OC 底层探索 16、类的加载 - 类的扩展 & 分类关联对象
一、类扩展
1、类扩展与分类
category:
- 准用来给类添加新方法;
- 不能添加成员变量,即使添加了也无法取到;
- 属性可添加,但只会生成 setter/getter 的声明而没有相应的实现 --> 可通过 runtime 进行关联实现。
extension:
- 可看做匿名分类;
- 可以给类添加成员属性,但是私有的;
- 可以给类添加方法,也是私有的。
类扩展:

类的扩展必须在实现前,如下图 error 信息:

类扩展的本质是什么呢?
2、类扩展 - Extension 的本质
1、cpp 文件的编译查看
在main.m 文件中添加如下简单代码,
clang -rewrite-objc main.m -o main.cpp
编译 main.m 文件成 .cpp:
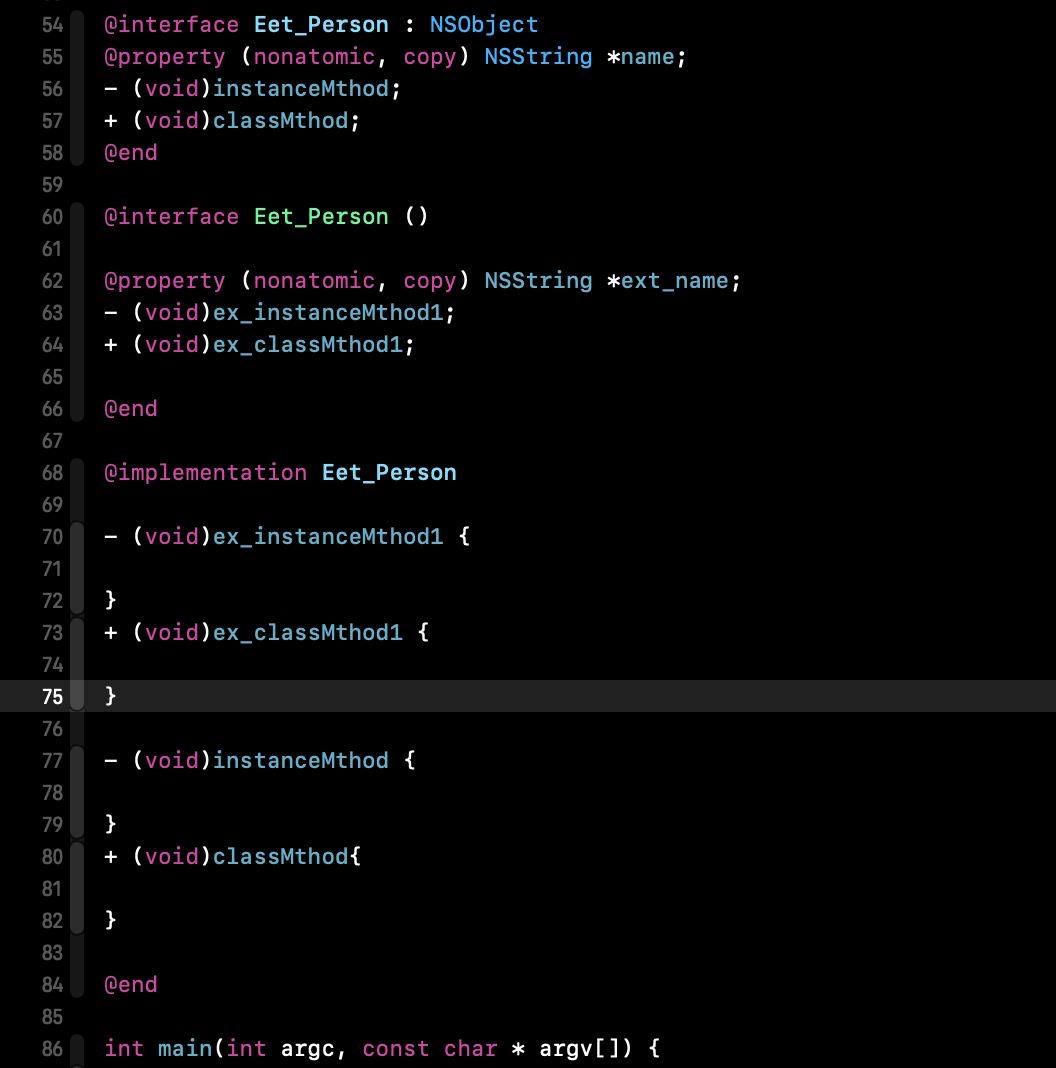
编译后文件代码:

setter/getter 的实现:
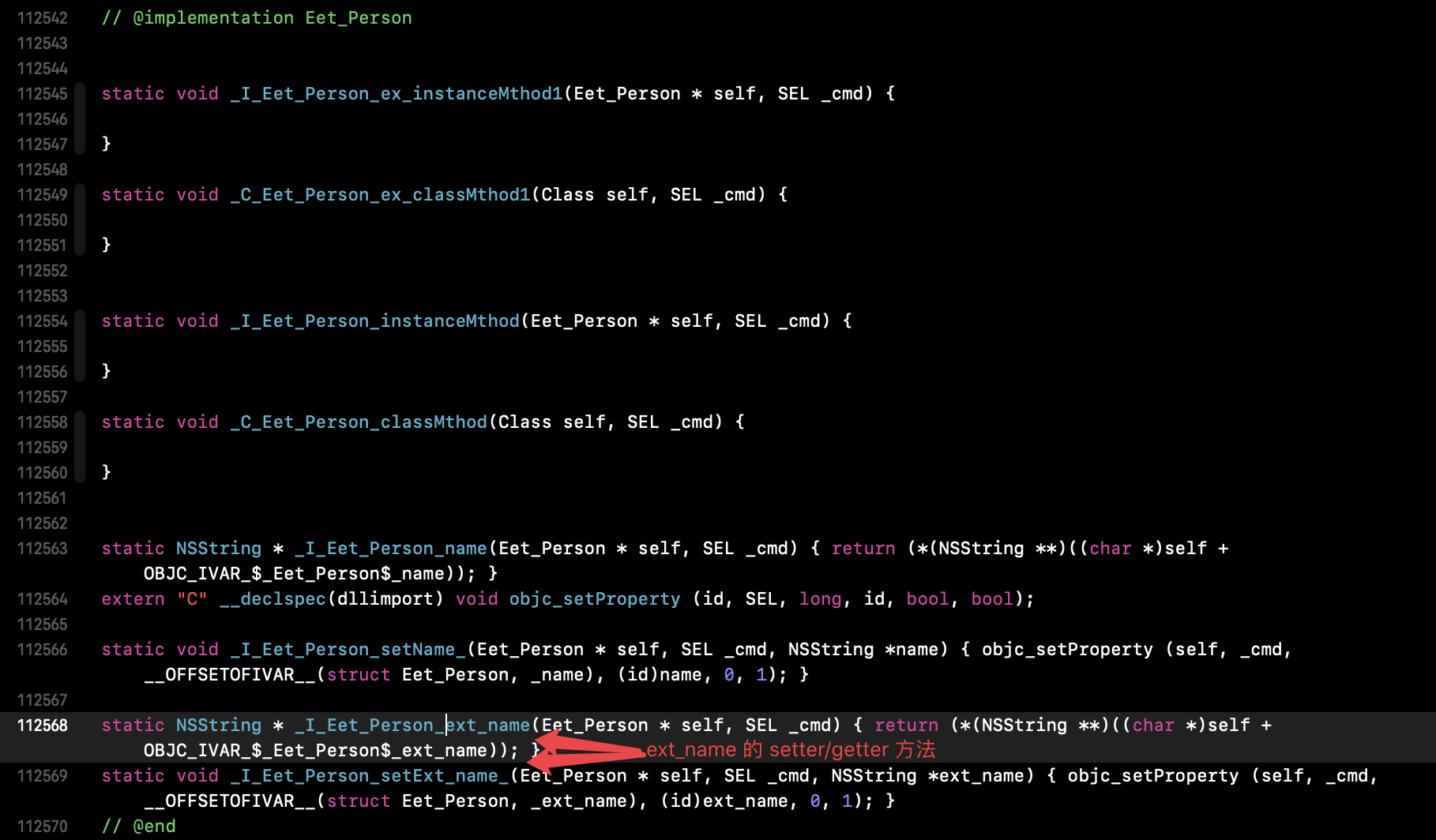
由上可验证:通过类扩展添加的属性变量,在编译时生成了 成员变量 ivar 和 setter(objc_setProperty()) / getter 方法的声明与实现。
方法列表 method_list 中,类扩展添加的方法和原本可重点二分法一样,编译时已经编译到 method_list 中了。

我们使用之前类加载分析时的 objc 源码工程 进行验证,运行:
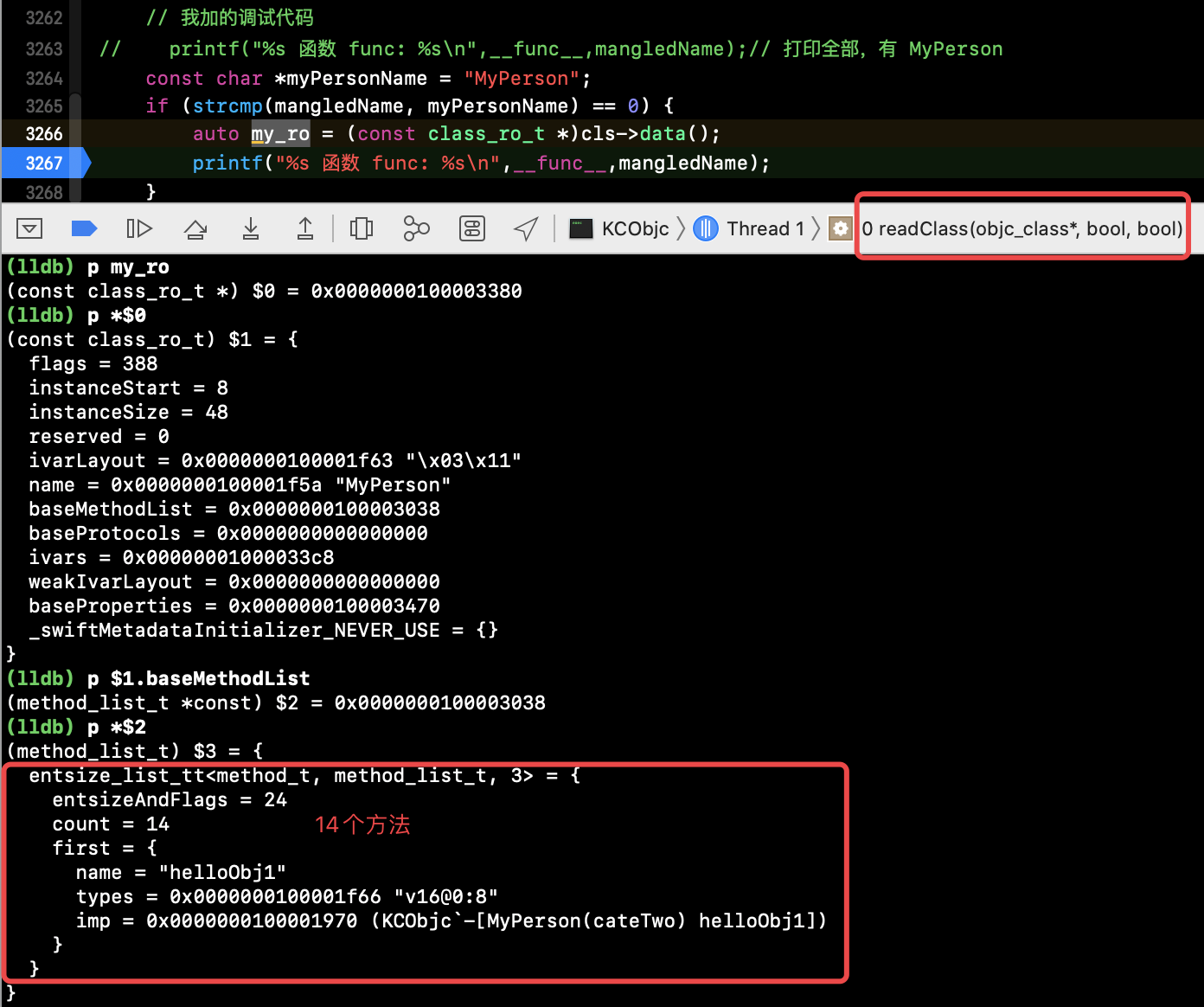
方法们见下图:

这里也可验证。更多操作:1、将添加的分类删除,重新运行,结果相同;2、将 MyPerson 类的 load 方法实现注释掉,依然相同:
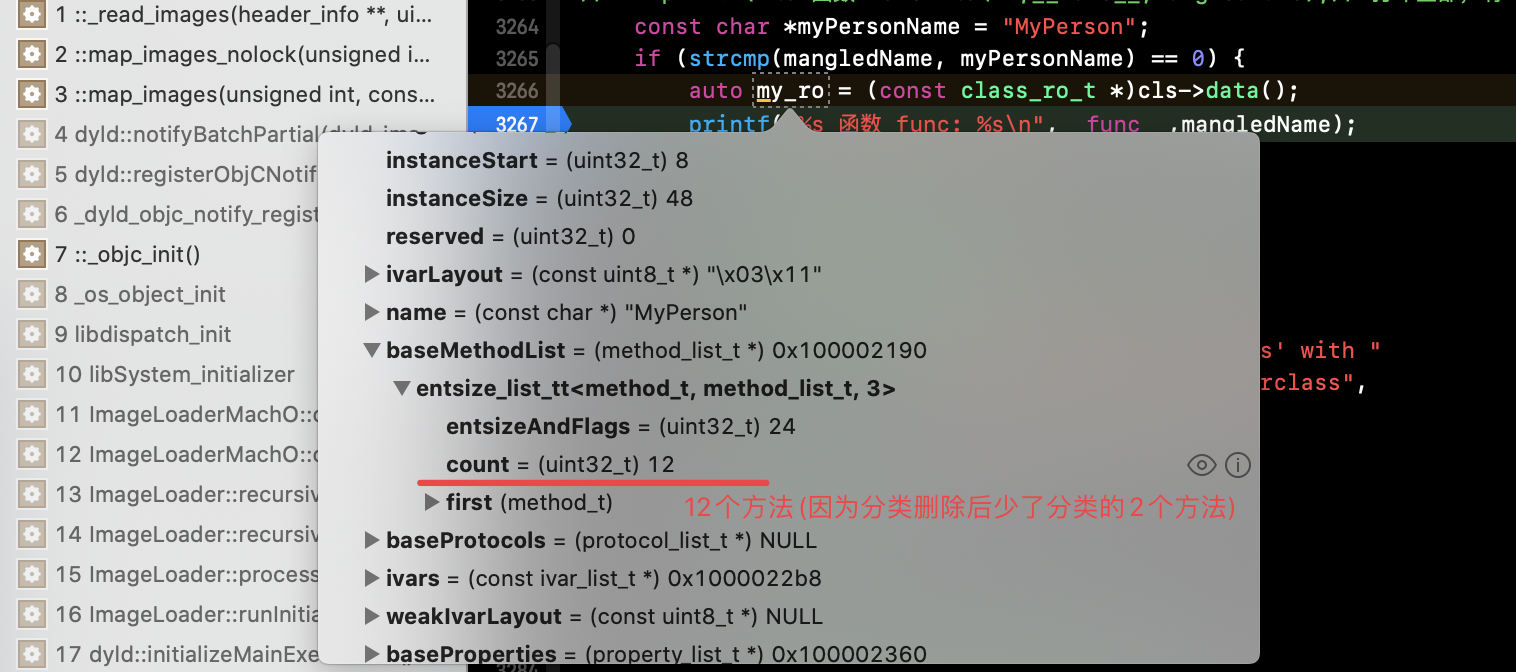
总结: 类的扩展在编译时就会被加载到类中了,直接成为为类的一部分和类共存了(自然类扩展添加的东西不存在脏内存问题,rwe 永远NULL)。
扩展和分类不同,分类更主要用于动态的添加。
二、关联对象
一直分类添加的属性是没有 setter/getter 方法的实现的,我们可通过 runtime 的关联方法进行动态添加。
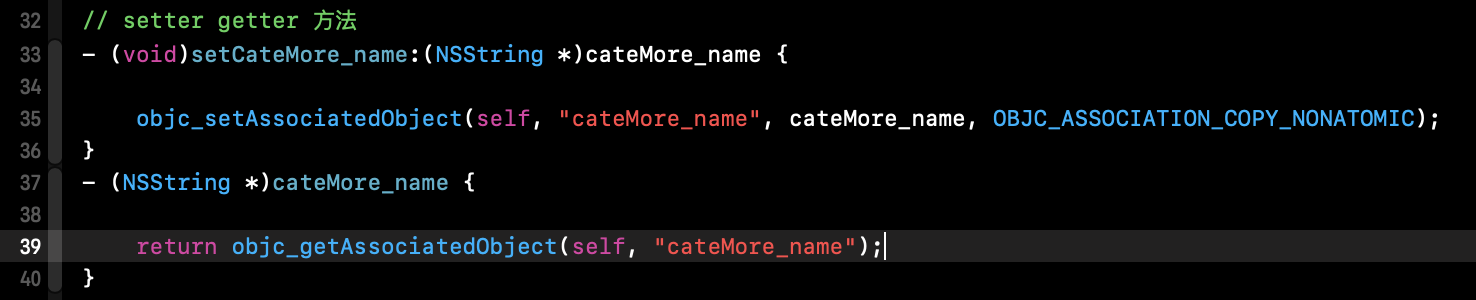
对 Myperson 的 cateMore_name 进行赋值,运行工程,断点在 setCateMore_name 处,进入源码:
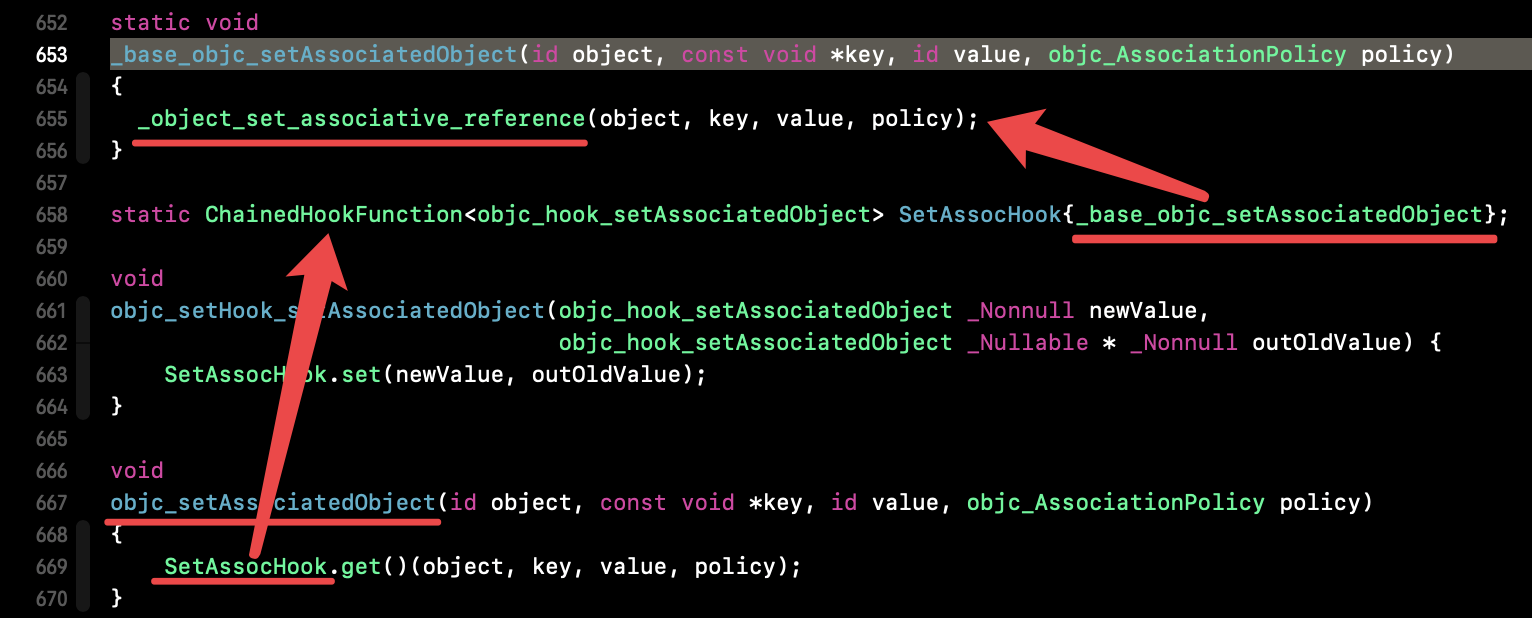
get() 点进去没有找到实现相关代码,进入 SetAssocHook: 发现是 _base_objc_setAssociatedObject 方法的调用,继续点进去,到了 _object_set_associative_reference。
1、源码分析
1)_object_set_associative_reference() 源码01:
1 void 2 _object_set_associative_reference(id object, const void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) 3 { 4 // This code used to work when nil was passed for object and key. Some code 5 // probably relies on that to not crash. Check and handle it explicitly. 