172322 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》实验二报告
172322 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》实验二报告
- 课程:《程序设计与数据结构》
- 班级: 1723
- 姓名: 张昊然
- 学号:20172322
- 实验教师:王志强
- 助教:张之睿/张师瑜
- 实验日期:2018年11月10日
- 必修/选修: 必修
1.实验内容
- 此处填写实验的具体内容:
实验内容过多,故参考作业:
-
- 参考教材p212,完成链树LinkedBinaryTree的实现(getRight,contains,toString,preorder,postorder), 用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的LinkedBinaryTree进行测试,提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息。
-
- 基于LinkedBinaryTree,实现基于(中序,先序)序列构造唯一一棵二㕚树的功能,比如给出中序HDIBEMJNAFCKGL和后序ABDHIEJMNCFGKL,构造出附图中的树,用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的功能进行测试,提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
-
- 自己设计并实现一颗决策树
-
- 输入中缀表达式,使用树将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并输出后缀表达式和计算结果(如果没有用树,则为0分)
-
- 完成PP11.3
-
- 参考http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/7483915.html对Java中的红黑树(TreeMap,HashMap)进行源码分析,并在实验报告中体现分析结果。
2.实验过程及结果
过程:
- 本次实验总共五个提交点。我也分为五个部分来写过程。
- 第一:要求实现
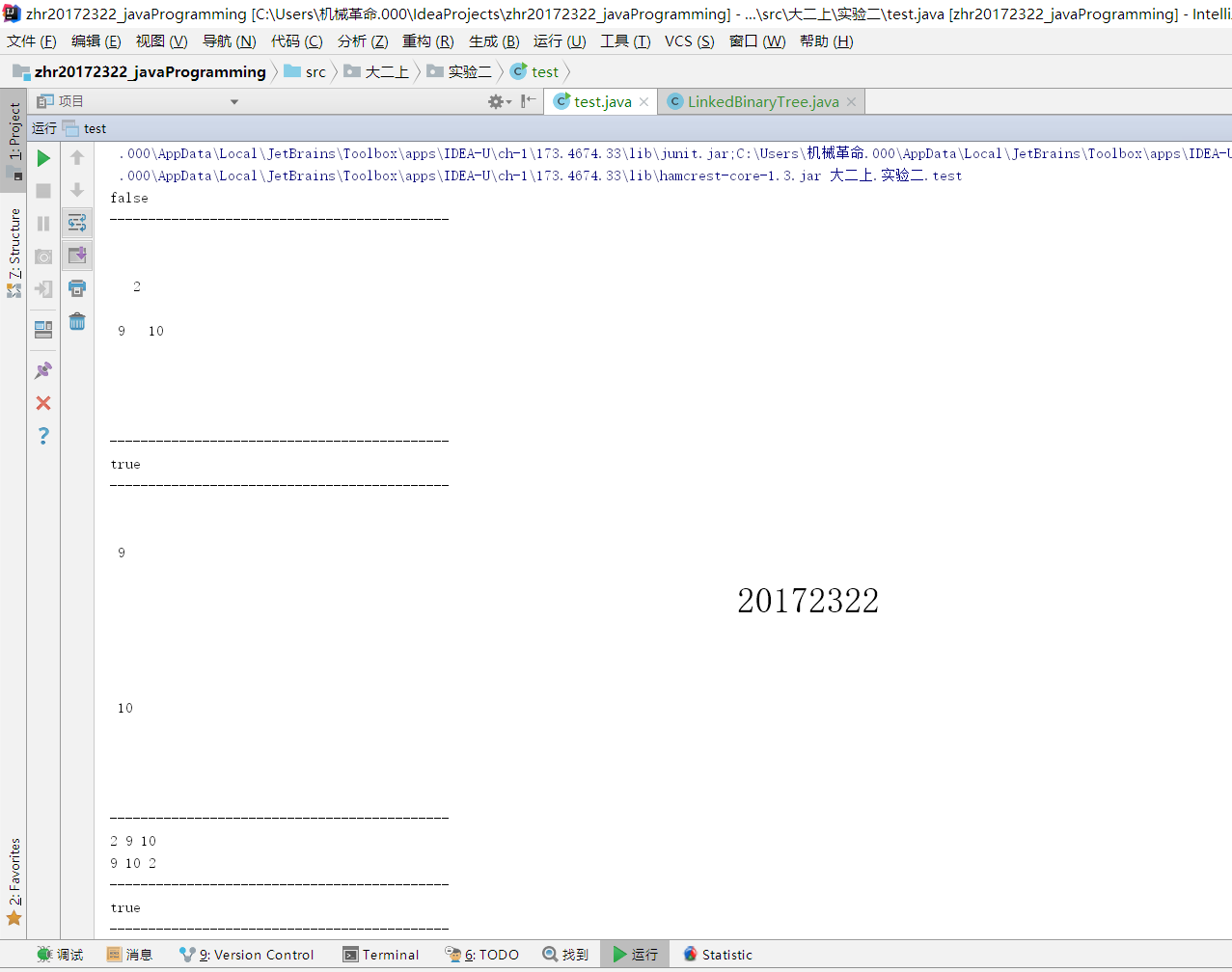
getRight,contains,toString,preorder,postorder,这些分别是得到右孩子,是否包含,输出,前序遍历,后续遍历,关键代码如下:
public LinkedBinaryTree1<T> getRight()
{
if(root == null) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("BinaryTree");
}
LinkedBinaryTree1<T> result = new LinkedBinaryTree1<>();
result.root = root.getRight();
return result;
public boolean contains(T targetElement)
{
BinaryTreeNode node = root;
BinaryTreeNode temp = root;
boolean result = false;
if (node == null){
result = false;
}
if (node.getElement().equals(targetElement)){
result = true;
}
while (node.right != null){
if (node.right.getElement().equals(targetElement)){
