Java NIO
Java NIO:
JAVA NIO核心部分是 Channel Buffer Selector。
所有IO在NIO中都从一个Channel开始,Channel有点像流,数据可以从Channel读到Buffer中,也可从Buffer读到Channel。Selector允许单线程处理多个Channel。
1、Buffer
步骤:1)写入数据到Buffer; 2)调用filp()方法; 3)从Buffer中读取数据; 4)调用clear()或者compact()方法
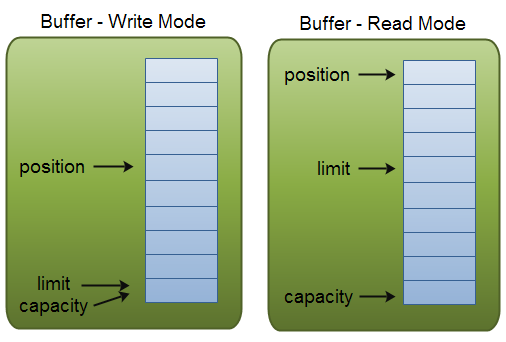
capacity:数组总长度;
position:下一个要操作的数据元素的位置
limit:缓存区数组总不可操作的下一个元素的位置
filp()方法将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式,position的值付给limit,然后position=0,读position->limit之间的数据。
clear()清空整个缓存区,compect()只清楚已经读过的数据,未读的数据移到缓冲区的起始处,新写入的数据放到缓冲区未读数据后面。
Buffer的分配:
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
CharBuffer buf=CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
Buffer的类型:ByteBuffer CharBuffer DoubleBuffer IntBuffer ...
Buffer中数据的读写操作:
写:
1)从Channel写到buffer
int bytesRead=inChannel.read(buf);
2)通过put()方法写入Buffer
buf.put(127)
读:
1)从Buffer读取数据到Channel
Int bytesWriten=inChannel.write(buf);
2)使用get()方法从Buffer中读取数据
byte aByte=buf.get();
package com.zhao.FileChannel; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; public class FileChannelDemo { /** * FileChannel从文件中读写数据 * * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileChannelDemo demo=new FileChannelDemo(); // demo.read(); demo.write(); } public void read() throws IOException { File file = new File("fileChannel.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); /* * 在使用FileChannel之前,必须先打开它。但是,我们无法直接打开一个FileChannel,需要通过使用一个InputStream、 * OutputStream或RandomAccessFile来获取一个FileChannel实例 */ FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel(); // 创建了一个48个byte的数组缓冲区 /** * capacity:缓冲区数组的总长度 position:下一个要操作的数据元素的位置 * limit:缓冲区数组中不可操作的下一个元素的位置。(在写模式下,limit就是最多能写多少数据;在读模式下, * limit就是最多能读多少数据) */ ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); /* * 将字节序列从此通道读入给定的缓冲区 。返回:读取的字节数,可能为零,如果该通道已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1 */ int count = fileChannel.read(buffer); System.out.println("读到字节数: " + count); while (count != -1) { // flip方法将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式。调用flip()方法会将position设回0,并将limit设置成之前position的值 buffer.flip(); // 在position和limit之间有元素 while (buffer.hasRemaining()) { System.out.print((char) buffer.get()); } // clear方法就是让position设回0,limit与capacity相等 buffer.clear(); count = fileChannel.read(buffer); System.out.println("\n终止条件: " + count); /* * compact()方法将所有未读的数据拷贝到Buffer起始处。然后将position设到最后一个未读元素正后面。 * limit属性依然像clear()方法一样,设置成capacity。现在Buffer准备好写数据了,但是不会覆盖未读的数据。 */ } randomAccessFile.close(); } public void write() throws IOException{ File file=new File("fileChannel.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } RandomAccessFile accessFile=new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); FileChannel channel=accessFile.getChannel(); String str="Channel Buffer Selector "+System.currentTimeMillis(); ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buffer.clear(); buffer.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("Position: "+channel.position()); buffer.flip(); while(buffer.hasRemaining()){ channel.write(buffer); } System.out.println("Channel Size: "+channel.size()); channel.close(); accessFile.close(); } }
2:Channel
Java NIO的通道类似流,但有些不同。
既可以在通道中读取数据,又可以写数据到通道,但流的读写是单向的。
通道可以异步读写。
通道的数据综上先读到一个Buffer或者从一个Buffer中写入。
FileChannel:从文件中读写数据
DatagramChannel: 能通过UDP读写网络中的数据
SocketChannel:能通过TCP读写网络中的数据
ServerSocketChannel 可以监听新进来的TCP连接,对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个SocketChannel.
