04 if选择结构
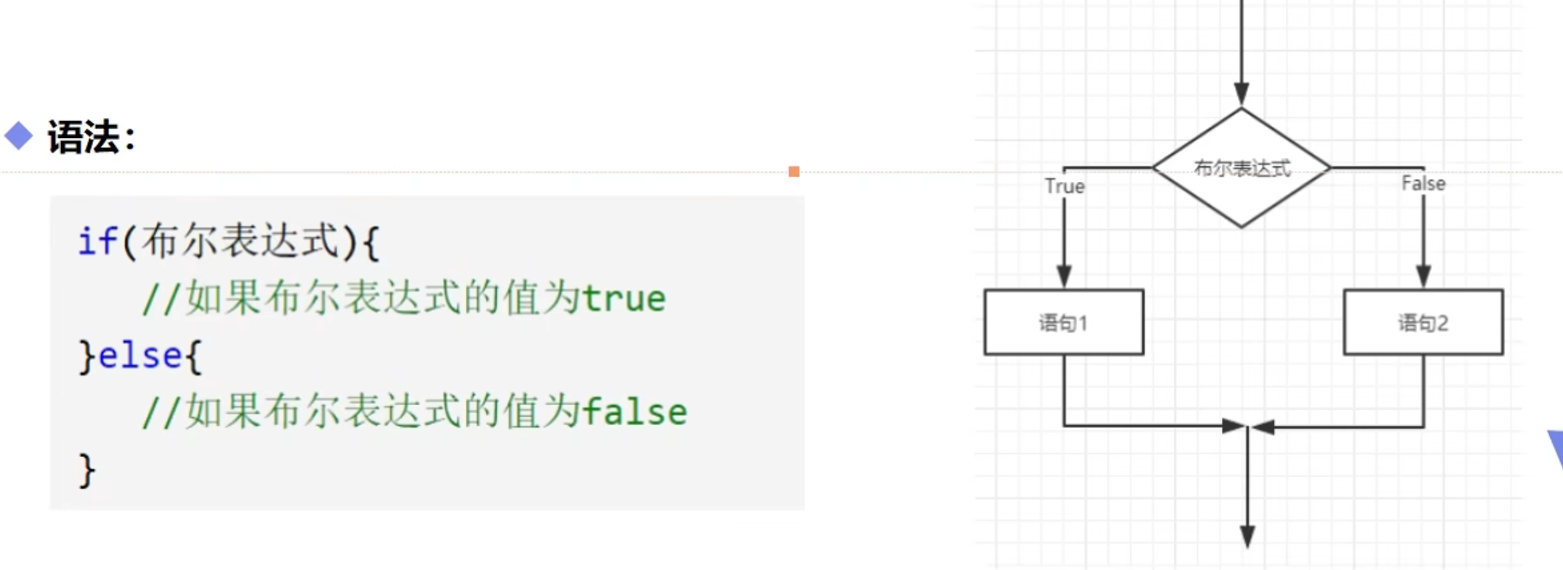
if 选择结构
equals() 方法
- 只能用来比较字符串?
==是判断两个变量是不是指向同一个内存空间,equals是判断两个变量值是不是相同
package com.zhan.base_2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo {
//equals() 的用法,注意与 == 的区别
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
if (str.equals("hello")) { // 判断字符串 是否等于 hello
System.out.println("相等");
} else System.out.println("不相等");
}
}
if 单选择结构

if 双选择结构
也可以用 三元运算符来实现 : x ?y :z
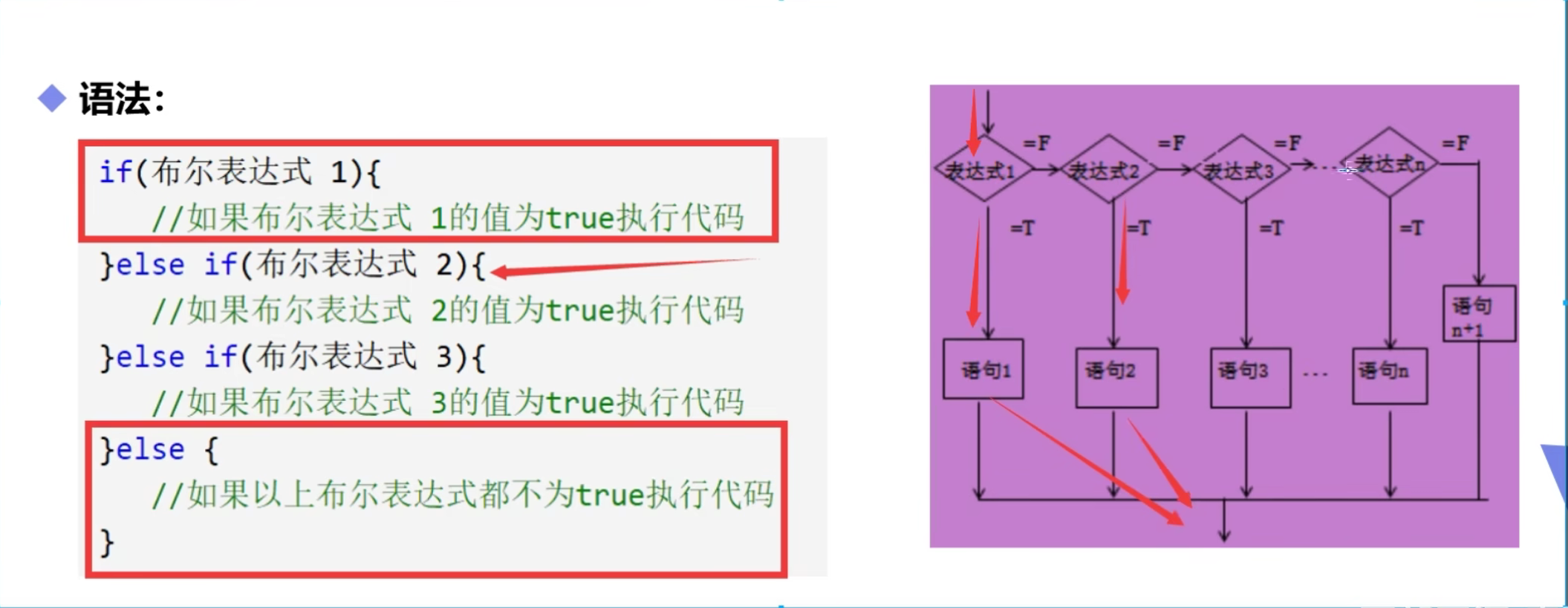
if 多选择结构
if 嵌套结构
可以用来二分查找等等,提高效率

要求这个数对应 1 - 10,分别进行不同的操作,此时进行if 嵌套可以提高效率,更别说数值更大的情况下
代码
package com.zhan.base_2;
import org.w3c.dom.ls.LSOutput;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test03_If {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
//单选择结构 if(){ } 单独只有一行内容的话可以不加 {}
if (score == 100)
System.out.println("满分!");
System.out.println("======================");
//双选择结构 if(){ } else{ }
if (score >= 60) {
System.out.println("及格");
} else System.out.println("不及格");
System.out.println("======================");
//多选择结构, 两种写法,还是使用第二种比较稳妥!
//第一种
if (score > 100 || score < 0) {
System.out.println("成绩无效!"); // 把少量的易知可能会出问题的地方排除掉,且放在第一位
} else if (score == 100) {
System.out.println("满分!");
} else if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B");
} else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C");
} else if (score >= 60) {
System.out.println("D");
} else { // 也可以 写成 else if (score>0),都一样
System.out.println("不及格");
} //else if (score>100 ||score<0) { //此时输入200 会输出A ,错误,因为前面已经执行了 else if (score>=90)
// System.out.println("成绩无效!");
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//第二种
