数据库学习之MySQL基础
数据库基础
一、数据库简介
数据库:存放数据的仓库
sql及其规范
sql是Structured Query Language(结构化查询语言)的缩写。SQL是专为数据库而建立的操作命令集,是一种功能齐全的数据库语言。
在使用它时,只需要发出“做什么”的命令,“怎么做”是不用使用者考虑的。SQL功能强大、简单易学、使用方便,已经成为了数据库操作的基础,并且现在几乎所有的数据库均支持sql。
<1> 在数据库系统中,SQL语句不区分大小写(建议用大写) 。但字符串常量区分大小写。建议命令大写,表名库名小写; <2> SQL语句可单行或多行书写,以“;”结尾。关键词不能跨多行或简写。 <3> 用空格和缩进来提高语句的可读性。子句通常位于独立行,便于编辑,提高可读性。 SELECT * FROM tb_table WHERE NAME="YUAN"; <4> 注释:单行注释:-- 多行注释:/*......*/ <5>sql语句可以折行操作 <6> DDL,DML和DCL
MYSQL常用命令
--
-- 启动mysql服务与停止mysql服务命令:
--
-- net start mysql
-- net stop mysql
--
--
-- 登陆与退出命令:
--
-- mysql -h 服务器IP -P 端口号 -u 用户名 -p 密码 --prompt 命令提示符 --delimiter 指定分隔符
-- mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 -uroot -p123
-- quit------exit----\q;
--
--
-- \s; ------my.ini文件:[mysql] default-character-set=gbk [mysqld] character-set-server=gbk
--
-- prompt 命令提示符(\D:当前日期 \d:当前数据库 \u:当前用户)
--
-- \T(开始日志) \t(结束日志)
--
-- show warnings;
--
-- help() ? \h
--
-- \G;
--
-- select now();
-- select version();
-- select user;
--
-- \c 取消命令
--
-- delimiter 指定分隔符
二、.数据库操作(DDL)
1.查看:
(1)查看所有数据库:show databases;
(2)查看某一数据库创建编码:show create database num;
2.创建:
create database if not exists sxmu; (如果不存在则创建,若存在不创建也不报错,但会warning.查看warning:show warnings;)
create database if not exists num character set gbk;
3.删除:drop database if exists kokusho;
4.修改:alter database num character set gbk;
5 使用:切换:use sxmu;
检测当前数据库:select database();
注:数据库文件默认存放路径(C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.7\Data)
默认创建的所有数据库都是一个文件夹,每一张表都是该文件夹下的一个文件。
故如果要迁移数据库文件,可直接复制数据库文件夹
select user();
select now();
三、数据表操作
主键:非空且唯一(not null,unique)
数据类型:
数值类型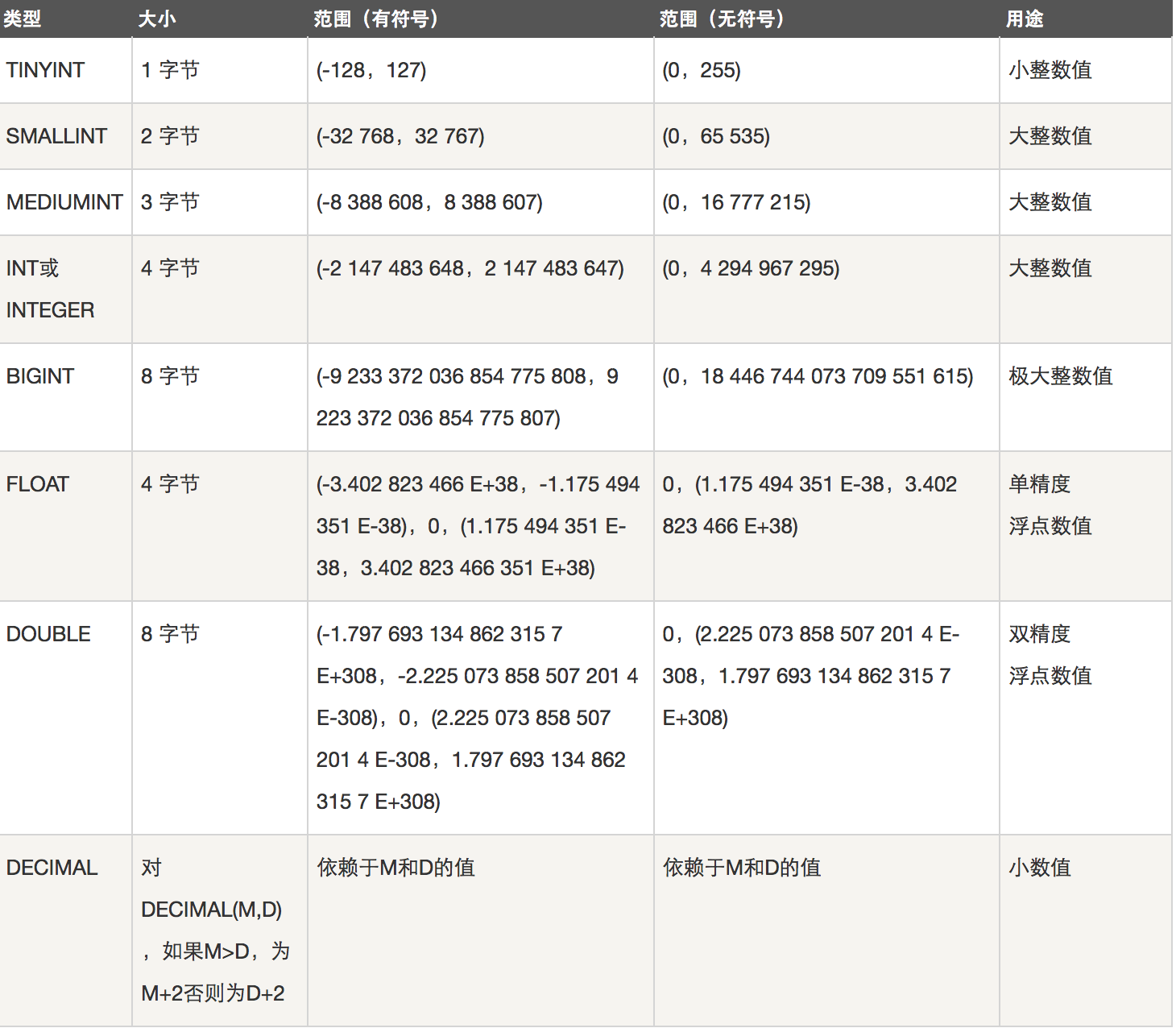
日期和时间类型
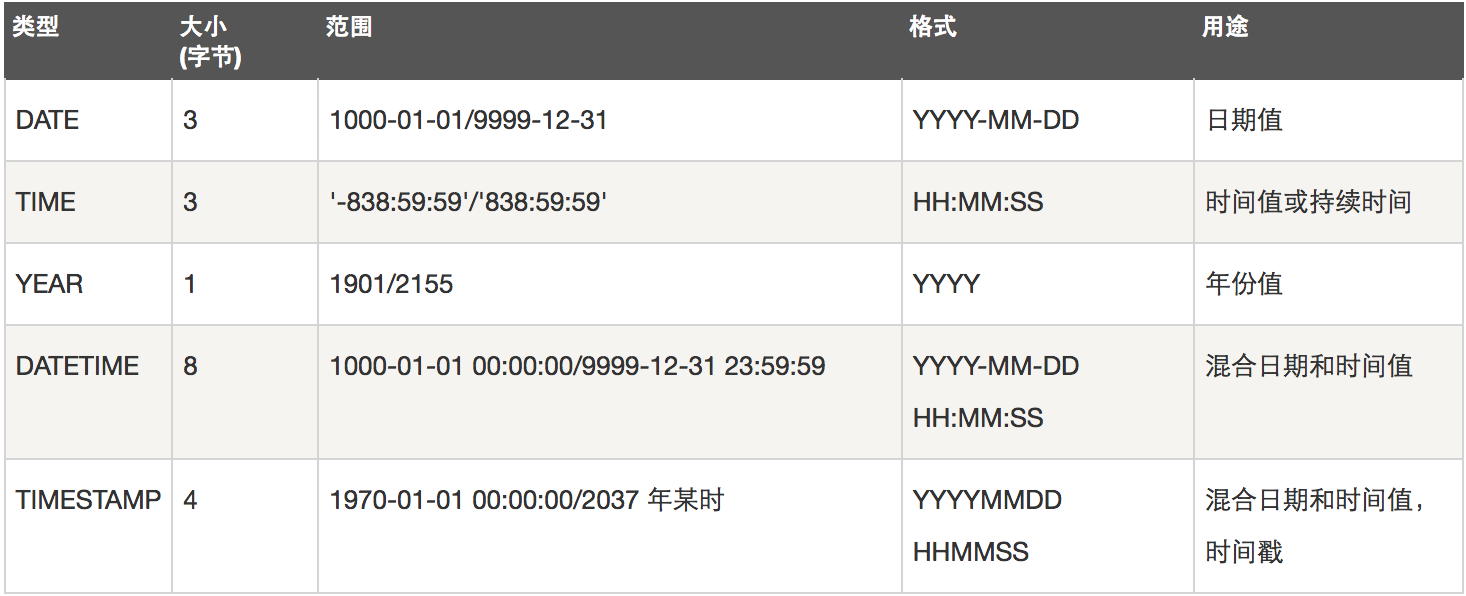
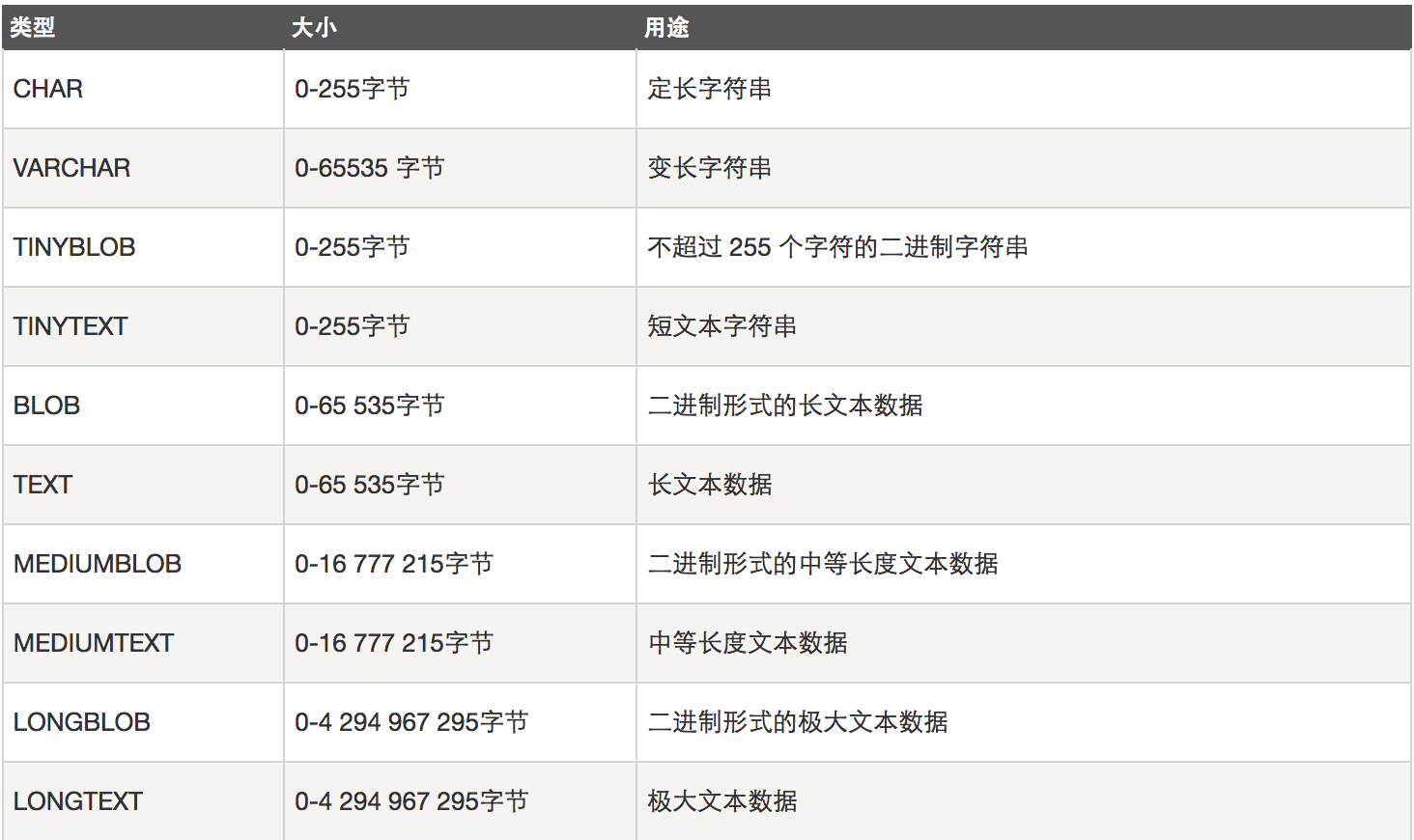
字符串类型
创建表:
create table tab_name(
field1 type[完整性约束条件],
field2 type,
...
fieldn type
)[character set xxx];
创建员工表:
CREATE TABLE employee(
id TINYINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(25),
gender BOOLEAN,
age INT,
department VARCHAR(20),
salary DOUBLE(7,2)
)
表结构:
1.查看
查看表结构:desc employee;
show columns from employee;
查看创建表语句:show create table employee;
查看当前数据库所有表:show tables;
2.增加字段:alter table employee add is_married tinyint(1);
alter table employee add entry_date date not null;
alter table employee add A int,add b varchar(20);
3.删除字段:alter table employee drop A;
alter table employee drop b,drop entry_date;
删除表:drop table emp;
4.修改字段信息:alter table employee modify age smallint not null default 18 after name;
alter table employee change department depart varchar(20) after salary;
修改表名: rename table employee to emp;
修改表所用字符集: alter table student character set utf8;
四、表记录操作
准备表数据
CREATE TABLE ExamResult( id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, name VARCHAR (20), JS DOUBLE , Django DOUBLE , OpenStack DOUBLE );
插入:insert [into] tab_name (field1,filed2,.......) values (value1,value2,.......)
删除:DELETE FROM emp WHERE id=11 OR id=2;
修改:UPDATE emp SET salary=salary+20000 WHERE name='yuan';
