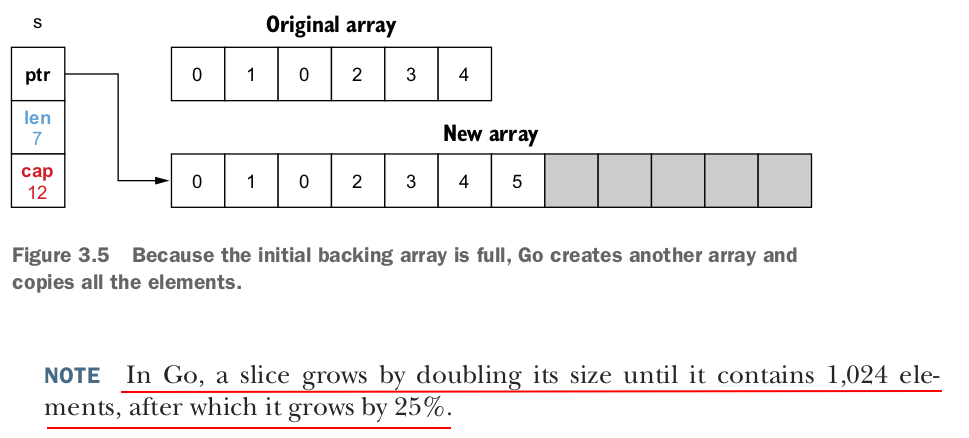
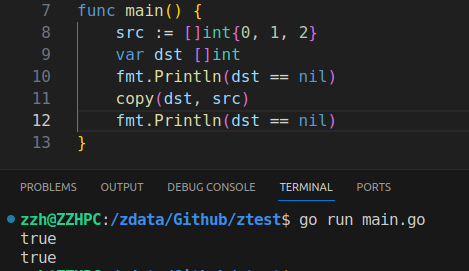
The slice now references the new backing array. What will happen to the previous backing array? If it’s no longer referenced, it’s eventually freed by the garbage collector (GC) if allocated on the heap.
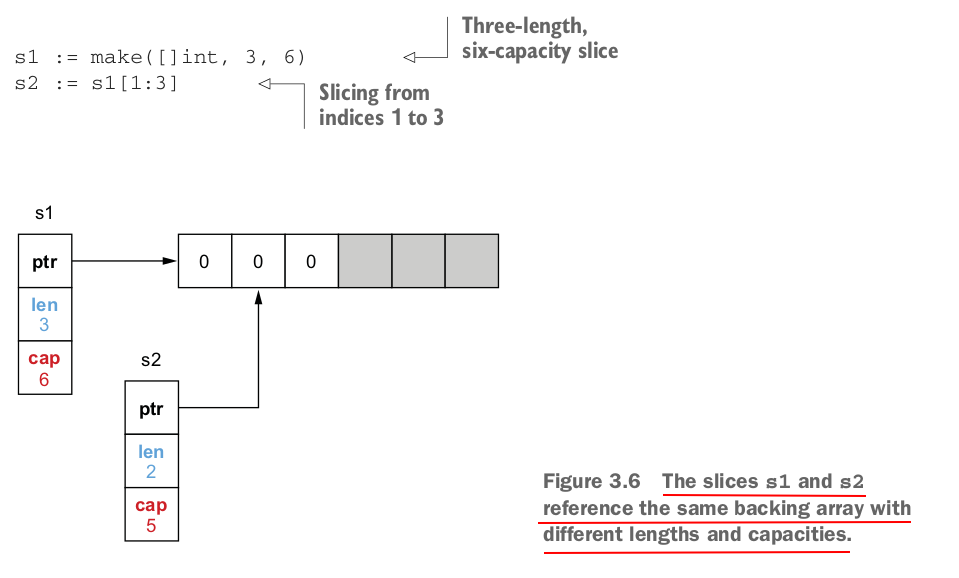
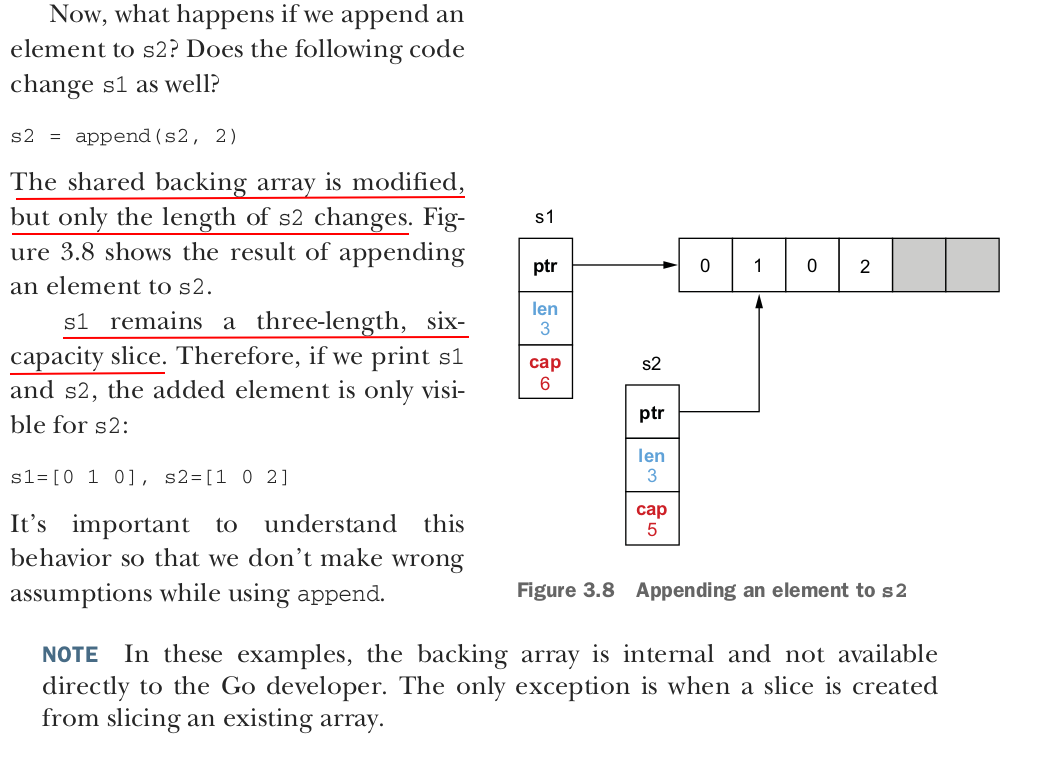


To summarize, the slice length is the number of available elements in the slice, whereas the slice capacity is the number of elements in the backing array. Adding an element to a full slice (length == capacity) leads to creating a new backing array with a new capacity, copying all the elements from the previous array, and updating the slice pointer to the new array.
func main() { var s []string log(1, s) s = []string(nil) log(2, s) s = []string{} log(3, s) s = make([]string, 0) log(4, s) } func log(i int, s []string) { fmt.Printf("%d: empty=%t\tnil=%t\n", i, len(s) == 0, s == nil) }
zzh@ZZHPC:/zdata/Github/ztest$ go run main.go 1: empty=true nil=true 2: empty=true nil=true 3: empty=true nil=false 4: empty=true nil=false











【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律