6 // rdar://problem/44094390 7 if (!object && !value) return; 8 9 if (object->getIsa()->forbidsAssociatedObjects()) 10 _objc_fatal("objc_setAssociatedObject called on instance (%p) of class %s which does not allow associated objects", object, object_getClassName(object)); 11 // DisguisedPtr 相当于 包装了一下原来的对象 12 DisguisedPtr<objc_object> disguised{(objc_object *)object}; 13 // 包装一下 policy 和 value 14 ObjcAssociation association{policy, value};// 构造函数 15 16 // retain the new value (if any) outside the lock. 17 association.acquireValue();/** 18 inline void acquireValue() { // 根据关联方法设置的类型 policy 处理 retain 和 copy,其他场景不处理 19 if (_value) { 20 switch (_policy & 0xFF) { 21 case OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_RETAIN:// retain 22 _value = objc_retain(_value); 23 break; 24 case OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_COPY:// copy 25 _value = ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(_value, @selector(copy)); 26 break; 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 */ 31 32 { 33 AssociationsManager manager;/** 34 // class AssociationsManager manages a lock / hash table singleton pair. 35 // Allocating an instance acquires the lock 36 37 class AssociationsManager { 38 using Storage = ExplicitInitDenseMap<DisguisedPtr<objc_object>, ObjectAssociationMap>; 39 static Storage _mapStorage; // 静态变量 40 41 public: 42 AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.lock(); } // 初始化, 加 lock 锁避免了多线程对其重复操作,但并非表明它不可多次操作 43 ~AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.unlock(); } // 析构 44 45 AssociationsHashMap &get() { 46 return _mapStorage.get(); 47 } 48 49 static void init() { 50 _mapStorage.init(); 51 } 52 }; 53 */ 54 55 // AssociationsHashMap 关联对象的表 全部的关联对象都在此表中 此表示唯一的 56 // _mapStorage.get() --> static Storage _mapStorage;//静态变量 全场唯一 57 AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get()); 58 59 if (value) { 60 auto refs_result = associations.try_emplace(disguised, ObjectAssociationMap{}); 61 /** refs_result: 62 $0 = { 63 first = { 64 Ptr = 0x00000001012000c0 65 End = 0x0000000101200100 66 } 67 second = true 68 } 69 */ 70 if (refs_result.second) {// refs_result 的 second 是个 bool 值 71 /* it's the first association we make */ 72 object->setHasAssociatedObjects(); 73 } 74 75 /* establish or replace the association */ // 进行 建立或替换 association 76 auto &refs = refs_result.first->second; // 空的桶子 77 auto result = refs.try_emplace(key, std::move(association)); 78 if (!result.second) { 79 association.swap(result.first->second);// swap 移动 80 } 81 } else {// value 是空值 --> 进行移除操作 82 auto refs_it = associations.find(disguised);// 通过 disguised 找 83 if (refs_it != associations.end()) { 84 auto &refs = refs_it->second; 85 auto it = refs.find(key); 86 if (it != refs.end()) { 87 association.swap(it->second); 88 refs.erase(it);// 消掉移除 89 if (refs.size() == 0) { 90 associations.erase(refs_it);// 消掉移除 91 92 } 93 } 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 98 // release the old value (outside of the lock). 99 association.releaseHeldValue(); 100 }
1、先运行一下工程,执行代码通过 lldb 先查看信息具体是什么:
_object_set_associative_reference() --> try_emplace()

2、try_emplace() 代码-源码02
1 // Inserts key,value pair into the map if the key isn't already in the map. 2 // The value is constructed in-place if the key is not in the map, otherwise 3 // it is not moved. 4 template <typename... Ts> 5 std::pair<iterator, bool> try_emplace(const KeyT &Key, Ts &&... Args) { 6 BucketT *TheBucket; 7 if (LookupBucketFor(Key, TheBucket))// 关联的 key 在不在 bucket 中 8 return std::make_pair( 9 makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true), 10 false); // Already in map.已经在了 11 12 // Otherwise, insert the new element. 13 // key 是新的,把 key 插入 bucket 中 14 TheBucket = InsertIntoBucket(TheBucket, Key, std::forward<Ts>(Args)...); 15 return std::make_pair( 16 makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true), 17 true); 18 }