result = true;
break;
}
else {
node = node.right;
}
}
while (temp.left.getElement().equals(targetElement)){
if (temp.left.getElement().equals(targetElement)){
result = true;
break;
}
else {
temp = temp.left;
}
}
return result;
}
public String toString()
{
UnorderedListADT<BinaryTreeNode<String>> nodes =
new ArrayUnorderedList<BinaryTreeNode<String>>();
UnorderedListADT<Integer> levelList =
new ArrayUnorderedList<Integer>();
BinaryTreeNode<String> current;
String result = "";
int printDepth = this.getHeight();
int possibleNodes = (int)Math.pow(2, printDepth + 1);
int countNodes = 0;
nodes.addToRear((BinaryTreeNode<String>) root);
Integer currentLevel = 0;
Integer previousLevel = -1;
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel);
while (countNodes < possibleNodes)
{
countNodes = countNodes + 1;
current = nodes.removeFirst();
currentLevel = levelList.removeFirst();
if (currentLevel > previousLevel)
{
result = result + "\n\n";
previousLevel = currentLevel;
for (int j = 0; j < ((Math.pow(2, (printDepth - currentLevel))) - 1); j++) {
result = result + " ";
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < ((Math.pow(2, (printDepth - currentLevel + 1)) - 1)) ; i++)
{
result = result + " ";
}
}
if (current != null)
{
result = result + (current.getElement()).toString();
nodes.addToRear(current.getLeft());
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel + 1);
nodes.addToRear(current.getRight());
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel + 1);
}
else {
nodes.addToRear(null);
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel + 1);
nodes.addToRear(null);
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel + 1);