查询:select [distinct] *|filed1,field2| [as 别名]|[别名] from tab_name;
mysql中五种查询字句
- where子句(条件查询):按照“条件表达式”指定的条件进行查询。
- group by子句(分组):按照“属性名”指定的字段进行分组。group by子句通常和count()、sum()等聚合函数一起使用。
- having子句(筛选):有group by才能having子句,只有满足“条件表达式”中指定的条件的才能够输出。
- order by子句(排序):按照“属性名”指定的字段进行排序。排序方式由“asc”和“desc”两个参数指出,默认是按照“asc”来排序,即升序
- limit(限制结果集)。
mysql查询执行顺序
(7) SELECT (8) DISTINCT <select_list> (1) FROM <left_table> (3) <join_type> JOIN <right_table> (2) ON <join_condition> (4) WHERE <where_condition> (5) GROUP BY <group_by_list> (6) HAVING <having_condition> (9) ORDER BY <order_by_condition> (10) LIMIT <limit_number>

(1)增删改查 insert into emp (id,age,name,gender,salary,depart,is_married) values(1,18,'alex',0,1700,'技术部',1); INSERT INTO emp(name,salary,depart) VALUES ('瞎驴',30000,'python'); INSERT INTO emp(name,salary,depart) VALUES ('xialv',30000,'python'), ('小雨',5000,'销售部'), ('冰冰',9000,'销售部'); insert emp set name='珊珊'; insert into emp values(10,'丹丹',29,0,3000,'销售部',1); INSERT INTO emp(name,salary,depart) VALUES ('yuan',30000,'python'); UPDATE emp SET salary=salary+20000,depart='保安部' WHERE name='xialv'; delete from emp; (删除表内容) truncate table emp; (先直接删除整个表,在创建一个相同表结构的空表。大量数据时使用,直接删除表速度快。) insert into examresult(name) value('周守成'); INSERT INTO ExamResult VALUES (1,"yuan",98,98,98), (2,"xialv",35,98,67), (3,"alex",59,59,62), (4,"wusir",88,89,82), (5,"alvin",88,98,67), (6,"yuan",86,100,55); 练习:select * from examresult; select name,JS,Django,flask from examresult; select name 姓名,JS+10 as JS,Django+10 as Django,flask+10 as flask from examresult; select distinct name from examresult; //去重 (1)where:where字句中可使用[比较运算符:< > <= >= <> !=,between and,in,like,逻辑运算符:and or not] 练习:select name,JS+Django+flask as 总成绩 from examresult where JS+flask+Django>200; select name,JS from examresult where JS!=80; select name,JS from examresult where JS between 90 and 100; select name,JS from examresult where JS in(88,99,77); select name,JS from examresult where name like 'y%'; // %: 任意多个字符 select name,JS from examresult where name like 'y_'; // _:一个字符 select name,JS from examresult where name='yuan' and JS>80; select name from examresult where JS is null; //空考的学生 (2)order by 指定排序的列(排序的列可以使表中的列名,也可以是select语句中的别名) --asc为升序,desc为降序,默认为asc,order by应为于select语句的结尾 select name,JS from examresult order by JS; select name,JS from examresult where JS between 70 and 100 order by JS; //默认升序 select name,JS from examresult where JS between 70 and 100 order by JS desc; //降序 select name,JS+Django+flask as 总成绩 from examresult order by 总成绩 desc; select name,JS+Django+flask as 总成绩 from examresult where name='yuan' order by 总成绩 desc; 注:select JS as JS总成绩 from examresult where JS总成绩>70; 这条语句不能正确执行 select语句的执行顺序:from 表名 -> where -> select ->......->order by (3)group by:分组查询 --常和聚合函数配合使用 注:-- 按分组条件分组后每一组只会显示第一条记录 -- group by字句,其后可以接多个列名,也可以跟having子句,对group by 的结果进行筛选。 