1)TCP
//客户端
package com.zhao.TCPSocket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; public class Client { /** * Java NIO中的SocketChannel是一个连接到TCP网络套接字的通道 * * @author zhao * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 打开套接字通道 SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); //可以设置 SocketChannel 为非阻塞模式(non-blocking mode).设置之后,就可以在异步模式下调用connect(), read() 和write()了 // socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 创建套接字地址,其中 IP 地址为通配符地址,端口号为指定值 InetAddress remote = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); // 连接此通道的套接字 socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(remote, 8888)); // 从socketChannel中读取数据 // ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer); // 写入socketChannel ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); String str = "zhao " + System.currentTimeMillis(); buffer2.put(str.getBytes()); buffer2.flip(); while (buffer2.hasRemaining()) { socketChannel.write(buffer2); } // 当用完SocketChannel之后调用SocketChannel.close()关闭SocketChannel socketChannel.close(); } }
//服务端
package com.zhao.TCPSocket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; public class Server { /** * Java NIO中的 ServerSocketChannel 是一个可以监听新进来的TCP连接的通道, * 就像标准IO中的ServerSocket一样 * * @author zhao * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 获取与此通道关联的服务器套接字 ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket(); // 创建套接字地址,其中 IP 地址为通配符地址,端口号为指定值 InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(8888); // 将 ServerSocket 绑定到特定地址(IP 地址和端口号) serverSocket.bind(address); // serverSocketChannel设置为非阻塞模式 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); while (true) { // 通过 ServerSocketChannel.accept() 方法监听新进来的连接。当 // accept()方法返回的时候,它返回一个包含新进来的连接的 SocketChannel。因此, // accept()方法会一直阻塞到有新连接到达。如果把serverSocketChannel设置为非阻塞模式,accept会离开返回。所以需要判断 SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); if (socketChannel != null) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buffer.clear(); int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer); if (bytesRead != -1) { buffer.flip(); while (buffer.hasRemaining()) { System.out.print((char)buffer.get()); } bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer); } } } } }
2)UDP
//客户端一
package com.zhao.UDPSocket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel; public class Client { /** * Java NIO中的DatagramChannel是一个能收发UDP包的通道。因为UDP是无连接的网络协议,所以不能像其它通道那样读取和写入。 * 它发送和接收的是数据包 * * @author zhao * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { DatagramChannel datagramChannel=DatagramChannel.open(); datagramChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888)); // ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // buffer.clear(); //接收数据 // datagramChannel.receive(buffer); //发送数据 ByteBuffer buffer2=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); String str="zhao "+System.currentTimeMillis(); buffer2.put(str.getBytes()); buffer2.flip(); InetAddress address=InetAddress.getLocalHost(); datagramChannel.send(buffer2, new InetSocketAddress(address, 8889)); System.out.println("发送"); datagramChannel.close(); } }
//客户端二
package com.zhao.UDPSocket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel; public class Client2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { DatagramChannel datagramChannel=DatagramChannel.open(); datagramChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8889)); ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buffer.clear(); datagramChannel.receive(buffer); buffer.flip(); System.out.println("接收"); while(buffer.hasRemaining()){ System.out.print((char)buffer.get()); } datagramChannel.close(); } }
3:通道之间的数据传输
package com.zhao.FileChannel; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; public class FileChannelTransferDemo { /** * FileChannel的transferFrom()方法可以将数据从源通道传输到FileChannel中 * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file=new File("from.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } RandomAccessFile fromRandomAccessFile=new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); FileChannel fromChannel=fromRandomAccessFile.getChannel(); file=new File("to.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } RandomAccessFile toRandomAccessFile=new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); FileChannel toChannel=toRandomAccessFile.getChannel(); long position=0; long count=fromChannel.size(); fromChannel.transferTo(position, count, toChannel); //toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel, position, count); } }
4:Scatter/Gather
Scatter:从Channel中读取是指在读操作是将读取的数据写入到多个Buffer中
Gather:写入Channe是指在写操作时将过个buffer的数据写入同一个Channel
package com.zhao.buffer; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; public class Scatter_Gather { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Scatter_Gather scatter_Gather = new Scatter_Gather(); scatter_Gather.gather(); scatter_Gather.scatter(); } public void scatter() throws IOException { File file = new File("fileChannel.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); FileChannel channel = accessFile.getChannel(); ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); ByteBuffer[] buffers = { buffer1, buffer2 }; channel.read(buffers); buffer1.flip(); buffer2.flip(); while (buffer1.hasRemaining()) { System.out.print((char) buffer1.get()); } System.out.println(); while (buffer2.hasRemaining()) { System.out.print((char) buffer2.get()); } buffer1.clear(); buffer2.clear(); accessFile.close(); } public void gather() throws IOException { File file=new File("fileChannel.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } RandomAccessFile accessFile=new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); FileChannel channel=accessFile.getChannel(); ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); ByteBuffer buffer2=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buffer.clear(); buffer2.clear(); String str="wang"; String str2="admin"; buffer.put(str.getBytes()); buffer2.put(str2.getBytes()); buffer.flip(); buffer2.flip(); ByteBuffer[] buffers={buffer,buffer2}; System.out.println(channel.size()); channel.write(buffers); channel.close(); accessFile.close(); } }