result = result + " ";
}
}
return result;
}
protected void preOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> node,
ArrayUnorderedList<T> tempList)
{
if (node != null){
tempList.addToRear(node.getElement());
preOrder(node.getLeft(),tempList);
preOrder(node.getRight(),tempList);
}
}
protected void postOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> node,
ArrayUnorderedList<T> tempList)
{
if (node != null){
postOrder(node.getLeft(),tempList);
postOrder(node.getRight(),tempList);
tempList.addToRear(node.getElement());
}
}
}
- 第二:利用中序和先序构建唯一的树,关键代码如下:
public BinaryTreeNode initTree(String[] preOrder, int start1, int end1, String[] inOrder, int start2, int end2) {
if (start1 > end1 || start2 > end2) {
return null;
}
String rootData = preOrder[start1];
BinaryTreeNode head = new BinaryTreeNode(rootData);
//找到根节点所在位置
int rootIndex = findIndexInArray(inOrder, rootData, start2, end2);
//构建左子树
BinaryTreeNode left = initTree(preOrder, start1 + 1, start1 + rootIndex - start2, inOrder, start2, rootIndex - 1);
//构建右子树
BinaryTreeNode right = initTree(preOrder, start1 + rootIndex - start2 + 1, end1, inOrder, rootIndex + 1, end2);
head.left = left;
head.right = right;
return head;
}
}
-
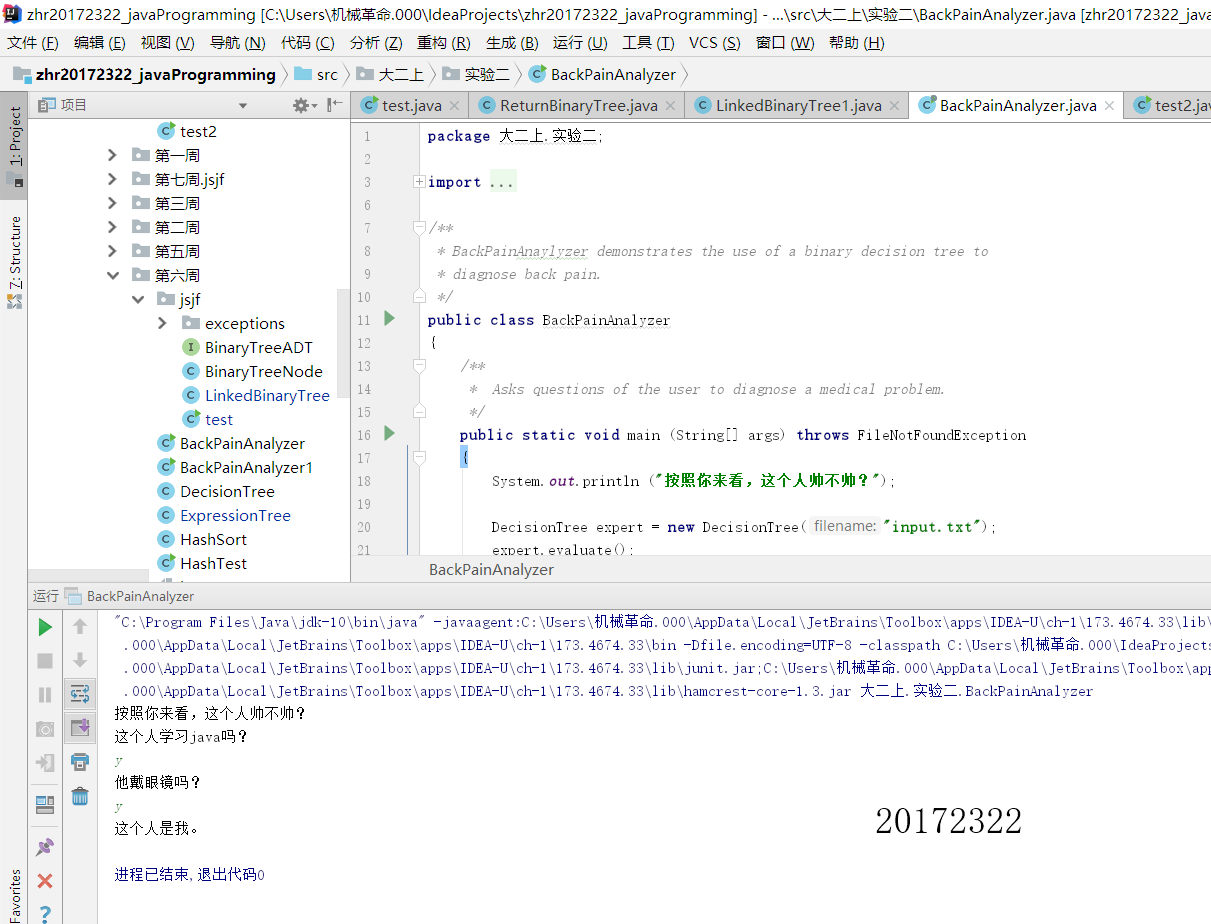
第三:对于书上的背部疼痛诊断器简单修改,无需放上。
-
第四:本次实验唯一的难点,关键代码:
public static String toSuffix(String infix) {
String result = "";
String[] array = infix.split("\\s+");
Stack<LinkedBinaryTree> num = new Stack();
Stack<LinkedBinaryTree> op = new Stack();
for (int a = 0; a < array.length; a++) {
if (array[a].equals("+") || array[a].equals("-") || array[a].equals("*") || array[a].equals("/")) {
if (op.empty()) {