3、LookupBucketFor(),有2个方法,外部进入下面的那个参数是非 const 的函数,但最终是会走到上面的函数中,并进行 while(){}:
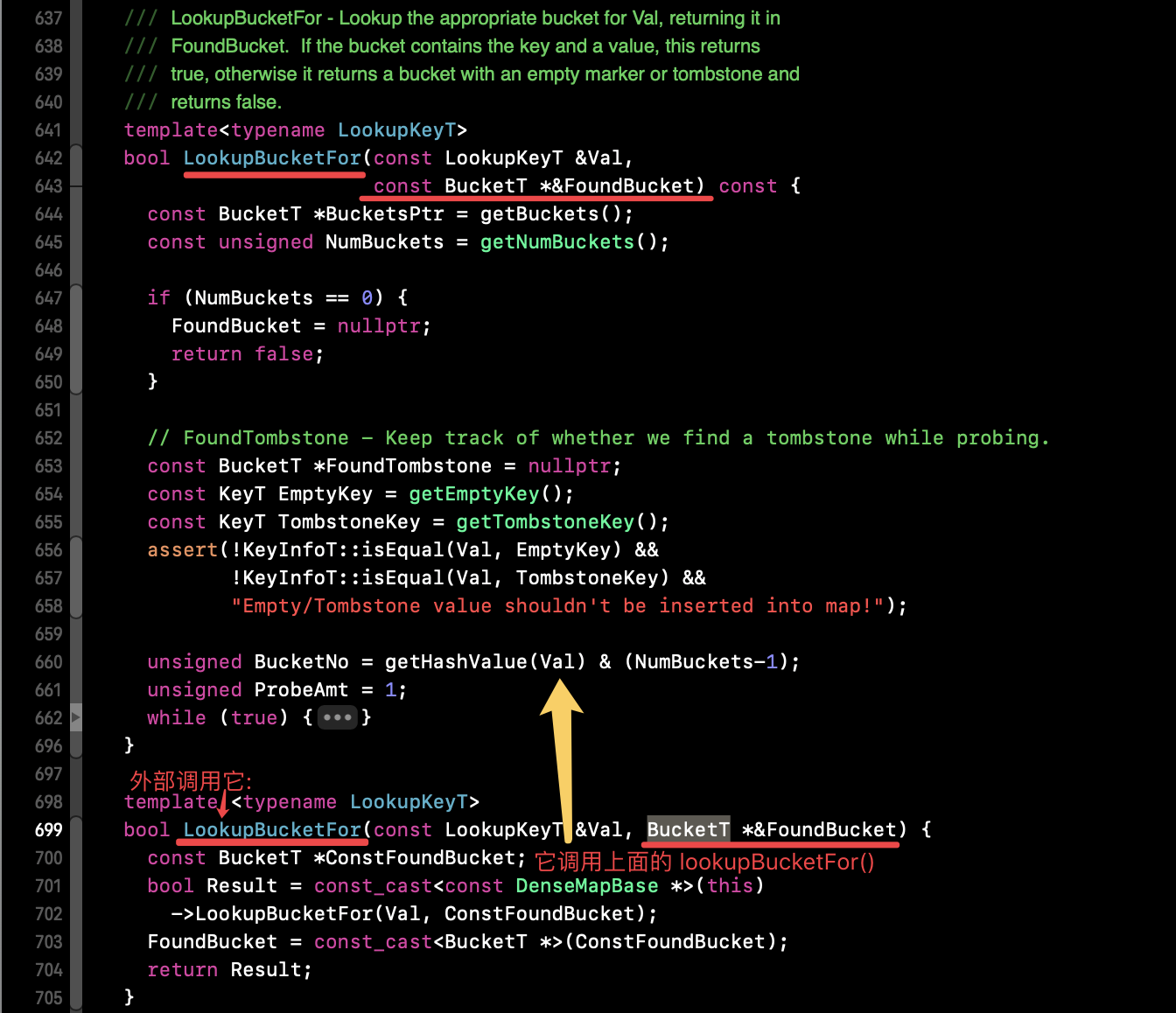
LookupBucketFor(const LookupKeyT &Val, const BucketT *&FoundBucket) 代码 - 源码03:
1 template<typename LookupKeyT> 2 bool LookupBucketFor(const LookupKeyT &Val, 3 const BucketT *&FoundBucket) const { 4 const BucketT *BucketsPtr = getBuckets(); 5 const unsigned NumBuckets = getNumBuckets(); 6 7 if (NumBuckets == 0) { 8 FoundBucket = nullptr; 9 return false; 10 } 11 12 // FoundTombstone - Keep track of whether we find a tombstone while probing. 13 const BucketT *FoundTombstone = nullptr; 14 const KeyT EmptyKey = getEmptyKey(); 15 const KeyT TombstoneKey = getTombstoneKey(); 16 assert(!KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, EmptyKey) && 17 !KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, TombstoneKey) && 18 "Empty/Tombstone value shouldn't be inserted into map!"); 19 20 unsigned BucketNo = getHashValue(Val) & (NumBuckets-1);// 哈希函数 算下标 21 unsigned ProbeAmt = 1; 22 // 开始 while 23 while (true) { 24 const BucketT *ThisBucket = BucketsPtr + BucketNo;// 指针位置移动 25 // Found Val's bucket? If so, return it. 26 // 找到了 value 的 bucket 则返回 bucket 赋给外部的值->FoundBucket,然后return寻找的结果为true 27 if (LLVM_LIKELY(KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, ThisBucket->getFirst()))) { 28 FoundBucket = ThisBucket; 29 return true; 30 } 31 32 // If we found an empty bucket, the key doesn't exist in the set. 33 // Insert it and return the default value. 34 // 找到了一个空的 bucket --> 插入一个空的 bucket 并赋给 FoundBucket,然后return查找结果为false 35 if (LLVM_LIKELY(KeyInfoT::isEqual(ThisBucket->getFirst(), EmptyKey))) { 36 // If we've already seen a tombstone while probing, fill it in instead 37 // of the empty bucket we eventually probed to. 38 FoundBucket = FoundTombstone ? FoundTombstone : ThisBucket; 39 return false; 40 } 41 42 // 处理 然后进行继续 while 循环操作 43 // If this is a tombstone, remember it. If Val ends up not in the map, we 44 // prefer to return it than something that would require more probing. 