Java中的IO
1、概念
IO(Input、Output)表示输入与输出。
Java 1.0中IO是流式IO,只能一个个字节的处理数据,所以也叫Stream IO,其响应是阻塞式的。
Java 1.4中的NIO(non-blocking)是非阻塞式,其处理数据是以Buffer的方式。
2、IO相关类
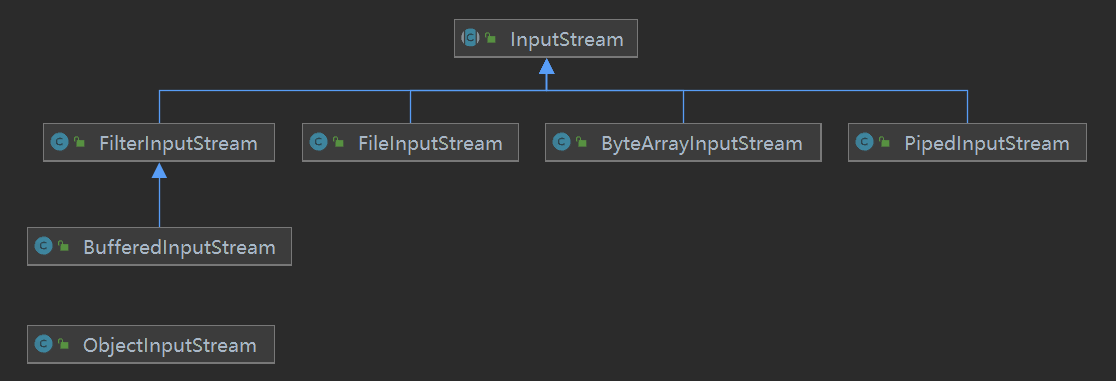
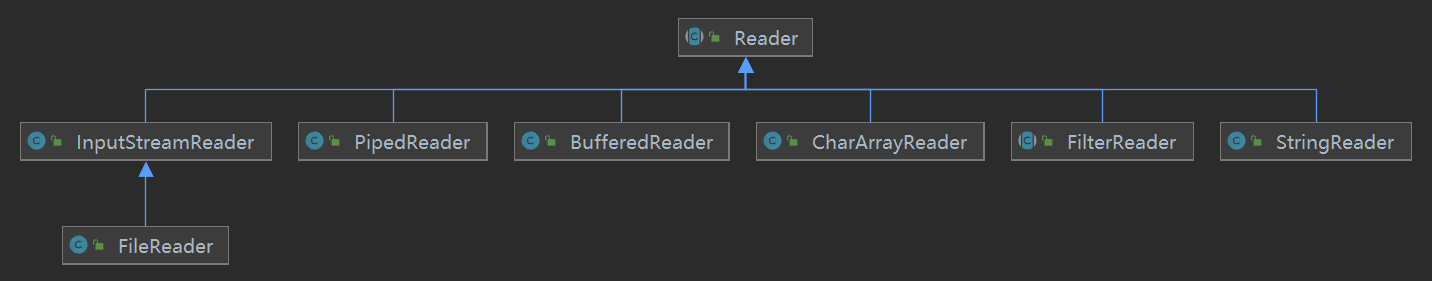
java的io相关接口和类都在java.io包下,最顶层最常用的抽象类有四个,分别是InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer,其关系图如下:

InputStream的子类很多,例如常见的FileInputStream、ByteArrayInputStream、PipedInputStream、FilterInputStream、ObjectInputStream,Input和Output成对出现,OutputStream同理。
Reader的子类也很多,BufferedReader、CharArrayReader、FileReader、FilterReader、InputStreamReader、PipedReader、StringReader,Reader和Writer成对出现,Writer同理。
3、分类
按字节和字符分:InputStream和OutputStream处理字节流,Reader和Writer处理字符流。
从介质上分有三种:数组ByteArrayInputStream、文件FileInputStream和字符串,有各自的使用场景,不是所有的数据都是以文件的形式存在,比如内存中的数据就是以字节数组的形式存在,可能是图片、视频等等。
总结:纯文本数据用Reader和Writer处理,非纯文本用InputStream和OutputStream处理,文件用FileInputStream处理,内存用ByteArrayInputStream处理。
4、使用场景
下面简述常用类的使用场景
- FileInputStream:在处理文件时会用到,不论是处理文本文件还是二进制文件都可以,一般搭配字节数组做缓冲区,类似于BufferInputStream。
- ByteArrayInputStream:在内存中创建一个字节数组缓冲区,用来处理内存中存在的数据。
- PipedInputStream:一般用来处理线程间的通信。因为现在有了更好的方式处理线程间通信的,比如BlockingQueue,所以在实际开发中用的比较少。
- FilterInputStream:本身没有新增什么功能,就是对于InputStream的外层封装,用于给其他类去继承。
- ObjectInputStream:顾名思义可以将流和对象进行转换,例如将自定义的对象序列化后保存到一个文件,将一个文件读取的流解析成一个对象。
- BufferedInputStream:本质就是将其他流存到了自己的缓冲数组里面,后续的操作从自身数组中读取。其逻辑是从其他流里面读取固定长度的数据,存到自身的字节数组,然后读取的时候先从自身的数组里读,当数组里的数据读完了,就会重新从流里缓存,直到把数据全部读完,相当于一个中转站。其继承了FilterInputStream,扩展了能力,用法和FileInputStream一致,当FileInputStream使用的缓存数组大小设置为8192时,和默认的BufferedInputStream没有区别。
- BufferedReader:和BufferedInputStream类似,构造方法是传入一个Reader,专门处理字符流。
- FilterReader:和FilterInputStream类似,就是给其他的类继承,好扩展功能。
- InputStreamReader:继承了Reader,专门将字节流转成字符流,是一个转换类,其构造方法入参就是InputStream。
- FileReader:继承了InputStreamReader,其实就是简化使用,不然得先从File获取字节流,再把字节流转换成字符流使用,FileReader直接从文件获取字符流,构造方法入参有两个,一个是文件路径,一个是文件。
- PipedReader:和PipedInputStream类似,用来处理线程间的通信。例如一个线程获取键盘输入,一个线程输出内容到控制台。
- CharArrayReader:其数据源是一个字符数组,讲一个字符数组作为输入源。
- StringReader:数据源是一个字符串,结合标记和重置方法,可以读取字符串任意位置的字符。
5、常用示例代码
- FileInputStream和FileOutputStream,复制文件A到文件B