按列名分组 select * from examresult group by name; 按位置字段分组 select * from examresult group by 2; 将成绩表按名字分组后,显示每一组JS成绩的分数总和 select name,sum(JS) from examresult group by name; 将成绩表按照名字分组后,显示每一类名字的Django的分数总和>150的类名字和Django总分 select name,sum(Django) from examresult group by name having sum(Django)>150; 查询每个部门中男性和女性的人数 select depart,gender,count(id) from emp group by depart,gender; having 和 where两者都可以对查询结果进行进一步的过滤,差别有: <1>where语句只能用在分组之前的筛选,having可以用在分组之后的筛选; <2>使用where语句的地方都可以用having进行替换 <3>having中可以用聚合函数,where中就不行。 (4)聚合函数:[count,sum,avg,max,min]--常和分组函数配合使用 --统计JS>70的人数 select count(id) from examresult where JS>70; --统计JS的平均分 select sum(JS)/count(name) from examresult; //算上了JS为null的情况 select avg(JS) from examresult; //不算JS为null -- 统计总分大于280的人数有多少? select count(name) from ExamResult where (ifnull(JS,0)+ifnull(Django,0)+ifnull(OpenStack,0))>280; --查询JS总分中最小值 select min(JS) from examresult; select min(ifnull(JS,0)) from examresult; --查询JS+Django+flask总分中最大的 select max(JS+Django+flask) from examresult; (5)limit: select * from examresult limit 3;显示前3条 select * from examresult limit 2,3; //跳过前两条显示接下来的3条 (6)重点: --sql语句书写顺序:select from where group by having order by --sql语句执行顺序:from where select group by having order by 例子: select JS as JS成绩 from examresult where JS成绩>70; //执行不成功 select JS as JS成绩 from examresult where JS成绩>70; //成功执行 (7)使用正则表达式查询 SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP '^yu'; SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'yun$'; SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'm{2}';
五、外键约束
创建外键
--- 每一个班主任会对应多个学生 , 而每个学生只能对应一个班主任
--1.数据准备:
----主表
CREATE TABLE ClassCharger(
id TINYINT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR (20),
age INT ,
is_marriged boolean -- show create table ClassCharger: tinyint(1)
);
INSERT INTO ClassCharger (name,age,is_marriged) VALUES ("冰冰",12,0),
("丹丹",14,0),
("歪歪",22,0),
("姗姗",20,0),
("小雨",21,0);
----子表
CREATE TABLE Student(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR (20),
charger_id TINYINT,
foreign key (charger_id) references classcharger(id) on delete cascade
) ENGINE=INNODB;
--切记:作为外键一定要和关联主键的数据类型保持一致
-- [ADD CONSTRAINT charger_fk_stu]FOREIGN KEY (charger_id) REFERENCES ClassCharger(id)
INSERT INTO Student2(name,charger_id) VALUES ("alvin1",2),
("alvin2",4),
("alvin3",1),
("alvin4",3),
("alvin5",5),
("alvin6",3),
("alvin7",3);
--2.外键约束练习
删除班主任丹丹
delete from classcharger where id=2; --会报错
先删除班主任丹丹关联的学生
update student set charger_id=4 where id=1 or id=7;
delete from classcharger where id=2; --成功执行
添加一个学生,班主任选择丹丹
insert into student(name,charger_id) values('sasa',2); --添加失败
-----------增加外键和删除外键---------
ALTER TABLE student ADD CONSTRAINT abc
FOREIGN KEY(charger_id)
REFERENCES classcharger(id);
ALTER TABLE student DROP FOREIGN KEY abc;
alter table student3 drop foreign key student3_ibfk_1;
alter table student3 add constraint s3_fk_c foreign key(charger_id) references C(id) on delete set null;
3.INNODB支持的on语句
--外键约束对子表的含义: 如果在父表中找不到候选键,则不允许在子表上进行insert/update
--外键约束对父表的含义: 在父表上进行update/delete以更新或删除在子表中有一条或多条对
-- 应匹配行的候选键时,父表的行为取决于:在定义子表的外键时指定的
-- on update/on delete子句
-----------------innodb支持的四种方式---------------------------------------