45 // Ditto for zero values. 46 if (KeyInfoT::isEqual(ThisBucket->getFirst(), TombstoneKey) && 47 !FoundTombstone) 48 FoundTombstone = ThisBucket; // Remember the first tombstone found. 49 if (ValueInfoT::isPurgeable(ThisBucket->getSecond()) && !FoundTombstone) 50 FoundTombstone = ThisBucket; 51 52 // Otherwise, it's a hash collision or a tombstone, continue quadratic 53 // probing. 54 if (ProbeAmt > NumBuckets) { 55 FatalCorruptHashTables(BucketsPtr, NumBuckets); 56 } 57 BucketNo += ProbeAmt++; 58 BucketNo &= (NumBuckets-1); 59 } 60 }
4、InsertIntoBucket() 代码:
1 template <typename KeyArg, typename... ValueArgs> 2 BucketT *InsertIntoBucket(BucketT *TheBucket, KeyArg &&Key, 3 ValueArgs &&... Values) { 4 TheBucket = InsertIntoBucketImpl(Key, Key, TheBucket); 5 6 TheBucket->getFirst() = std::forward<KeyArg>(Key); 7 ::new (&TheBucket->getSecond()) ValueT(std::forward<ValueArgs>(Values)...); 8 return TheBucket; 9 }
InsertIntoBucketImpl() 代码:
1 template <typename LookupKeyT> 2 BucketT *InsertIntoBucketImpl(const KeyT &Key, const LookupKeyT &Lookup, 3 BucketT *TheBucket) { 4 // If the load of the hash table is more than 3/4, or if fewer than 1/8 of 5 // the buckets are empty (meaning that many are filled with tombstones), 6 // grow the table. 7 // 8 // The later case is tricky. For example, if we had one empty bucket with 9 // tons of tombstones, failing lookups (e.g. for insertion) would have to 10 // probe almost the entire table until it found the empty bucket. If the 11 // table completely filled with tombstones, no lookup would ever succeed, 12 // causing infinite loops in lookup. 