op.push(new LinkedBinaryTree<>(array[a]));
} else {
if ((op.peek().root.element).equals("+") || (op.peek().root.element).equals("-") && array[a].equals("*") || array[a].equals("/")) {
op.push(new LinkedBinaryTree(array[a]));
} else {
LinkedBinaryTree right = num.pop();
LinkedBinaryTree left = num.pop();
LinkedBinaryTree temp = new LinkedBinaryTree(op.pop().root.element, left, right);
num.push(temp);
op.push(new LinkedBinaryTree(array[a]));
}
}
} else {
num.push(new LinkedBinaryTree<>(array[a]));
}
}
while (!op.empty()) {
LinkedBinaryTree right = num.pop();
LinkedBinaryTree left = num.pop();
LinkedBinaryTree temp = new LinkedBinaryTree(op.pop().root.element, left, right);
num.push(temp);
}
Iterator itr=num.pop().iteratorPostOrder();
while (itr.hasNext()){
result+=itr.next()+" ";
}
return result;
}
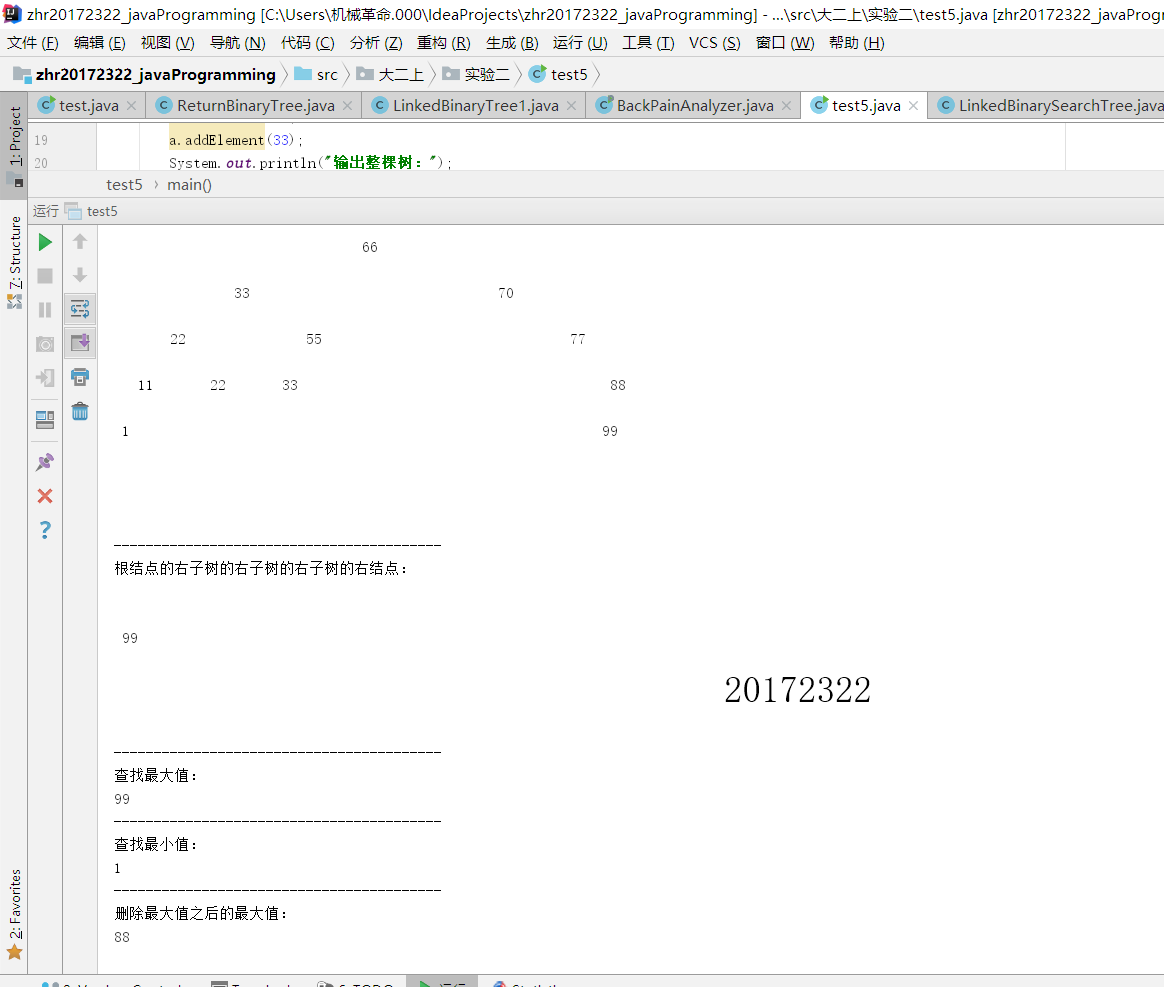
- 第五:运行PP11.3之前的作业。
- 第六:对Java中的红黑树(TreeMap,HashMap)进行源码分析。
红黑树(TreeMap,HashMap)源码分析。
- 首先是对储存结构进行分析,利用备注的形式在代码中标出。
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key; // 键
V value; // 值
Entry<K,V> left = null; // 左孩子
Entry<K,V> right = null; // 右孩子
Entry<K,V> parent; // 双亲节点
boolean color = BLACK; // 当前节点颜色
// 构造函数
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
- 之后是对
TreeMap的构造方法进行分析,TreeMap一共四个构造方法。
1.无参数构造方法
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
2.带有比较器的构造方法
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
3.带Map的构造方法
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
4.带有SortedMap的构造方法
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
- 对于第三个带Map的构造方法,该方法不指定比较器,调用putAll方法将Map中的所有元素加入到TreeMap中。putAll的源码如下:
// 将map中的全部节点添加到TreeMap中
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {
// 获取map的大小
int mapSize = map.size();
// 如果TreeMap的大小是0,且map的大小不是0,且map是已排序的“key-value对”
if (size==0 && mapSize!=0 && map instanceof SortedMap) {
Comparator c = ((SortedMap)map).comparator();
// 如果TreeMap和map的比较器相等;
// 则将map的元素全部拷贝到TreeMap中,然后返回!
if (c == comparator || (c != null && c.equals(comparator))) {
++modCount;
try {
buildFromSorted(mapSize, map.entrySet().iterator(),
null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
return;
}
}
// 调用AbstractMap中的putAll();
// AbstractMap中的putAll()又会调用到TreeMap的put()
super.putAll(map);
}
显然,如果Map里的元素是排好序的,就调用buildFromSorted方法来拷贝Map中的元素,这在下一个构造方法中会重点提及,而如果Map中的元素不是排好序的,就调用AbstractMap的putAll(map)方法,该方法源码如下:
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
put方法,同样的,利用备注的形式在代码中标出。
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
// 若红黑树为空,则插入根节点
if (t == null) {
// throw NullPointerException
// compare(key, key); // type check
root = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
// 找出(key, value)在二叉排序树中的插入位置。
// 红黑树是以key来进行排序的,所以这里以key来进行查找。
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
// 为(key-value)新建节点
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
// 插入新的节点后,调用fixAfterInsertion调整红黑树。
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
- 删除操作及对应
TreeMap的deleteEntry方法,deleteEntry方法同样也只需按照二叉排序树的操作步骤实现即可,删除指定节点后,再对树进行调整即可。deleteEntry方法的实现源码如下:
// 删除“红黑树的节点p”
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor (p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
}
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) {
root = null;
} else {
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
对于红黑树的源码分析到此就告一段落,因为最近时间有限,如果后期有空闲时间会继续对其源码进行分析。
结果:
1.
