【转载】Linux中的preempt_count
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「tangyongxiang_cn」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/tangyongxiang_cn/article/details/121704682
preempt_count本质上是一个per-CPU的32位变量
,它在各种处理器架构下的存放位置和命名不尽相同,但其值都可以使用preempt_count()函数统一获取。preempt_count逻辑相关的核心代码位于include/linux/preempt.h,虽然只是一个32位变量,但由于其和中断、调度/抢占密切相关,因此在系统中发挥的作用不容小觑。
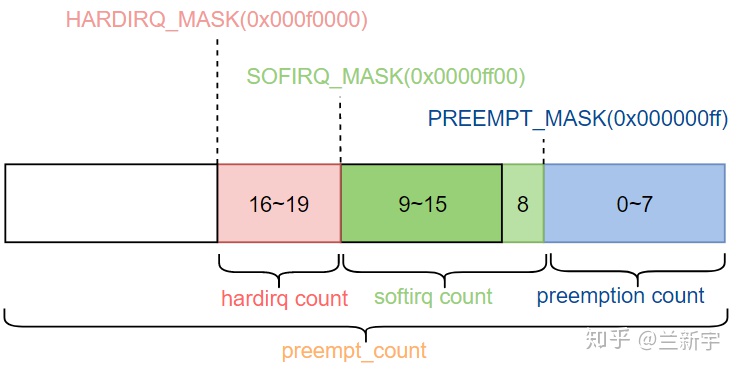
来看下preempt_count是怎样构成的:
hardirq相关
preempt_count中的第16到19个bit表示hardirq count,它记录了进入hardirq/top half的嵌套次数,在这篇文章介绍的do_IRQ()中,irq_enter()用于标记hardirq的进入,此时hardirq count的值会加1。irq_exit
()用于标记hardirq的退出,hardirq count的值会相应的减1。如果hardirq count的值为正数,说明现在正处于hardirq上下文中,代码中可借助in_irq()宏实现快速判断。注意这里的命名是"in_irq"而不是"in_hardirq"。
hardirq count占据4个bits,理论上可以表示16层嵌套,但现在Linux系统并不支持hardirq的嵌套执行,所以实际使用的只有1个bit。
之所以采用4个bits,一是历史原因,因为早期Linux并不是将中断处理的过程分为top half和bottom half,而是将中断分为fast interrupt handler和slow interrupt handler,而slow interrupt handler是可以嵌套执行的,二是某些 driver 代码可能在top half中重新使能hardirq。
softirq相关
preempt_count中的第8到15个bit表示softirq count
,它记录了进入softirq的嵌套次数,如果softirq count的值为正数,说明现在正处于softirq上下文中。由于softirq在单个CPU上是不会嵌套执行的,因此和hardirq count一样,实际只需要一个bit(bit 8)就可以了。但这里多出的7个bits并不是因为历史原因多出来的,而是另有他用。
这个"他用"就是表示在进程上下文中,为了防止进程被softirq所抢占,关闭/禁止softirq的次数,比如每使用一次local_bh_disable(),softirq count高7个bits(bit 9到bit 15)的值就会加1,使用local_bh_enable()则会让softirq count高7个bits的的值减1。
代码中可借助in_softirq()宏快速判断当前是否在softirq上下文:
这篇文章曾提到:进入softirq是在softirq上下文,关闭softirq抢占也是在softirq上下文,但还是有办法区分的。办法就是使用in_serving_softirq()宏来确切地表示现在是在处理softirq。
上下文
不管是hardirq上下文还是softirq上下文,都属于我们俗称的中断上下文(interrupt context)。
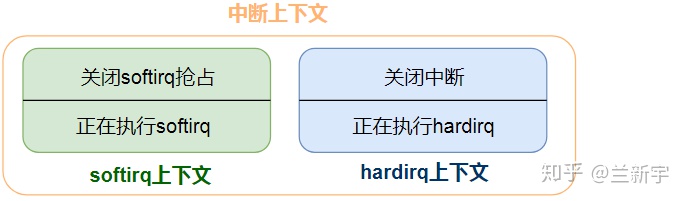
为此,有一个名为in_interrupt()的宏专门用来判断当前是否在中断上下文中。
与中断上下文相对应的就是俗称的进程上下文(process context)
#define in_task() (!(preempt_count() & (HARDIRQ_MASK | SOFTIRQ_OFFSET | NMI_MASK)))
需要注意的是,并不是只有进程才会处在process context,内核线程
依然可以运行在process context。
在中断上下文中,调度是关闭的,不会发生进程的切换,这属于一种隐式的禁止调度,而在代码中,也可以使用preempt_disable
()来显示地关闭调度,关闭次数由第0到7个bits组成的preemption count(注意不是preempt count)来记录。每使用一次preempt_disable(),preemption count
的值就会加1,使用preempt_enable()则会让preemption count的值减1。preemption count占8个bits,因此一共可以表示最多256层调度关闭的嵌套。
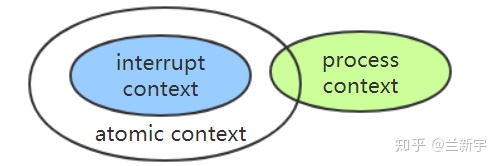
处于中断上下文,或者显示地禁止了调度,preempt_count()的值都不为0,都不允许睡眠/调度的发生,这两种场景被统称为atomic上下文,可由in_atomic()宏给出判断。
#define in_atomic() (preempt_count() != 0)
中断上下文、进程上下文和atomic上下文的关系大概可以表示成这样:
-
/*
-
* low level task data that entry.S needs immediate access to.
