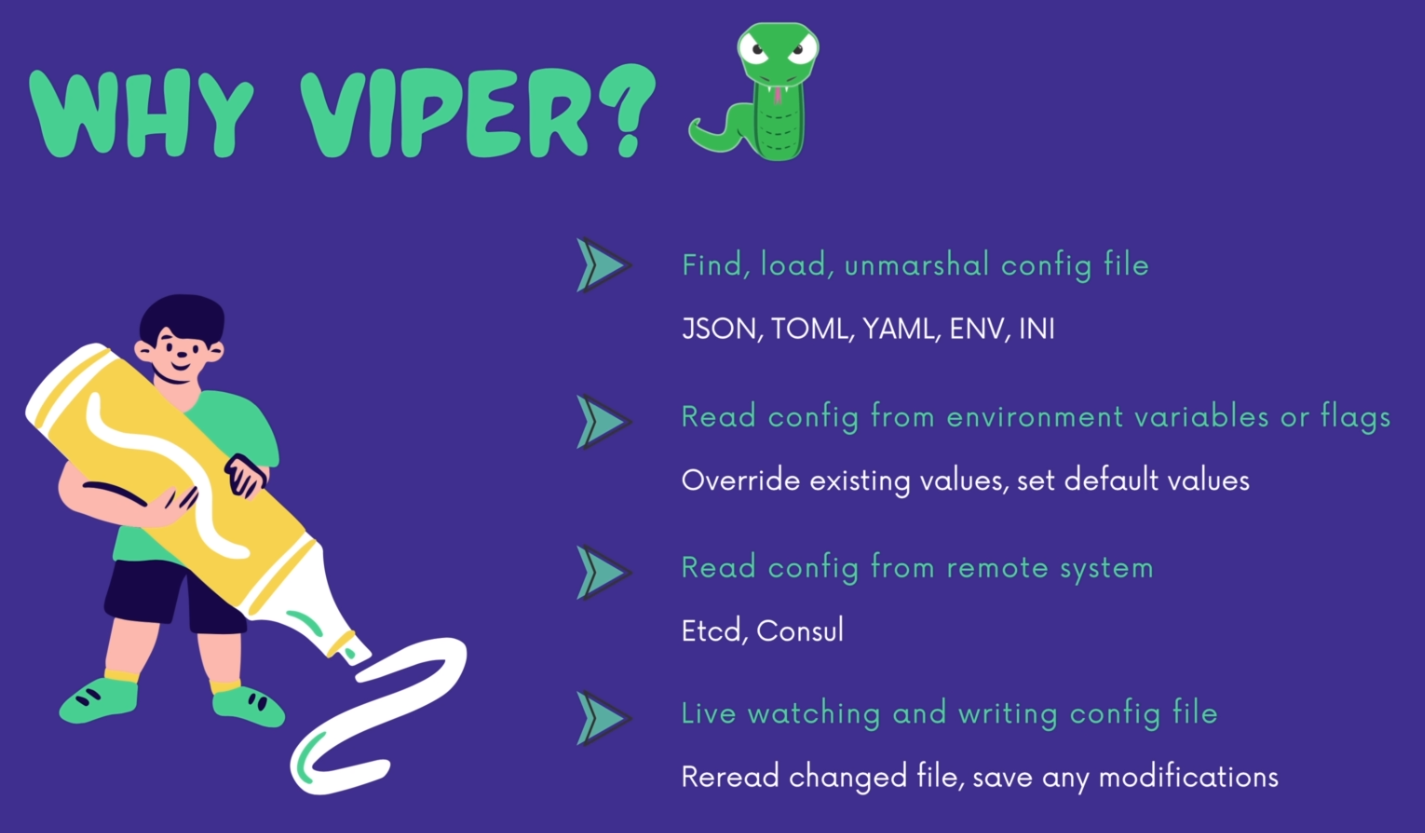
Viper uses github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure under the hood for unmarshaling values which uses mapstructure tags by default.
supported extensions are "json", "toml", "yaml", "yml", "properties", "props", "prop", "env", "dotenv"
Example:
package util import "github.com/spf13/viper" // Config stores all configuration of the application. type Config struct { Environment string `mapstructure:"ENVIRONMENT"` DBSource string `mapstructure:"DB_SOURCE"` HTTPServerAddress string `mapstructure:"HTTP_SERVER_ADDRESS"` } // LoadConfig reads configuration from file or environment variables. func LoadConfig(path string) (config Config, err error) { viper.AddConfigPath(path) viper.SetConfigName("app") viper.SetConfigType("env") viper.AutomaticEnv() err = viper.ReadInConfig() if err != nil { return } err = viper.Unmarshal(&config) return }

Read multiple config files:
// LoadConfig reads configuration from files or environment variables. func LoadConfig(path string) (config Config, err error) { viper.AddConfigPath(path) viper.SetConfigType("env") viper.SetConfigName("app") err = viper.ReadInConfig() if err != nil { return } viper.SetConfigName("app_prod_overwrite") err = viper.MergeInConfig() // ReadInConfig() again does not work if err != nil { return } viper.AutomaticEnv() err = viper.Unmarshal(&config) return }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律