SpringMVC 全局异常处理
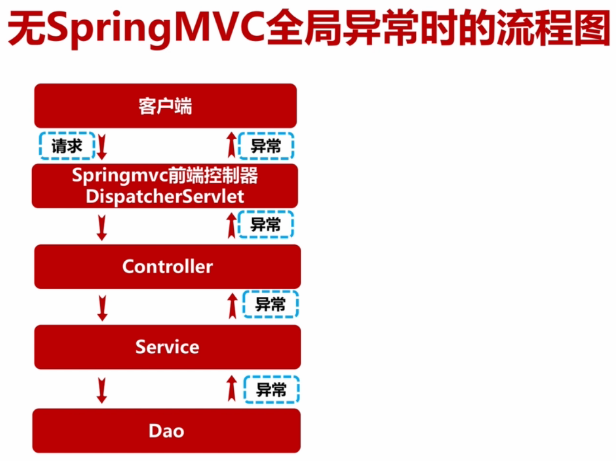
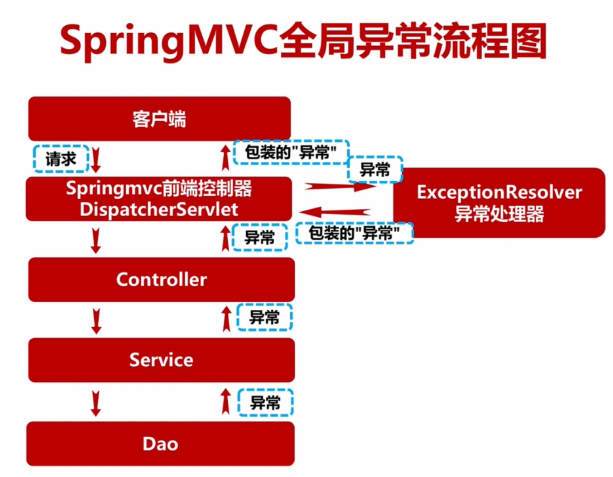
(二)、Spring及SpringMVC扫描包隔离及配置文件优化
1、删除applicationContext-datasource.xml文件里context:component-scan
<context:component-scan base-package="com.mmall" annotation-config="true"/>
2、applicationContext.xml文件
<!-- 扫描com.mmall包下的注解,就可以很方便的在类中进行注入-->
<!-- 排除controller注解-->
<!-- ApplicationContext.xml 是spring 全局配置文件,用来控制spring 特性的-->
<!-- dispatcher-servlet.xml 是spring mvc里面的,控制器、拦截uri转发view Controller扫描放到这里,其他扫描放到ApplicationContext.xml-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.mmall" annotation-config="true">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
3、dispatcher-servlet.xml文件
<!-- 只扫描controller注解,其他bean的applicationContext.xml 扫描放到 只要有方法使用了@Controller,就会扫描到-->
<!-- use-default-filter 关闭默认扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.mmall.controller" annotation-config="true" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
备注:
转载地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/parryyang/p/5783399.html
applicationContext.xml和dispatcher-servlet.xml的区别
在SpringMVC项目中我们一般会引入applicationContext.xml和dispatcher-servlet.xml两个配置文件,这两个配置文件具体的区别是什么呢?
Spring 官方文档介绍如下:
Spring lets you define multiple contexts in a parent-child hierarchy. The applicationContext.xml defines the beans for the "root webapp context", i.e. the context associated with the webapp. The spring-servlet.xml (or whatever else you call it) defines the beans for one servlet's app context. There can be many of these in a webapp, one per Spring servlet (e.g. spring1-servlet.xml for servlet spring1, spring2-servlet.xml for servlet spring2). Beans in spring-servlet.xml can reference beans in applicationContext.xml, but not vice versa. All Spring MVC controllers must go in the spring-servlet.xml context. In most simple cases, the applicationContext.xml context is unnecessary. It is generally used to contain beans that are shared between all servlets in a webapp. If you only have one servlet, then there's not really much point, unless you have a specific use for it.