-
* __switch_to() assumes cpu_context follows immediately after cpu_domain.
-
*/
-
struct thread_info {
-
unsigned long flags; /* low level flags */
-
mm_segment_t addr_limit; /* address limit */
-
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
-
struct exec_domain *exec_domain; /* execution domain */
-
struct restart_block restart_block;
-
int preempt_count; /* 0 => preemptable, <0 => bug */
-
int cpu; /* cpu */
-
};
在支持可抢占的系统中,一个进程的thread_info信息定义如上。其中preempt_count代表的是该进程是否可以被抢占,根据注释的说明当peermpt_count等于0的时候当前进程可以被抢占,当小于0存在bug,当大于0说明当前进程不可以被抢占。比如当前进程在中断上下文中或者使用了锁。
-
<linux/include/preempt_mask.h>
-
------------------------------------------
-
/*
-
* We put the hardirq and softirq counter into the preemption
-
* counter. The bitmask has the following meaning:
-
*
-
* - bits 0-7 are the preemption count (max preemption depth: 256)
-
* - bits 8-15 are the softirq count (max # of softirqs: 256)
-
*
-
* The hardirq count could in theory be the same as the number of
-
* interrupts in the system, but we run all interrupt handlers with
-
* interrupts disabled, so we cannot have nesting interrupts. Though
-
* there are a few palaeontologic drivers which reenable interrupts in
-
* the handler, so we need more than one bit here.
-
*
-
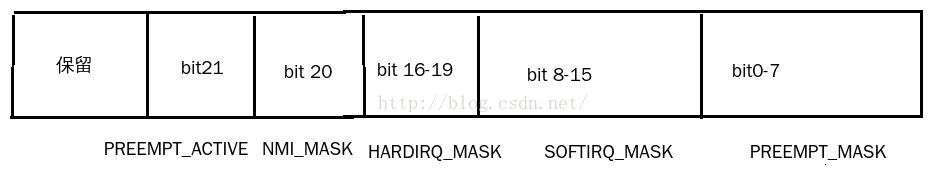
* PREEMPT_MASK: 0x000000ff
-
* SOFTIRQ_MASK: 0x0000ff00
-
* HARDIRQ_MASK: 0x000f0000
-
* NMI_MASK: 0x00100000
-
* PREEMPT_ACTIVE: 0x00200000
-
*/
-
-
-
-
结合上述的示图和代码的定义可知,bit0-7代表的是抢占的次数,最大抢占深度为256次,bit8-15代表的是软中断的次数,最大也是256次,bit16-19表示中断的次数,注释的大概意思是避免中断嵌套,但是也不能防止某些驱动中断嵌套使用中断,所以嵌套16层也是最大次数了。bit20代表的NMI中断,bit21代表当前抢占是否active。
Linux系统为了方便得出各个字段的值,提供了一系列宏定义如下:
从上述的定义可以得出,如果想知道硬中断的次数就使用hardirq_count,如果想知道中断次数就使用softirq_count,如果想知道所有中断的次数就使用irq_count。
-
/*
-
* Are we doing bottom half or hardware interrupt processing?
-
* Are we in a softirq context? Interrupt context?
-
* in_softirq - Are we currently processing softirq or have bh disabled?
-
* in_serving_softirq - Are we currently processing softirq?
-
*/
-
-
-
-
其中in_irq用于判断当前进程是否在硬中断中,in_softirq用于判断是否当前进程在软件中断或者有别的进程disable了软中断,in_interrupt用于判断当前进程是否在中断中,而in_serving_softirq用于判断当前进程是否在软件中断中,通过bit8这一位来判断。
#define in_atomic() ((preempt_count() & ~PREEMPT_ACTIVE) != 0)
这个宏可以判断当前进程是否处于原子操作中。