if (score == 100) { // 把严格遵守明确条件的内容写在前面
System.out.println("满分!");
} else if (score < 100 && score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (score < 90 && score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B");
} else if (score < 800 && score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C");
} else if (score < 70 && score >= 60) {
System.out.println("D");
} else if (score < 60 && score >= 0) {
System.out.println("不及格");
} else System.out.println("成绩无效!"); // 把很多的可能会出现问题的地方放在最后一起解决掉
System.out.println("=========================================================");
// if 嵌套语句
//可以用来二分查找等等
//要求这个成绩对应 10个分数段,分别进行不同的操作,此时进行if 嵌套可以提高效率,更别说数值更大的情况下
if (score <= 100 && score >= 0) {
if (score >= 60) {
if (score == 100) { // 把严格遵守明确条件的内容写在前面
System.out.println("满分!");
}else if (score < 100 && score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (score < 90 && score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B");
} else if (score < 800 && score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C");
} else if (score < 70 && score >= 60) {
System.out.println("D");
}
}
if (score<60){
if (score < 60 && score >= 50) {
System.out.println("-A");
} else if (score < 50 && score >= 40) {
System.out.println("-B");
} else if (score < 40 && score >= 30) {
System.out.println("-C");
} else if (score < 30 && score >= 20) {
System.out.println("-D");
} else if (score < 20 && score >= 10) {
System.out.println("-E");
} else if (score < 10 && score >= 0) {
System.out.println("难办咯");
}
}
}
scanner.close(); // 一定要记得关闭,养成良好习惯,最好是一开始直接写好再去操作其他事情
}
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?