13 unsigned NewNumEntries = getNumEntries() + 1; 14 unsigned NumBuckets = getNumBuckets(); 15 if (LLVM_UNLIKELY(NewNumEntries * 4 >= NumBuckets * 3)) { 16 this->grow(NumBuckets * 2); 17 LookupBucketFor(Lookup, TheBucket); 18 NumBuckets = getNumBuckets(); 19 } else if (LLVM_UNLIKELY(NumBuckets-(NewNumEntries+getNumTombstones()) <= 20 NumBuckets/8)) { 21 this->grow(NumBuckets); 22 LookupBucketFor(Lookup, TheBucket); 23 } 24 ASSERT(TheBucket); 25 26 // Only update the state after we've grown our bucket space appropriately 27 // so that when growing buckets we have self-consistent entry count. 28 // If we are writing over a tombstone or zero value, remember this. 29 if (KeyInfoT::isEqual(TheBucket->getFirst(), getEmptyKey())) { 30 // Replacing an empty bucket. 31 incrementNumEntries(); 32 } else if (KeyInfoT::isEqual(TheBucket->getFirst(), getTombstoneKey())) { 33 // Replacing a tombstone. 34 incrementNumEntries(); 35 decrementNumTombstones(); 36 } else { 37 // we should be purging a zero. No accounting changes. 38 ASSERT(ValueInfoT::isPurgeable(TheBucket->getSecond())); 39 TheBucket->getSecond().~ValueT(); 40 } 41 42 return TheBucket; 43 }
5、setHasAssociatedObjects() 源码见下面代码:
执行到‘源码01’ 处,second 值的判断(try_emplace() 的返回值),是第一次插入则为 true
--> setHasAssociatedObjects(), nopointer isa --> isa.has_assoc 关联标志位设为了 true。 isa结构见《OC 底层探索 03 中isa 结构》。
1 inline void 2 objc_object::setHasAssociatedObjects() 3 { 4 if (isTaggedPointer()) return; 5 6 retry: 7 isa_t oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits); 8 isa_t newisa = oldisa; 9 if (!newisa.nonpointer || newisa.has_assoc) { 10 ClearExclusive(&isa.bits); 11 return; 12 } 13 newisa.has_assoc = true;// isa 的关联标志位 14 if (!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits)) goto retry; 15 }
2、执行流程
1)断点调试执行流程
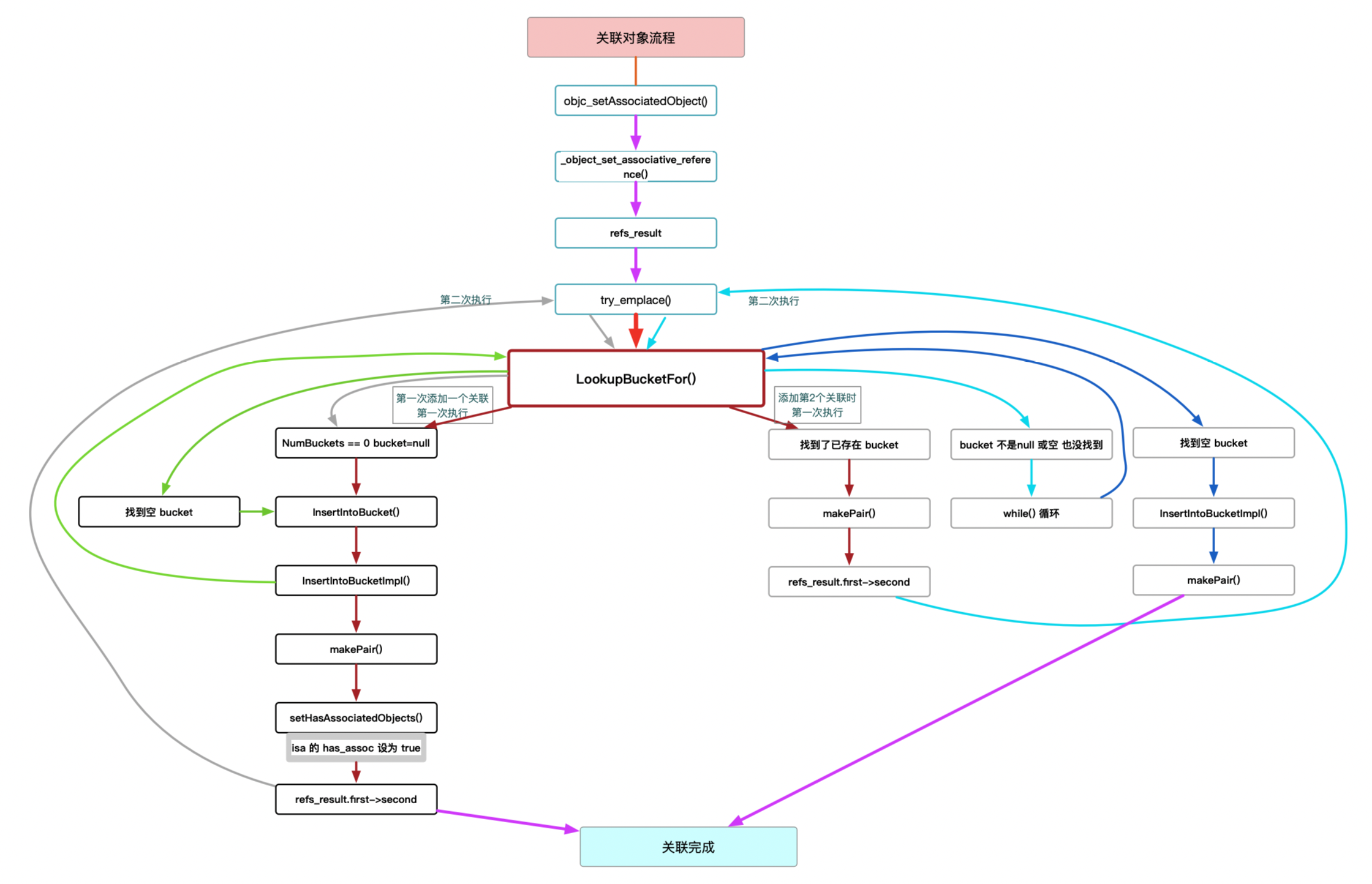
1、处理第一此关联:
走进 try_emplace() 第一次执行 de 流程:
_object_set_associative_reference() - 开始set关联