可见, applicationContext.xml 和 dispatch-servlet.xml形成了两个父子关系的上下文。
1) 一个bean如果在两个文件中都被定义了(比如两个文件中都定义了component scan扫描相同的package), spring会在application context和 servlet context中都生成一个实例,他们处于不同的上下文空间中,他们的行为方式是有可能不一样的。
2) 如果在application context和 servlet context中都存在同一个 @Service 的实例, controller(在servlet context中) 通过 @Resource引用时, 会优先选择servlet context中的实例。
不过最好的方法是:在applicationContext和dispatcher-servlet定义的bean最好不要重复, dispatcher-servlet最好只是定义controller类型的bean。
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
applicationContext.xml 是spring 全局配置文件,用来控制spring 特性的
dispatcher-servlet.xml 是spring mvc里面的,控制器、拦截uri转发view
Contronller bean放在dispatcher-servlet.xml,其他bean放在applicationContext.xml
(三)、 SpringMVC全局异常实战
新建ExceptionResolver文件
@Slf4j @Component public class ExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver { @Override public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) { // 必须加e,不然在控制台不会输出完整的错误 log.error("{} Exception", httpServletRequest.getRequestURI(), e); // 当使用jackjson2.x的时候使用MappingJackson2JsonView,课程中使用的是1.9,所以使用MappingJacksonJsonView // MappingJacksonJsonView是为了将model转换成json ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(new MappingJacksonJsonView()); modelAndView.addObject("status", ResponseCode.ERROR.getCode()); modelAndView.addObject("msg", "接口异常,详细请查看服务端日志的异常信息"); modelAndView.addObject("data", e.toString()); return modelAndView; } }

(四)、上面的全局异常用的是HandlerExceptionResolver,实际中还有一种方法,是用 @ExceptionHandler和@controlleradvice
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiang--liu/p/11422504.html
把 @ExceptionHandler、HandlerExceptionResolver、@controlleradvice 三兄弟放在一起来写更有比较性。这三个东西都是用来处理异常的,但是它们使用的场景都不一样。看本文给你详细的讲解,再也不怕面试被问到了!
这三个注解都是来自于 SpringMVC 的,都能进行异常处理。
Java 程序员都非常的痛恨异常,很多人讨厌 Java 就是因为它的异常处理机制。到处的 try-catch-finally,再不是就是到处抛出异常。
所以 Spring 深知 Java 的疼点,推出了:@ExceptionHandler、HandlerExceptionResolver、@controlleradvice 来方便我们处理一些异常!
@ExceptionHandler 注解
用于局部方法捕获,与抛出异常的方法处于同一个 Controller 类。源码如下:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface ExceptionHandler { Class<? extends Throwable>[] value() default {}; }
从源码中可以看出,@ExceptionHandler 注解只能作用为对象的方法上,并且在运行时有效,value() 可以指定异常类。由该注解注释的方法可以具有灵活的输入参数。
异常参数可以包括一般的异常或特定的异常(即自定义异常),如果注解没有指定异常类,会默认进行映射。
用法代码如下:
@Controller public class XttblogController { @ExceptionHandler({NullPointerException.class}) public String exception(NullPointerException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); e.printStackTrace(); return "null pointer exception"; } @RequestMapping("test") public void test() { throw new NullPointerException("出错了!"); } }
上面这段代码只会捕获 XttblogController 类中的 NullPointerException 异常。
HandlerExceptionResolver 接口
HandlerExceptionResolver 是 Spring 提供的一个接口。它可以用来处理全局异常!
@Component public class GlobalExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver{ private ObjectMapper objectMapper; public CustomMvcExceptionHandler() { objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); } @Override public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,Object o, Exception ex) { response.setStatus(200); response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE); response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, must-revalidate"); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); if (ex instanceof NullPointerException) { map.put("code", ResponseCode.NP_EXCEPTION); } else if (ex instanceof IndexOutOfBoundsException) { map.put("code", ResponseCode.INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS_EXCEPTION); } else { map.put("code", ResponseCode.CATCH_EXCEPTION); } try { map.put("data", ex.getMessage()); response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return new ModelAndView(); } }
在 Spring 源码中,我们可以看出它会获取一个实现了 HandlerExceptionResolver 接口的列表 List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers; 如果这个列表不为空,则循环处理其中的异常。
HandlerExceptionResolve 虽然能够处理全局异常,但是 Spring 官方不推荐使用它。
@controlleradvice 注解
另外一个能够处理全局异常的就是 @controlleradvice 注解了。
@controlleradvice 注解根据它的源码,我们知道它也只能作用在类上,并且作用于运行时。下面我们来看一个例子。
@ControllerAdvice public class ExceptionController { @ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class) public ModelAndView handlerRuntimeException(RuntimeException ex) { if (ex instanceof MaxUploadSizeExceededException) { return new ModelAndView("error").addObject("msg", "文件太大!"); } return new ModelAndView("error").addObject("msg", "未知错误:" + ex); } @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public ModelAndView handlerMaxUploadSizeExceededException(Exception ex) { if (ex != null) { return new ModelAndView("error").addObject("msg", ex); } return new ModelAndView("error").addObject("msg", "未知错误:" + ex); } }
需要注意的是,@ControllerAdvice 一般是和 @ExceptionHandler 组合在一起使用的。官方也推荐用这种方式处理统一全局异常。