-----cascade方式 在父表上update/delete记录时,同步update/delete掉子表的匹配记录
-----外键的级联删除:如果父表中的记录被删除,则子表中对应的记录自动被删除--------
FOREIGN KEY (charger_id) REFERENCES ClassCharger(id)
ON DELETE CASCADE
------set null方式 在父表上update/delete记录时,将子表上匹配记录的列设为null
-- 要注意子表的外键列不能为not null
FOREIGN KEY (charger_id) REFERENCES ClassCharger(id)
ON DELETE SET NULL
------Restrict方式 :拒绝对父表进行删除更新操作(了解)
------No action方式 在mysql中同Restrict,如果子表中有匹配的记录,则不允许对父表对应候选键
-- 进行update/delete操作(了解)
六、连表查询
1、内联接(典型的联接运算,使用像 = 或 <> 之类的比较运算符)。包括相等联接和自然联接。
- inner join(等值连接) 只返回两个表中联结字段相等的行
2、外联接。外联接可以是左向外联接、右向外联接或完整外部联接。
- left join(左联接) 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录
- right join(右联接) 返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中联结字段相等的记录
- full join(全联接) 返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中所有的记录
3、交叉联接
交叉联接返回左表中的所有行,左表中的每一行与右表中的所有行组合。交叉联接也称作笛卡尔积。
FROM 子句中的表或视图可通过内联接或完整外部联接按任意顺序指定;但是,用左或右向外联接指定表或视图时,表或视图的顺序很重要。有关使用左或右向外联接排列表的更多信息,请参见使用外联接。

mysql> use flask_code Database changed mysql> show tables; +----------------------+ | Tables_in_flask_code | +----------------------+ | record | | userinfo | +----------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record; +----+------+------------+---------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | +----+------+------------+---------+ | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | +----+------+------------+---------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from userinfo; +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select userinfo.nickname,record.line from record,userinfo where record.us er_id = userinfo.id; +--------------+------+ | nickname | line | +--------------+------+ | 就是这么牛逼 | 1000 | | 张亚飞 | 5000 | | 张亚飞 | 3000 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | +--------------+------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select userinfo.nickname,record.line from record inner join userinfo on u serinfo.id = record.user_id; +--------------+------+ | nickname | line | +--------------+------+ | 就是这么牛逼 | 1000 | | 张亚飞 | 5000 | | 张亚飞 | 3000 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | +--------------+------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select userinfo.nickname,record.line from record left join userinfo on us erinfo.id = record.user_id; +--------------+------+ | nickname | line | +--------------+------+ | 就是这么牛逼 | 1000 | | 张亚飞 | 5000 | | 张亚飞 | 3000 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | +--------------+------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select userinfo.nickname,record.line from record right join userinfo on u serinfo.id = record.user_id; +--------------+------+ | nickname | line | +--------------+------+ | 就是这么牛逼 | 1000 | | 张亚飞 | 5000 | | 张亚飞 | 3000 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | | 张亚飞 | 269 | | 看把你牛逼的 | NULL | +--------------+------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record right join userinfo on userinfo.id = record.user_id; +------+------+------------+---------+----+------------+------------------------ ----------+--------------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | id | username | password | nickname | +------+------+------------+---------+----+------------+------------------------ ----------+--------------+ | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415db b905e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415db b905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415db b905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415db b905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415db b905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415db b905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | +------+------+------------+---------+----+------------+------------------------ ----------+--------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select userinfo.id,nickname,ifnull(sum(line),0) as line from record right join userinfo on userinfo.id=record.user_id group by userinfo.id order by line desc; +----+--------------+------+ | id | nickname | line | +----+--------------+------+ | 3 | 张亚飞 | 8538 | | 1 | 就是这么牛逼 | 1000 | | 2 | 看把你牛逼的 | 0 | +----+--------------+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)

mysql> select * from record; +----+------+------------+---------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | +----+------+------------+---------+ | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | +----+------+------------+---------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from userinfo; +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 姚明 | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record cross join userinfo; +----+------+------------+---------+----+------------+-------------------------- --------+--------------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------+------------+---------+----+------------+-------------------------- --------+--------------+ | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | +----+------+------------+---------+----+------------+-------------------------- --------+--------------+ 20 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record,userinfo; +----+------+------------+---------+----+------------+-------------------------- --------+--------------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------+------------+---------+----+------------+-------------------------- --------+--------------+ | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb9 05e2d8a | 姚明 | +----+------+------------+---------+----+------------+-------------------------- --------+--------------+ 20 rows in set (0.00 sec)
七、联合查询
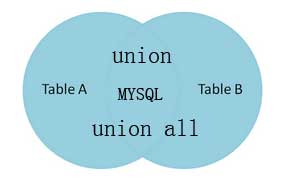
一、UNION和UNION ALL的作用和语法
UNION 用于合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果集,并消去表中任何重复行。
UNION 内部的 SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列,列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。
同时,每条 SELECT 语句中的列的顺序必须相同.