/** * 复制原文件到一个新的文件 * * @param file 原文件 * @param newFile 新文件 * @throws IOException */ private void copyFileByFileStream(File file, File newFile) throws IOException { if (newFile.exists() || newFile.createNewFile()) { try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(newFile); InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file)) { //设置缓冲区大小为2Kb byte[] bytes = new byte[2048]; //记录缓冲区存储的数据大小 int length; //循环从inputStream读取最多2kb的数据,直到取完所有的数据 while ((length = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { //将缓冲区实际保存的数据写入outputStream outputStream.write(bytes, 0, length); } } } }
- BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream,复制文件A到文件B
/** * 复制原文件到一个新的文件 * * @param file 原文件 * @param newFile 新文件 * @throws IOException */ private static void copyFileByBufferStream(File file, File newFile) throws IOException { if (newFile.exists() || newFile.createNewFile()) { try (BufferedOutputStream outputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(newFile)); BufferedInputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) { //设置缓冲区大小为2Kb byte[] bytes = new byte[2048]; //记录缓冲区存储的数据大小 int length; //循环从inputStream读取最多2kb的数据,直到取完所有的数据 while ((length = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { //将缓冲区实际保存的数据写入outputStream outputStream.write(bytes, 0, length); } } } }
- BufferedReader打印文本文件内容,入参是InputStreamReader(将字节流转成字符流)
/** * BufferedReader只能处理字符流 * InputStreamReader是字节流转字符流的桥梁 * 所以需要用到InputStreamReader将字节流转成字符流 * * @param file * @throws IOException */ private static void testFileInputStream(File file) throws IOException { try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)))) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); String str; while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null) { builder.append(str).append(System.getProperty("line.separator")); } System.out.println(builder); } }
- BufferedReader打印文本文件内容,入参是FileReader(将文件转成字符流)
/** * BufferedReader只能处理字符流 * FileReader继承了InputStreamReader,其提供了将文件直接转换成字符流的构造方法 * * @param file * @throws IOException */ private static void testFileReader(File file) throws IOException { try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); String str; while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null) { builder.append(str).append(System.getProperty("line.separator")); } System.out.println(builder); } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通