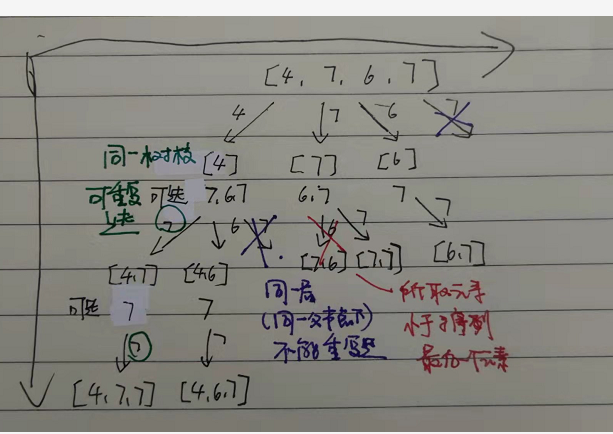
代码:
class Solution { private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) { backtracking(nums,0); return res; } private void backtracking (int[] nums, int start) { if (path.size() > 1) { res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));//注意这里不要加return,要取树上的节点 } //记录[-100,100]这些数字出现的个数 //[-100,100]对应索引[0,201] int[] used = new int[201]; for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) { if (used[nums[i] + 100] == 1) continue; if (!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.get(path.size() - 1)) continue; used[nums[i] + 100] = 1;//记录这个元素在本层用过了,本层后面不能再用了 path.add(nums[i]); backtracking(nums, i + 1); path.remove(path.size() - 1); } } }