SQL UNION 语法:
sql脚本代码如下:
1 SELECT column_name FROM table1 2 UNION 3 SELECT column_name FROM table2
注释:默认地,UNION 操作符选取不同的值。如果允许重复的值,请使用 UNION ALL。
当 ALL 随 UNION 一起使用时(即 UNION ALL),不消除重复行
SQL UNION ALL 语法
sql脚本代码如下:
1 SELECT column_name FROM table1 2 UNION ALL 3 SELECT column_name FROM table2
注释:另外,UNION 结果集中的列名总是等于 UNION 中第一个 SELECT 语句中的列名。
注意:1、UNION 结果集中的列名总是等于第一个 SELECT 语句中的列名
2、UNION 内部的 SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列。列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。同时,每条 SELECT 语句中的列的顺序必须相同
二、union的用法及注意事项
union:联合的意思,即把两次或多次查询结果合并起来。
要求:两次查询的列数必须一致
推荐:列的类型可以不一样,但推荐查询的每一列,想对应的类型以一样
可以来自多张表的数据:多次sql语句取出的列名可以不一致,此时以第一个sql语句的列名为准。
如果不同的语句中取出的行,有完全相同(这里表示的是每个列的值都相同),那么union会将相同的行合并,最终只保留一行。也可以这样理解,union会去掉重复的行。
如果不想去掉重复的行,可以使用union all。
如果子句中有order by,limit,需用括号()包起来。推荐放到所有子句之后,即对最终合并的结果来排序或筛选。
如:sql脚本代码如下:
1 (select * from a order by id) union (select * from b order id);
在子句中,order by 需要配合limit使用才有意义。如果不配合limit使用,会被语法分析器优化分析时去除。
三、学习例子

# 选择数据库 mysql> use flask_code Database changed # 查看表 mysql> show tables; +----------------------+ | Tables_in_flask_code | +----------------------+ | record | | userinfo | +----------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from userinfo; +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 姚明 | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.08 sec) # 创建和已有表结构相同的额表 mysql> create table userinfo2 like userinfo; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.48 sec) # 插入和另一个结构相同的表的数据 mysql> insert into userinfo2 select * from userinfo limit 1,3; Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.12 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> insert into userinfo2(username,password,nickname) values('kobe', '317b 64bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a', '科比'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec) mysql> select * from userinfo2; +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 姚明 | | 5 | kobe | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 科比 | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) # union:上下连接两张表,且去重重复的行 mysql> select * from userinfo -> union -> select * from userinfo2; +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 姚明 | | 5 | kobe | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 科比 | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) # union all:上下连接两张表,不去除重复的行 mysql> select * from userinfo union all select * from userinfo2; +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | id | username | password | nickname | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ | 1 | zhangsan | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 就是这么牛逼 | | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 姚明 | | 2 | lisi | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 看把你牛逼的 | | 3 | zhangyafei | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 张亚飞 | | 4 | yaoming | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 姚明 | | 5 | kobe | 317bc264bfd3d562fa415dbb905e2d8a | 科比 | +----+------------+----------------------------------+--------------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
八、limit分页
Limit子句可以被用于强制 SELECT 语句返回指定的记录数。Limit接受一个或两个数字参数。参数必须是一个整数常量。如果给定两个参数,第一个参数指定第一个返回记录行的偏移量,第二个参数指定返回记录行的最大数目。
//初始记录行的偏移量是 0(而不是 1):
mysql> SELECT * FROM table LIMIT 5,10; //检索记录行6-15
//如果只给定一个参数,它表示返回最大的记录行数目。换句话说,LIMIT n 等价于 LIMIT 0,n:
mysql> SELECT * FROM table LIMIT 5; //检索前 5 个记录行
Limit的效率高?
常说的Limit的执行效率高,是对于一种特定条件下来说的:即数据库的数量很大,但是只需要查询一部分数据的情况。
高效率的原理是:避免全表扫描,提高查询效率。
比如:每个用户的email是唯一的,如果用户使用email作为用户名登陆的话,就需要查询出email对应的一条记录。
SELECT * FROM t_user WHERE email=?;
上面的语句实现了查询email对应的一条用户信息,但是由于email这一列没有加索引,会导致全表扫描,效率会很低。
SELECT * FROM t_user WHERE email=? LIMIT 1;
加上LIMIT 1,只要找到了对应的一条记录,就不会继续向下扫描了,效率会大大提高。
Limit的效率低?