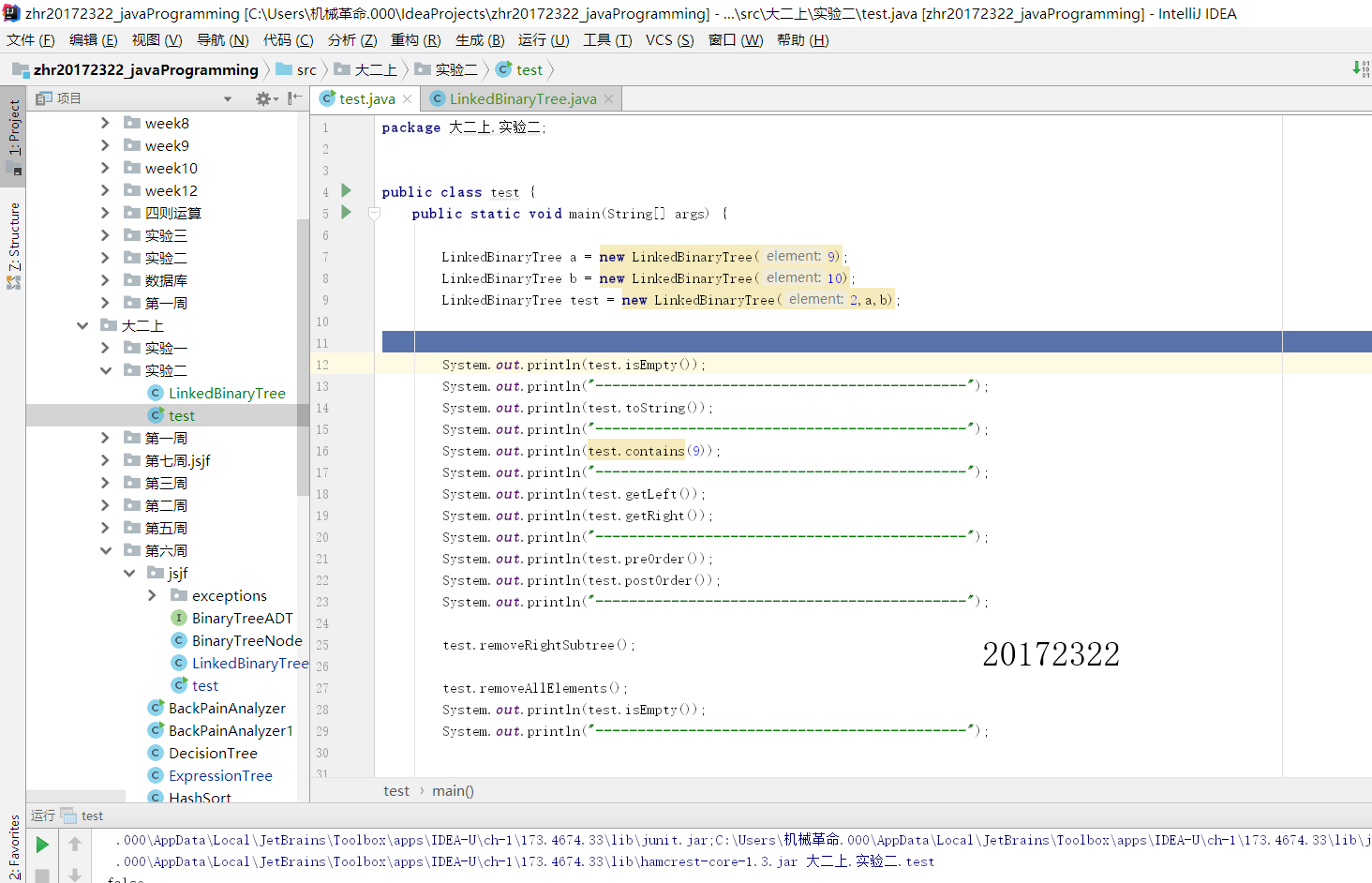
2.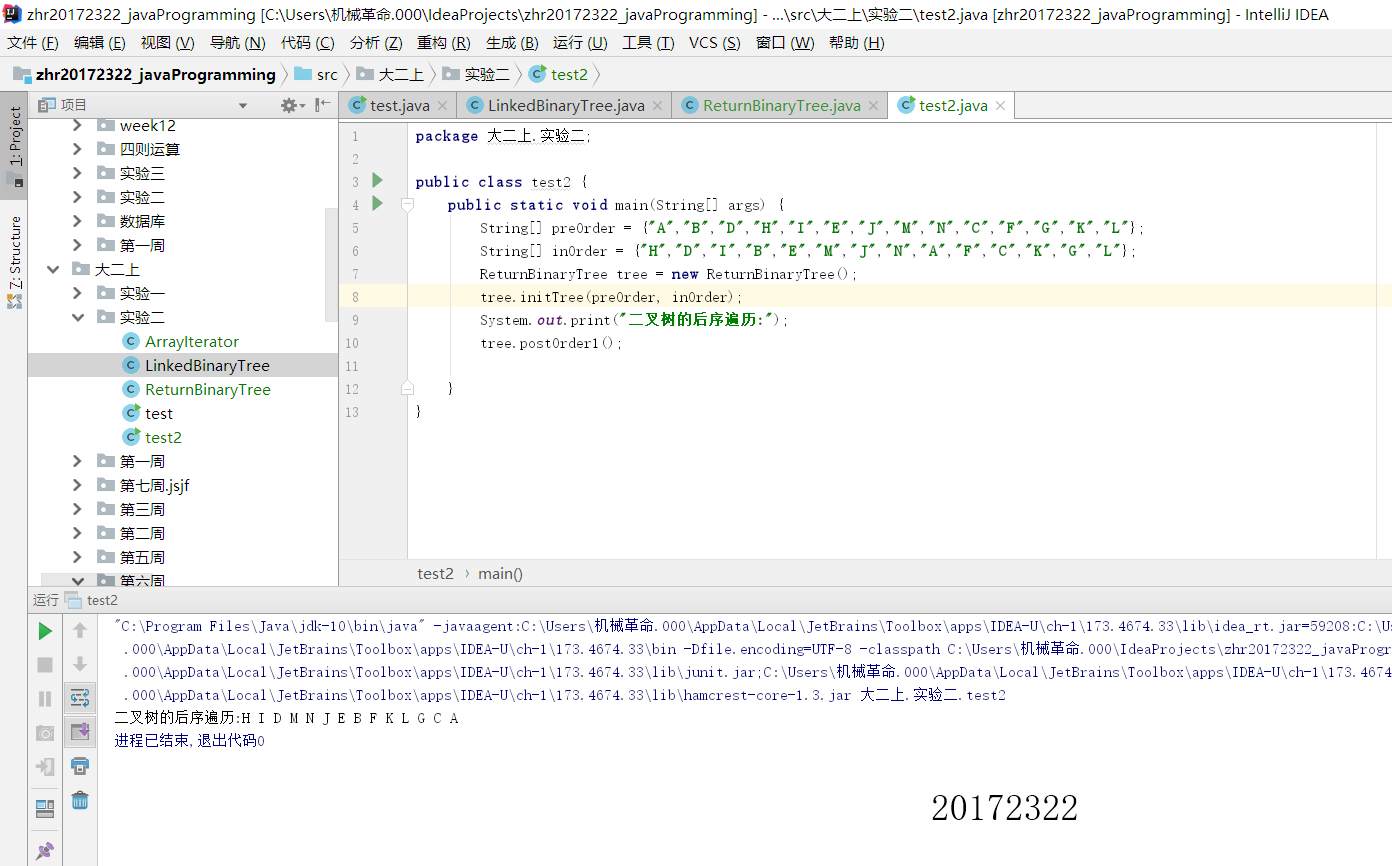
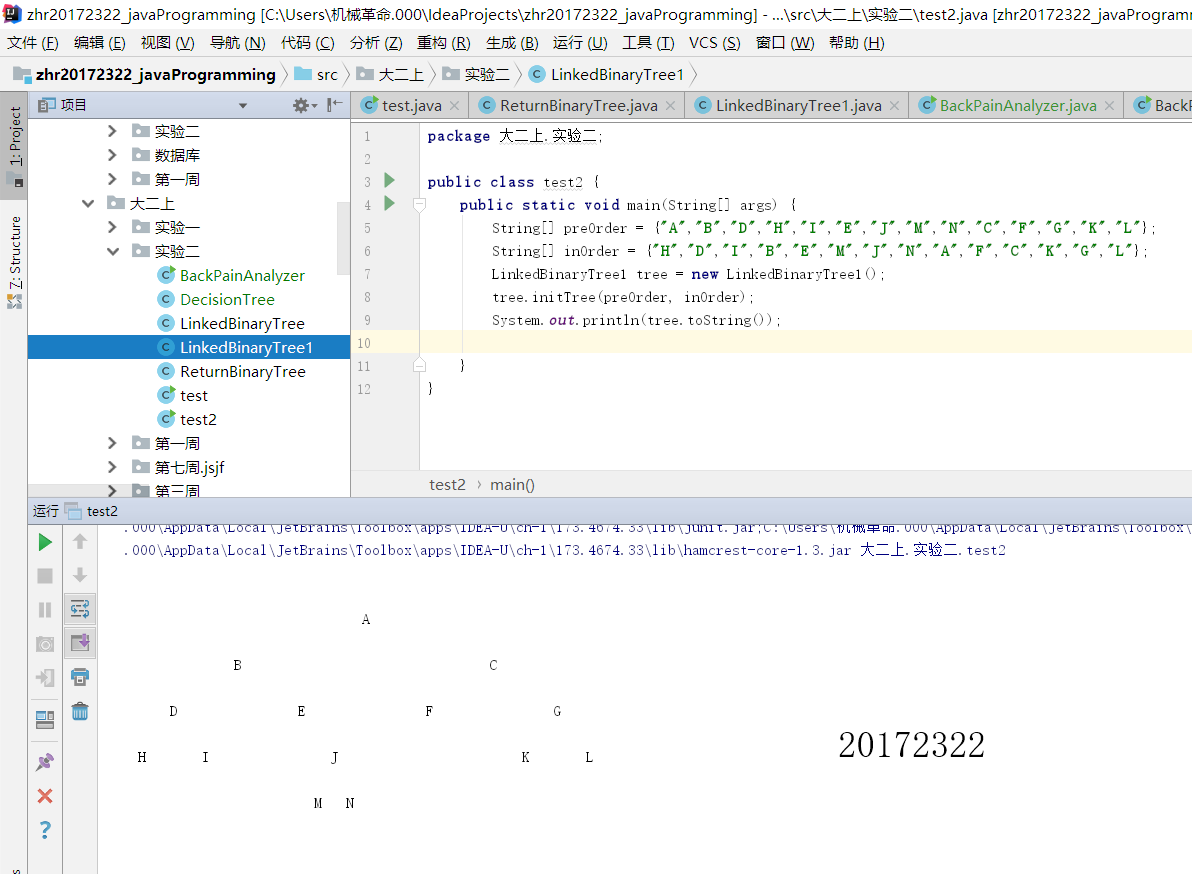
3.
4.
5.
3.实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
-
问题1:在完成节点四的时候,以为只是简单的将书上的表达式树的代码改一改就好。
-
问题1解决方案:在寝室中跟王文彬同学讨论相应问题的时候他提醒我说“虽然对于一棵表达式树来说中序遍历得到的就是中缀表达式,后序遍历得到的就是后续表达式,但书上是利用后缀表达式构建了一棵树,而我们的要求是利用中缀表达式构建一棵树。”这让我意识到了问题所在。好像问题没有那么简单,事实也证明如此,的确没有那么简单。
-
问题2:在做节点六时,从IDEA中打开了
TreeMap的源代码,看到那3013行代码时,脑壳都大了一圈。 -
问题2解决方案:好在有于欣月同学的提醒,网上有类似的分析,所以在网上搜了一下相应的问题,发现果然有类似的源码分析,便去参考了一番。
其他(感悟、思考等)
感悟
- 学海无涯苦作舟。


