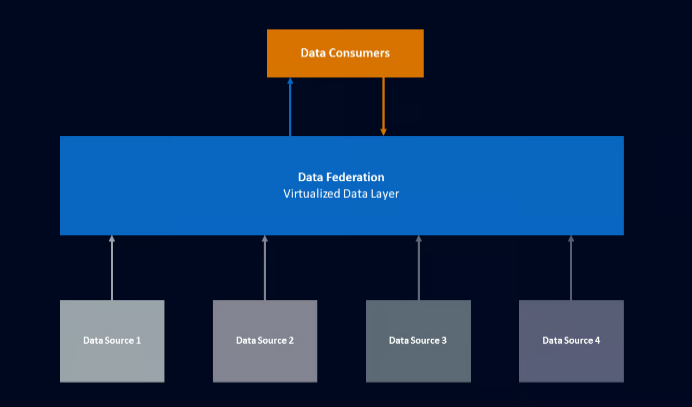
Schema mapping
A schema is a blueprint that defines how data is organized within a database. Data sources often have different schemas, meaning they organize and label their data differently. Schema mapping involves aligning these schemas to create a consistent data view.
For example, one data source might use "CustomerID" to refer to a customer identifier, while another might use "CustID." Schema mapping translates these different labels to be understood as the same entity.
By harmonizing the different schemas, data federation tools ensure that data from diverse sources can be integrated seamlessly. This provides a consistent and reliable data model that users can trust for accurate analysis and reporting.
Query processing
When we submit a query to a federated system, it first goes to the federation layer. Think of the federation layer as a smart translator. It takes our main query and breaks it down into smaller sub-queries. Each sub-query is customized to fetch data from different sources where that information is stored, like databases or cloud storage.
These sub-queries are then sent to the various data sources in real time. Each source processes its part of the query and sends back the results. The federation layer then collects all these results and combines them into one aggregated result.
This streamlined process allows us to access and analyze data from multiple sources as if they were a single, unified dataset. This makes it easier to collect data from all over the organization.
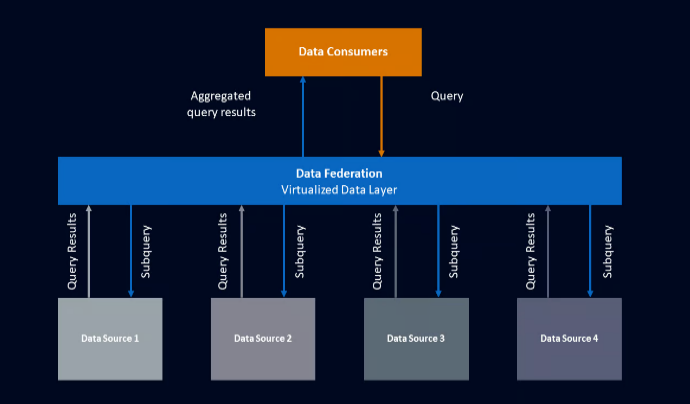
The above graphic is a simplified view of this process. A data consumer queries the data federation. It breaks up that query into a series of subqueries and sends them out to the appropriate data source. Each source sends back its results, which the data federation then aggregates to relay to the data consumer.
Challenges of Data Federation
While offering numerous advantages, data federation also presents several challenges that organizations must address.
Performance
Performance issues may arise due to the complexity of queries across multiple sources. Optimization efforts can help to ensure efficient data retrieval and processing. It’s important to invest in robust infrastructure and use query optimization techniques. These can mitigate performance bottlenecks and maintain responsiveness in data access and analysis.
Complexity
Another significant challenge is schema complexity. Mapping schemas from diverse sources can be daunting. The disparate structures of data sources require sophisticated tools and techniques to harmonize schemas and ensure consistency across the federated data. Data professionals can use data modeling and schema mapping strategies to overcome these challenges. This way, we can create a unified view of the data that accurately reflects its underlying semantics.
To learn more about schema mapping, I suggest you check out this Database Design course.
Data governance
Data governance can be a challenge with federated data. Organizations must establish and enforce policies for data quality, security, and privacy across federated sources. It’s important to implement data governance processes, like data lineage tracking, access controls, and privacy measures. These help to mitigate risks and maintain the integrity of federated data.
For more information on data governance, check out Making Data Governance Fun and How Data Leaders Can Make Data Governance a Priority. This data governance cheat sheet is also a good resource.
Implementing Data Federation
Depending on your data landscape, implementing a data federation may be a challenge. But with careful planning, selection of appropriate tools, and consideration of our organization’s requirements, it is a manageable task that will pay dividends. Here are a few steps to consider in any federation implementation.
Assess the data landscape
We must begin by thoroughly assessing our organization's current data landscape. Identify the data sources present across different systems, databases, and applications. Learn the types of data stored in each source and how often they are updated. This will help ensure that our data federation solution can accommodate real-time access to the most current data.
Define use cases and requirements
As with any project, it’s important to clearly define our goals. Lay out the use cases and requirements for data federation within the organization. Determine the specific business objectives you aim to achieve through data federation. These might be improving data accessibility, streamlining data integration processes, or enabling real-time analytics. Identify key stakeholders and involve them in this step to ensure the solution meets their needs, too.
Select the right tools
Choose the appropriate tools and technologies based on the organization's requirements and budget constraints. Consider factors such as data virtualization capabilities, scalability, ease of integration with existing systems, and support for various data sources. Evaluate both commercial and open-source options to find the best fit for our needs. Below is a table with a few popular tools used in data federation.
|
Tool |
Features |
Licensing Model |
|
Real time data access, schema mapping, query optimization |
Paid |
|
|
Flexible and extensible, custom data federation solutions |
Open-source |
|
|
Query data stored in Amazon S3 using standard SQL |
Paid |
Design the federation
Design a federation that aligns with the organization's requirements and use cases. Determine the placement of the federation layer within the existing infrastructure and define the integration points with data sources and data consumers. Consider data security, performance optimization, and scalability to ensure that the federation can support both current and future data needs.
Implement and test
Once our data federation is set up and configured to connect to our data sources, it’s important to make sure it’s working properly. Test the solution thoroughly to identify any issues or performance bottlenecks and refine our implementation as needed.
Deploy and monitor
Deploy the data federation solution into production and monitor its performance and reliability. Establish monitoring and alerting mechanisms to detect and address any issues proactively. Continuously optimize the federation architecture and data integration processes to ensure the solution remains effective and aligned with evolving business needs.
Selectly copied from: https://www.datacamp.com/blog/data-federation




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
2023-12-24 ZIMP - statik error: no zip data registered
2023-12-24 ZIMP - Display API Docs using swagger-ui
2023-12-24 ZIMP - import error
2020-12-24 Shell - shebang line