在一种情况下,使用limit效率低,那就是:只使用limit来查询语句,并且偏移量特别大的情况
做以下实验:
语句1:
select * from table limit 150000,1000;
语句2:
select * from table while id>=150000 limit 1000;
语句1为0.2077秒;语句2为0.0063秒
两条语句的时间比是:语句1/语句2=32.968
比较以上的数据时,我们可以发现采用where...limit....性能基本稳定,受偏移量和行数的影响不大,而单纯采用limit的话,受偏移量的影响很大,当偏移量大到一定后性能开始大幅下降。不过在数据量不大的情况下,两者的区别不大。
所以应当先使用where等查询语句,配合limit使用,效率才高
ps:在sql语句中,limt关键字是最后才用到的。以下条件的出现顺序一般是:where->group by->having-order by->limit
附录:OFFSET
为了与 PostgreSQL 兼容,MySQL 也支持句法: LIMIT # OFFSET #。
经常用到在数据库中查询中间几条数据的需求
比如下面的sql语句:
① selete * from testtable limit 2,1;
② selete * from testtable limit 2 offset 1;
注意:
1.数据库数据计算是从0开始的
2.offset X是跳过X个数据,limit Y是选取Y个数据
3.limit X,Y 中X表示跳过X个数据,读取Y个数据
这两个都是能完成需要,但是他们之间是有区别的:
①是从数据库中第三条开始查询,取一条数据,即第三条数据读取,一二条跳过
②是从数据库中的第二条数据开始查询两条数据,即第二条和第三条。

mysql> select * from proxy limit 5; +----+-----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+--------- --------+ | ID | IP | PORT | POSITION | TYPE | SPEED | LIVE_TIME | LAST_CHE CK_TIME | +----+-----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+--------- --------+ | 1 | 111.72.154.107 | 53128 | 江西宜春 | HTTPS | 1.221 | 17分钟 | 18-07-17 09:01 | | 2 | 125.121.120.14 | 6666 | 浙江杭州 | HTTPS | 1.542 | 1分钟 | 18-07-17 21:01 | | 3 | 1.197.59.174 | 41869 | 河南漯河 | HTTPS | 3.032 | 292天 | 18-07-17 08:55 | | 4 | 125.118.247.32 | 6666 | 浙江杭州 | HTTPS | 0.19 | 33天 | 18-07-18 09:22 | | 5 | 125.121.117.139 | 6666 | 浙江杭州 | HTTP | 0.161 | 4分钟 | 18-07-18 05:20 | +----+-----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+--------- --------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from proxy limit 5,10; +----+----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+---------- -------+ | ID | IP | PORT | POSITION | TYPE | SPEED | LIVE_TIME | LAST_CHEC K_TIME | +----+----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+---------- -------+ | 6 | 117.86.19.111 | 18118 | 江苏南通 | HTTPS | 4.954 | 1分钟 | 18-07-17 21:01 | | 7 | 110.73.41.238 | 8123 | 广西南宁 | HTTP | 3.16 | 609天 | 18-07-17 12:30 | | 8 | 182.86.189.123 | 48148 | 江西 | HTTPS | 0.224 | 1分钟 | 18-07-17 16:22 | | 9 | 221.228.17.172 | 8181 | 江苏无锡 | HTTPS | 6.462 | 73天 | 18-07-18 17:41 | | 10 | 115.223.65.147 | 8010 | 浙江温州 | HTTPS | 0.785 | 1分钟 | 18-07-17 08:46 | | 11 | 49.87.135.30 | 53128 | 江苏淮安 | HTTPS | 0.3 | 1分钟 | 18-07-18 09:22 | | 12 | 183.15.121.130 | 28094 | 广东深圳 | HTTP | 0.481 | 1分钟 | 18-07-17 06:30 | | 13 | 183.128.241.77 | 6666 | 浙江杭州 | HTTPS | 3.093 | 25天 | 18-07-18 01:40 | | 14 | 49.74.91.98 | 53281 | 江苏南京 | HTTP | 7.233 | 14天 | 18-07-18 05:20 | | 15 | 114.231.68.16 | 18118 | 江苏南通 | HTTPS | 6.159 | 5分钟 | 18-07-17 21:01 | +----+----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+---------- -------+ 10 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select count(*) from proxy; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 1800 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from proxy limit 1795,-1; ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '-1' a t line 1 mysql> select * from proxy limit 795,-1; ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '-1' a t line 1 mysql> select * from proxy limit 2 offset 1; +----+----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+---------- -------+ | ID | IP | PORT | POSITION | TYPE | SPEED | LIVE_TIME | LAST_CHEC K_TIME | +----+----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+---------- -------+ | 2 | 125.121.120.14 | 6666 | 浙江杭州 | HTTPS | 1.542 | 1分钟 | 18-07-17 21:01 | | 3 | 1.197.59.174 | 41869 | 河南漯河 | HTTPS | 3.032 | 292天 | 18-07-17 08:55 | +----+----------------+-------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+---------- -------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
九、 数据库引擎
Mysql引擎种类:innodb,mysaim
- innodb:支持事务,锁(支持行锁和表锁)
- mysaim:不支持事务。锁(支持表锁),优势速度快
Innodb引擎 Innodb引擎提供了对数据库ACID事务的支持,并且实现了SQL标准的四种隔离级别,关于数据库事务与其隔离级别的内容请见数据库事务与其隔 离级别这篇文章。
该引擎还提供了行级锁和外键约束,它的设计目标是处理大容量数据库系统,它本身其实就是基于MySQL后台的完整数据库系统,MySQL 运行时Innodb会在内存中建立缓冲池,
用于缓冲数据和索引。但是该引擎不支持FULLTEXT类型的索引,而且它没有保存表的行数,当SELECT COUNT(*) FROM TABLE时需要扫描全表。当需要使用数据库事务时,
该引擎当然是首选。由于锁的粒度更小,写操作不会锁定全表,所以在并发较高时,使用Innodb引擎 会提升效率。但是使用行级锁也不是绝对的,如果在执行一个SQL语句时
MySQL不能确定要扫描的范围,InnoDB表同样会锁全表。 MyIASM引擎 MyIASM是MySQL默认的引擎,但是它没有提供对数据库事务的支持,也不支持行级锁和外键,因此当INSERT(插入)或UPDATE(更 新)数据时即写操作需要锁定整个表,
效率便会低一些。不过和Innodb不同,MyIASM中存储了表的行数,于是SELECT COUNT(*) FROM TABLE时只需要直接读取已经保存好的值而不需要进行全表扫描。
如果表的读操作远远多于写操作且不需要数据库事务的支持,那么MyIASM也是很好的选 择。 两种引擎的选择 大尺寸的数据集趋向于选择InnoDB引擎,因为它支持事务处理和故障恢复。数据库的大小决定了故障恢复的时间长短,InnoDB可以利用事务日志 进行数据恢复,
这会比较快。主键查询在InnoDB引擎下也会相当快,不过需要注意的是如果主键太长也会导致性能问题,关于这个问题我会在下文中讲到。大 批的INSERT语句
(在每个INSERT语句中写入多行,批量插入)在MyISAM下会快一些,但是UPDATE语句在InnoDB下则会更快一些,尤 其是在并发量大的时候。 Index——索引 索引(Index)是帮助MySQL高效获取数据的数据结构。MyIASM和Innodb都使用了树这种数据结构做为索引,关于树我也曾经写过一篇文章树是一种伟大的数据结构,
