A natural way to deal with uncertainty is to introduce probabilistic rules. In the simplest case, we can imagine an FSM-like device having no commands but clock ticks associated with probabilities (see Figure 7.10).
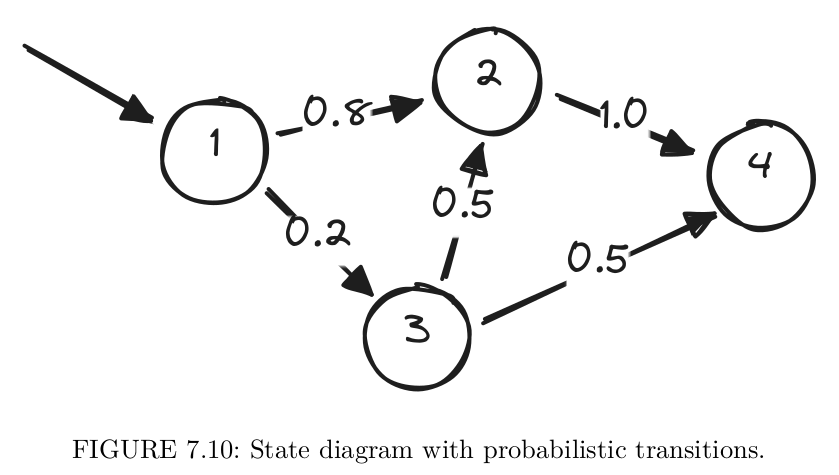
This device starts its operation in state 1. The next clock tick switches it either to state 2 (80% chance) or to state 3 (20% chance). There is just one option to go from state 2, but state 3 has two equally probable paths.
This kind of device is known as a Markov process or Markov chain. Its primary function is to represent certain processes rather than to control something: there is no command sequence in a Markov chain model, so we can only watch it switching from state to state.
This device is suitable for modeling processes that satisfy Markov property: future evolution of a process should not depend on its history.




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
2023-08-15 Go - Predeclared identifiers, Keywords, Operators and punctuation