fibonacci.go
package algorithms // Dynamic Programming func Fibonacci1(n int) int { if n <= 0 { return 0 } if n <= 2 { return 1 } previous1 := 1 previous2 := 1 currentVal := 0 for i := 3; i <= n; i++ { currentVal = previous1 + previous2 previous1 = previous2 previous2 = currentVal } return currentVal } var store = map[int]int{ 1: 1, 2: 1, } func Fibonacci2(n int) int { if n <= 0 { return 0 } if v, ok := store[n]; ok == true { return v } val := Fibonacci2(n-2) + Fibonacci2(n-1) store[n] = val return val }
fibonacci_test.go
package algorithms import ( "testing" ) type TestCase struct { name string input any expected any } func BenchmarkFibonacci1(b *testing.B) { for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ { _ = Fibonacci1(i) } } func BenchmarkFibonacci2(b *testing.B) { for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ { _ = Fibonacci2(i) } } func getFiboTests() []TestCase { tests := []TestCase{ {"Case 1", 0, 0}, {"Case 2", 2, 1}, {"Case 3", 3, 2}, {"Case 4", 4, 3}, {"Case 5", 5, 5}, {"Case 6", 6, 8}, {"Case 7", 7, 13}, } return tests } func TestFibonacci1(t *testing.T) { tests := getFiboTests() for _, tc := range tests { result := Fibonacci1(tc.input.(int)) if result != tc.expected { t.Errorf("%s failed. Input: %v Output: %v Expected: %v", tc.name, tc.input, result, tc.expected) } } } func TestFibonacci2(t *testing.T) { tests := getFiboTests() for _, tc := range tests { result := Fibonacci2(tc.input.(int)) if result != tc.expected { t.Errorf("%s failed. Input: %v Output: %v Expected: %v", tc.name, tc.input, result, tc.expected) } } }
Performance comparison:
zzh@ZZHPC:/zdata/MyPrograms/Go/algorithms$ go test -run NONE -bench Benchmark -benchmem goos: linux goarch: amd64 pkg: algorithms cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9600K CPU @ 3.70GHz BenchmarkFibonacci1-6 1000000 110601 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op BenchmarkFibonacci2-6 5645918 187.9 ns/op 46 B/op 0 allocs/op PASS ok algorithms 111.910s
zzh@ZZHPC:/zdata/MyPrograms/Go/algorithms$ go test -run NONE -bench Benchmark -benchmem -benchtime 100000x goos: linux goarch: amd64 pkg: algorithms cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9600K CPU @ 3.70GHz BenchmarkFibonacci1-6 100000 11151 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op BenchmarkFibonacci2-6 100000 172.7 ns/op 106 B/op 0 allocs/op PASS ok algorithms 1.136s
Fibonacci2 is much better than Fibonacci1.
After refectoring Fibonacci2 to below (not using a global variable to store the cached results):
func Fibonacci2(n int) int { var store = map[int]int{ 1: 1, 2: 1, } return fibonacci2(n, store) } func fibonacci2(n int, store map[int]int) int { if n <= 0 { return 0 } if store[n] != 0 { return store[n] } val := fibonacci2(n-2, store) + fibonacci2(n-1, store) store[n] = val return val }
函数调用时,map是指针传递:
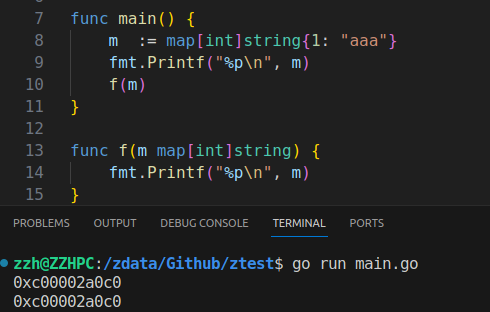
Performance comparison:
zzh@ZZHPC:/zdata/MyPrograms/Go/algorithms$ go test -run NONE -bench Benchmark -benchmem goos: linux goarch: amd64 pkg: algorithms cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9600K CPU @ 3.70GHz BenchmarkFibonacci1-6 1000000 111584 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op BenchmarkFibonacci2-6 10000 440063 ns/op 396952 B/op 110 allocs/op PASS ok algorithms 116.000s
Fibonacci1 is much better than Fibonacci2.
Refactor Fibonacci2 to below using closure:
func Fibonacci2(n int) int { fibo := fibonacci2() return fibo(n) } func fibonacci2() func(int) int { s := []int{1, 1} return func(n int) int { if n <= 0 { return 0 } if n > len(s) { for i := len(s); i < n; i++ { s = append(s, s[i-2] + s[i-1]) } } return s[n-1] } }
Performance comparison:
zzh@ZZHPC:/zdata/MyPrograms/Go/algorithms$ go test -run NONE -bench Benchmark -benchmem goos: linux goarch: amd64 pkg: algorithms cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9600K CPU @ 3.70GHz BenchmarkFibonacci1-6 1000000 110783 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op BenchmarkFibonacci2-6 46876 139588 ns/op 874814 B/op 18 allocs/op PASS ok algorithms 117.599s
Fibonacci1 is much better than Fibonacci2.





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
2020-09-18 VirtualBox - Guest OS resolution setting cannot be saved