--> try_emplace() - refs_result
--> LookupBucketFor() - 找bucket : return false --> InsertIntoBucket() - 插入一个空的 bucket :
--> InsertIntoBucketImpl() --> LookupBucketFor() - 得到一个空的bucket
--> setHasAssociatedObjects() - isa.hsa_assoc设为true
--> 再次 执行到 try_emplace() - refs_result.first->second
继续执行工程,第二次走进入 try_emplace() ,bucket 不为空:
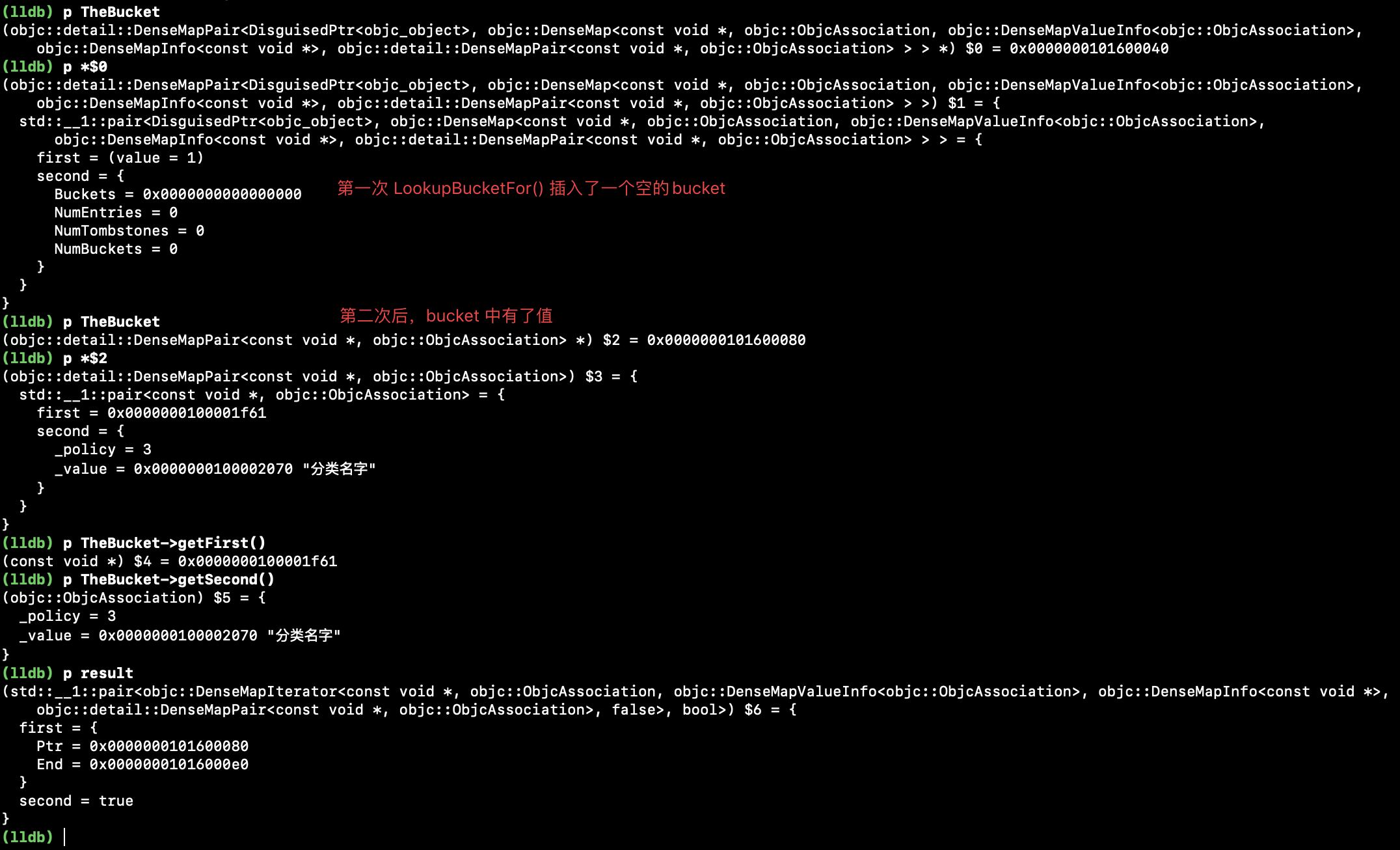
2、添加第2个关联时执行:
对象关联流程图:
2)关联类的 map 的结构分析
1、lldb 数据分析:
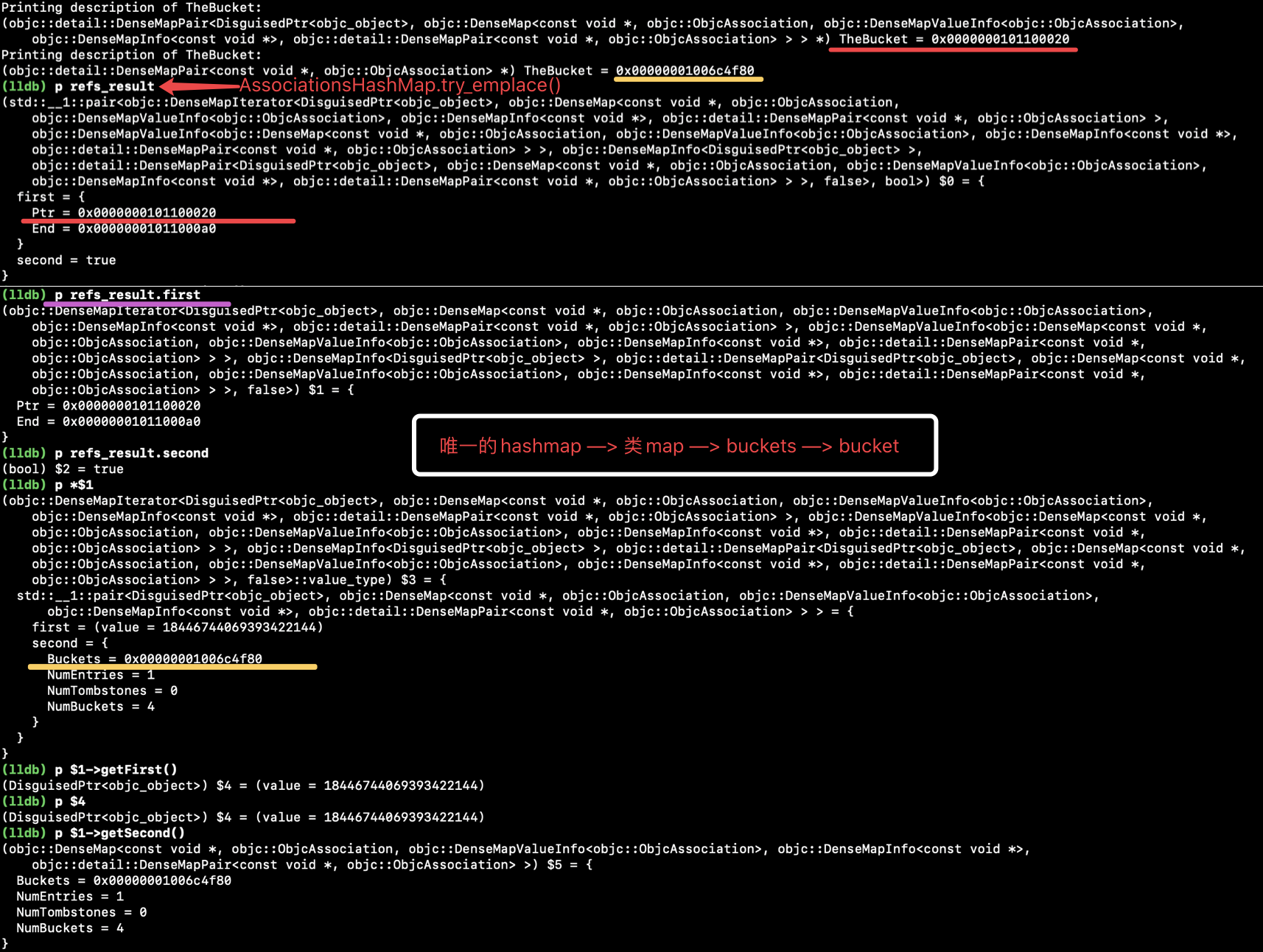
2、类型de 结构分析:
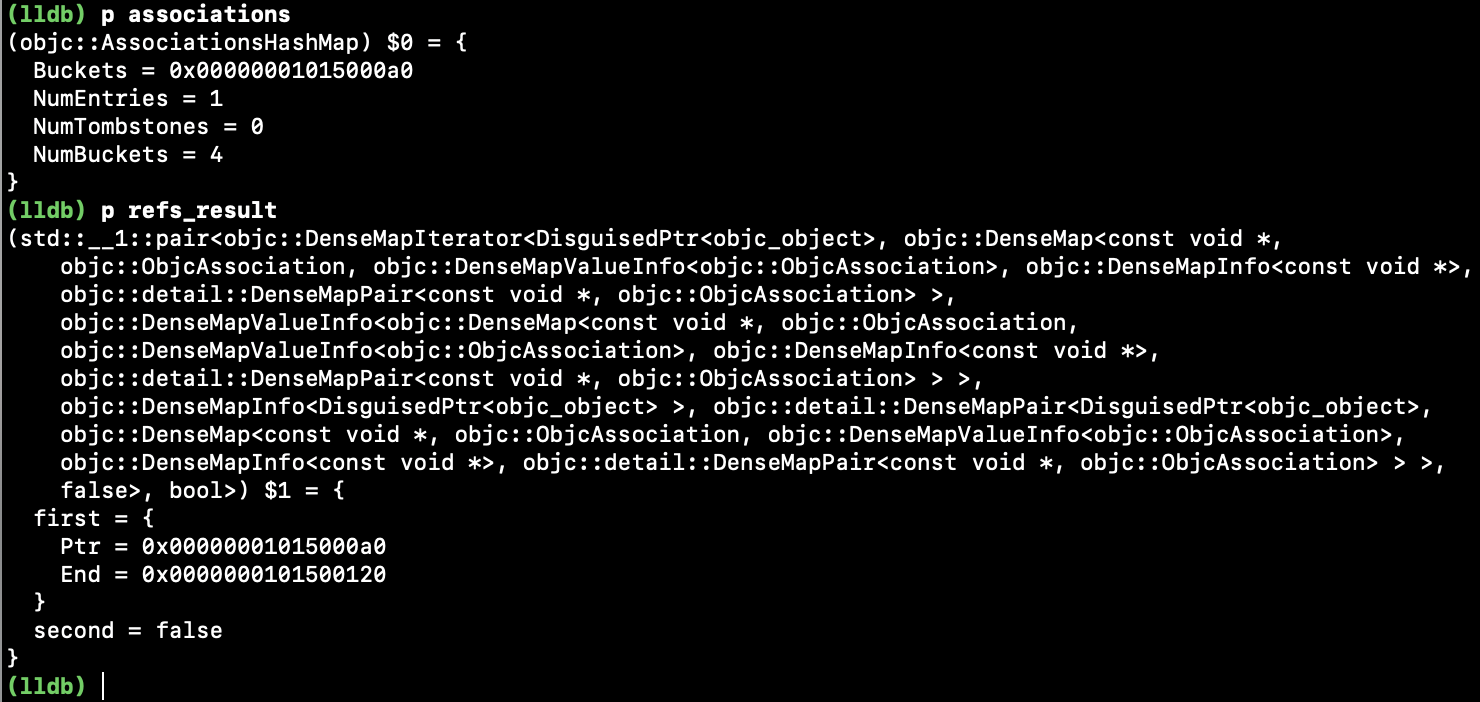
首次 try_emplace() 数据:
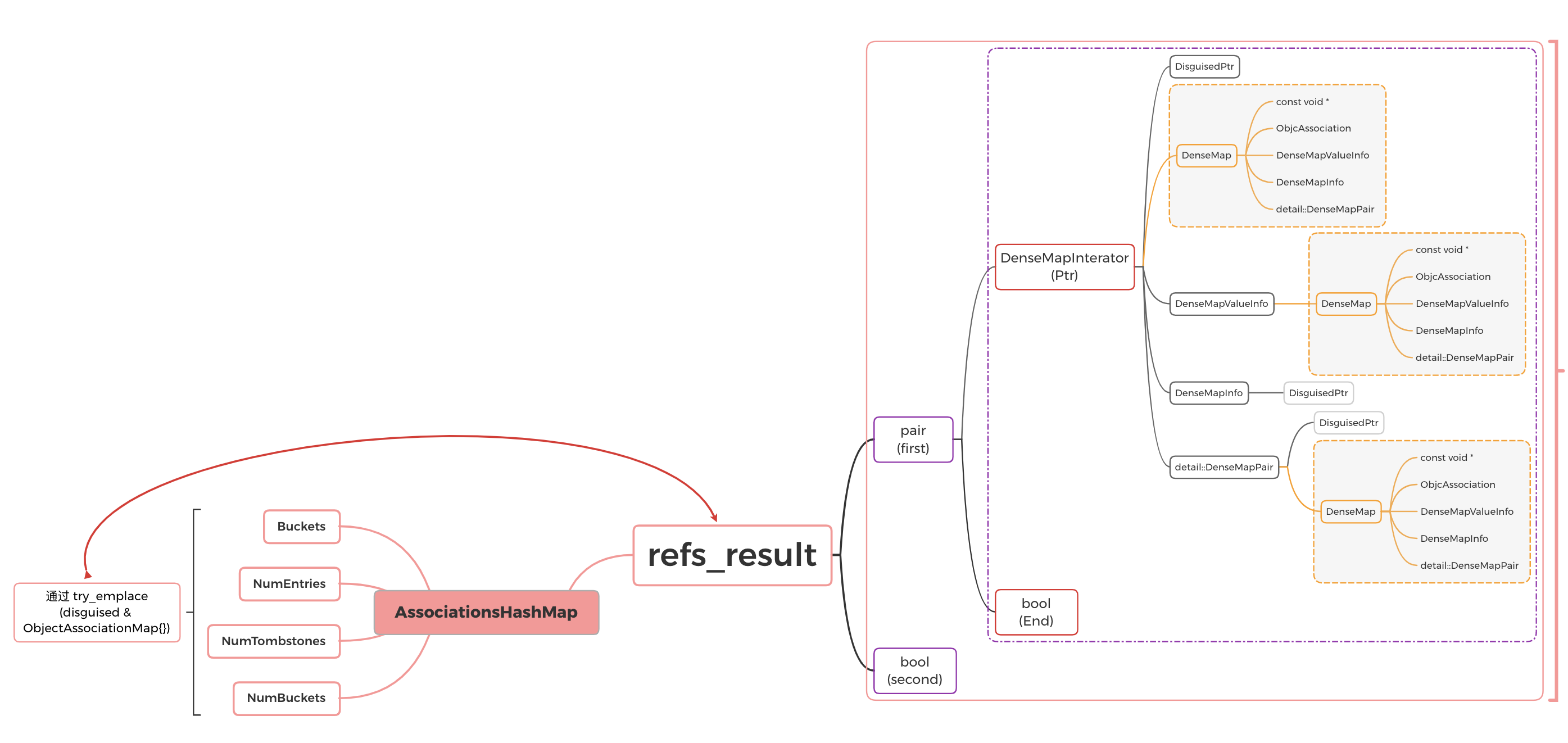
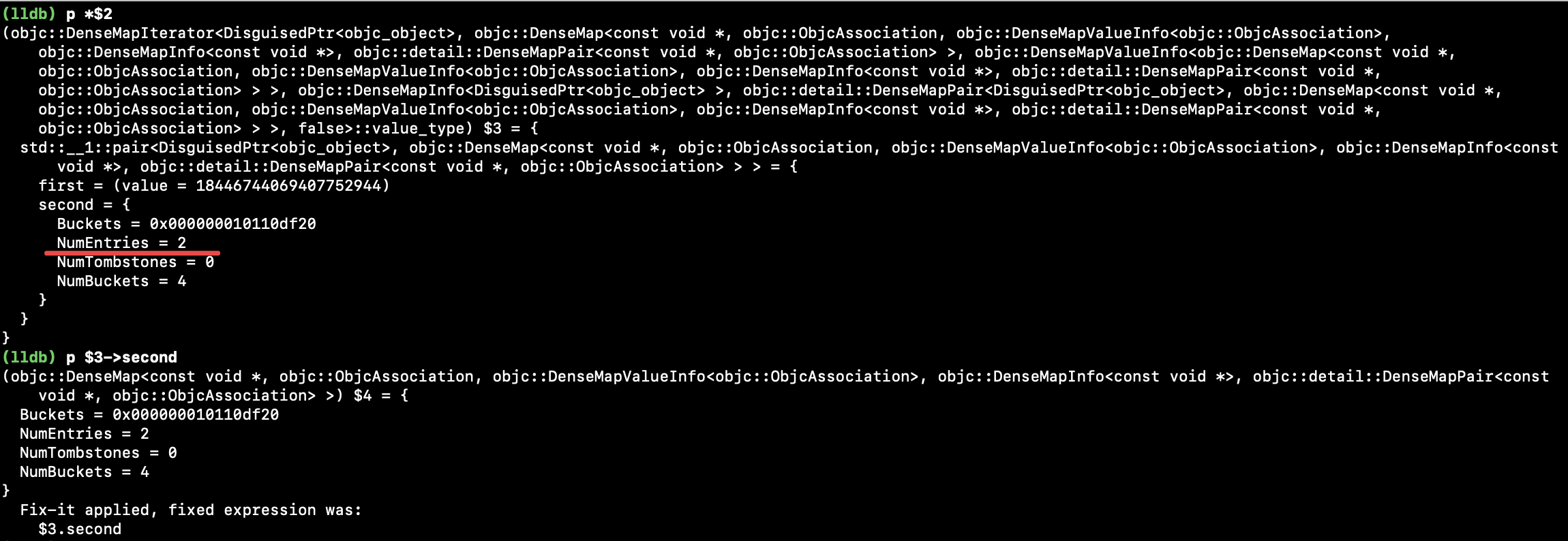
第 2 次 try_emplace() 数据:
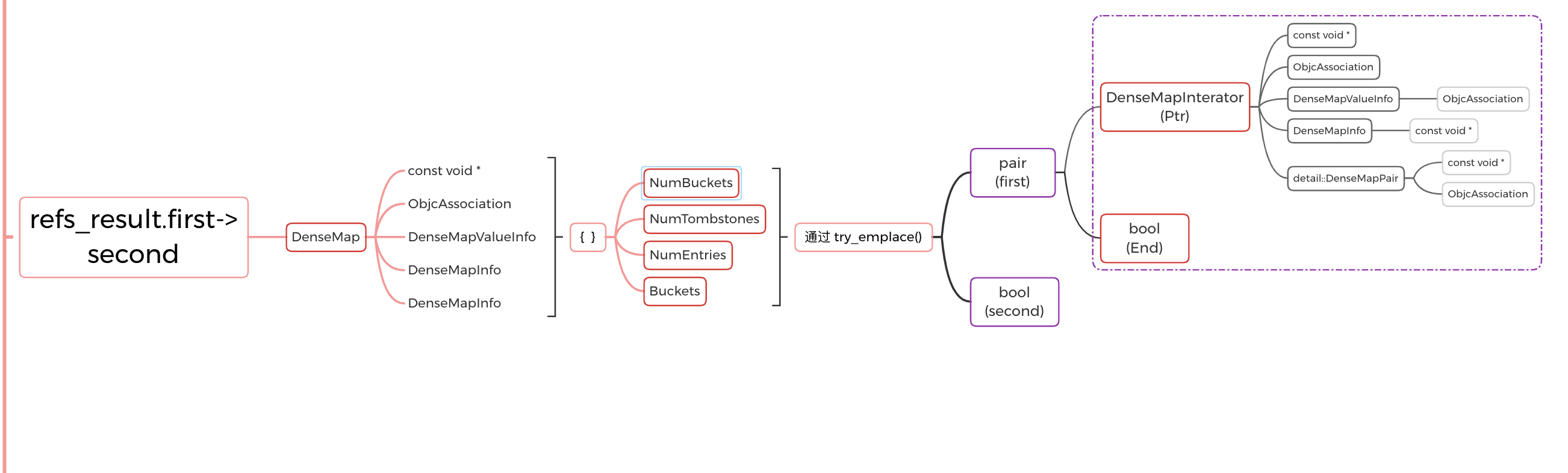
总结(套娃,buckets 中装了 buckets 又装了 bucket):

tips:关联对象移除吗?需要!--> dealloc 流程 如下:
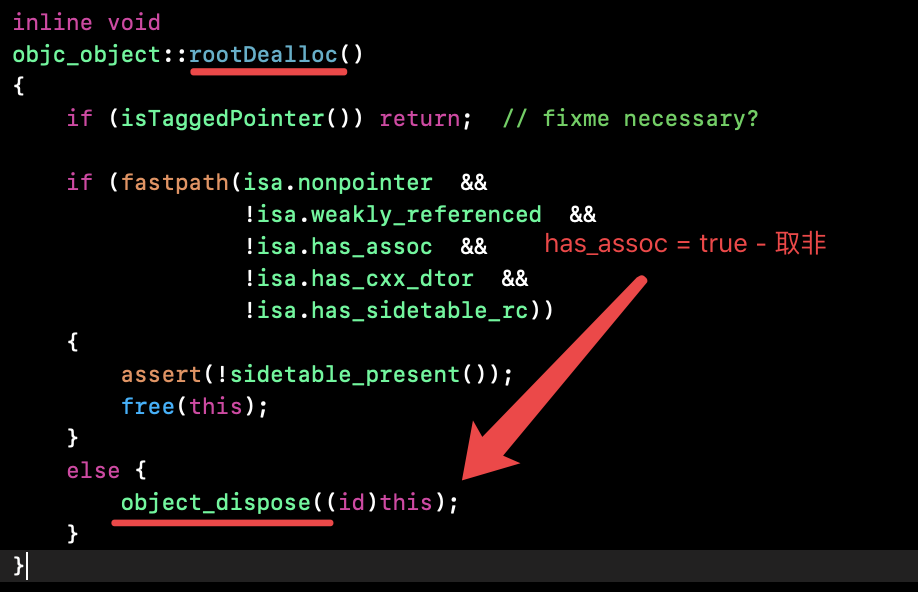


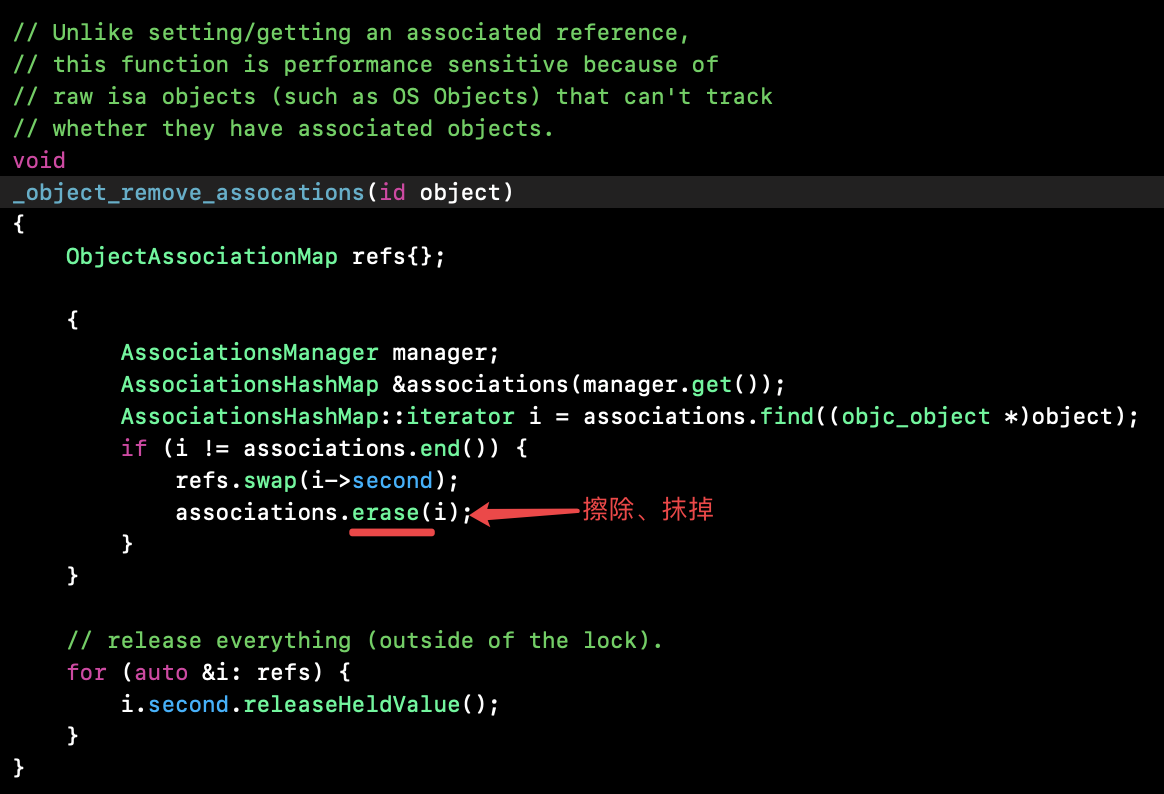
源码:
1 // rootDealloc 2 inline void 3 objc_object::rootDealloc() 4 { 5 if (isTaggedPointer()) return; // fixme necessary? 6 7 if (fastpath(isa.nonpointer && 8 !isa.weakly_referenced && 9 !isa.has_assoc && 10 !isa.has_cxx_dtor && 11 !isa.has_sidetable_rc)) 12 { 13 assert(!sidetable_present()); 14 free(this); 15 } 16 else {// isa.has_assoc = true - 有关联对象 17 object_dispose((id)this); 18 } 19 } 20 21 /*********************************************************************** 22 * object_dispose 23 * fixme 24 * Locking: none 25 **********************************************************************/ 26 id 27 object_dispose(id obj) 28 { 29 if (!obj) return nil; 30 31 objc_destructInstance(obj); 32 free(obj); 33 34 return nil; 35 } 36 37 /*********************************************************************** 38 * objc_destructInstance 39 * Destroys an instance without freeing memory. 40 * Calls C++ destructors. 41 * Calls ARC ivar cleanup. 42 * Removes associative references. 43 * Returns `obj`. Does nothing if `obj` is nil. 44 **********************************************************************/ 45 void *objc_destructInstance(id obj) 46 { 47 if (obj) { 48 // Read all of the flags at once for performance. 49 bool cxx = obj->hasCxxDtor(); 50 bool assoc = obj->hasAssociatedObjects(); 51 52 // This order is important. 53 if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj); 54 if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj); 55 obj->clearDeallocating(); 56 } 57 58 return obj; 59 } 60 61 // Unlike setting/getting an associated reference, 62 // this function is performance sensitive because of 63 // raw isa objects (such as OS Objects) that can't track 64 // whether they have associated objects. 65 void 66 _object_remove_assocations(id object) 67 { 68 ObjectAssociationMap refs{}; 69 70 { 71 AssociationsManager manager; 72 AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get()); 73 AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find((objc_object *)object); 74 if (i != associations.end()) { 75 refs.swap(i->second); 76 associations.erase(i);// 擦除抹掉 77 } 78 } 79 80 // release everything (outside of the lock).释放所有 81 for (auto &i: refs) { 82 i.second.releaseHeldValue(); 83 /** 84 inline void releaseHeldValue() { 85 if (_value && (_policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_RETAIN)) { 86 objc_release(_value); 87 } 88 } 89 */ 90 } 91 } 92 93 // clearDeallocating 94 inline void 95 objc_object::clearDeallocating() 96 { 97 if (slowpath(!isa.nonpointer)) { 98 // Slow path for raw pointer isa. 99 sidetable_clearDeallocating(); 100 } 101 else if (slowpath(isa.weakly_referenced || isa.has_sidetable_rc)) { 102 // Slow path for non-pointer isa with weak refs and/or side table data. 103 clearDeallocating_slow(); 104 } 105 106 assert(!sidetable_present()); 107 }
以上。