只是自己的理解,有兴趣的朋友可以去阅读。下面我接着讲这两种引擎使用的索引结构,讲到这里,首先应该谈一下B-Tree和B+Tree。 B-Tree和B+Tree B+Tree是B-Tree的变种,那么我就先讲B-Tree吧,相信大家都知道红黑树,这是我前段时间学《算法》一书时,实现的一颗红黑树,大家 可以参考。
其实红黑树类似2,3-查找树,这种树既有2叉结点又有3叉结点。B-Tree也与之类似,它的每个结点做多可以有d个分支(叉),d称为B- Tree的度,如下图所示,
它的每个结点可以有4个元素,5个分支,于是它的度为5。B-Tree中的元素是有序的,比如图中元素7左边的指针指向的结点 中的元素都小于7,而元素7和16之间
的指针指向的结点中的元素都处于7和16之间,正是满足这样的关系,才能高效的查找:首先从根节点进行二分查找,找 到就返回对应的值,否则就进入相应的区间
结点递归的查找,直到找到对应的元素或找到null指针,找到null指针则表示查找失败。这个查找是十分高效 的,其时间复杂度为O(logN)(以d为底,当d很大时,
树的高度就很低),因为每次检索最多只需要检索树高h个结点。
mysql什么时候需要加锁:计数- 应用场景- 商品数量
mysql如何加锁:
终端1: begin; select * from tb for update; commit; 终端2: begin; select * from tb for update; commit;

mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record where id=2 for update; +----+------+------------+---------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | +----+------+------------+---------+ | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | +----+------+------------+---------+ row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record for update; +----+------+------------+---------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | +----+------+------------+---------+ | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | +----+------+------------+---------+ rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql加锁(行锁和表锁)示例
一般情况下,mysql会默认提供多种存储引擎,你可以通过下面的查看:
-
 mysql查看存储引擎
mysql查看存储引擎mysql> show engines; +--------------------+---------+------------------------------------------------ ----------------+--------------+------+------------+ | Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints | +--------------------+---------+------------------------------------------------ ----------------+--------------+------+------------+ | InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and f oreign keys | YES | YES | YES | | MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO | | MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for tempor ary tables | NO | NO | NO | | BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO | | MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO | | CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO | | ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO | | PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO | | FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL | +--------------------+---------+------------------------------------------------ ----------------+--------------+------+------------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show variables like '%storage_engine%'; +----------------------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------------+--------+ | default_storage_engine | InnoDB | | default_tmp_storage_engine | InnoDB | | disabled_storage_engines | | | internal_tmp_disk_storage_engine | InnoDB | +----------------------------------+--------+ 4 rows in set, 1 warning (0.11 sec) mysql> show create table record; +--------+---------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +--------+---------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------+ | record | CREATE TABLE `record` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `line` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `ctime` date DEFAULT NULL, `user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `user_id` (`user_id`), CONSTRAINT `record_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `userinfo` (`id` ) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 | +--------+---------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
 mysql加锁(行锁和表锁)示例
mysql加锁(行锁和表锁)示例mysql> begin; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record where id=2 for update; +----+------+------------+---------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | +----+------+------------+---------+ | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | +----+------+------------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from record for update; +----+------+------------+---------+ | id | line | ctime | user_id | +----+------+------------+---------+ | 1 | 1000 | 2018-12-19 | 1 | | 2 | 5000 | 2018-12-17 | 3 | | 3 | 3000 | 2018-12-21 | 3 | | 5 | 269 | 2018-12-26 | 3 | | 6 | 269 | 2018-12-27 | 3 | +----+------+------------+---------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
pymysql cursor.execute('select * from record for update') django with trancation.automic(): models.User.objects.all().for_update()
补充:
 执行计划
执行计划explain select * from tb; id 查询顺序标识 如:mysql> explain select * from (select nid,name from tb1 where nid < 10) as B; +----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9 | NULL | | 2 | DERIVED | tb1 | range | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | NULL | 9 | Using where | +----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+-------------+ 特别的:如果使用union连接气值可能为null select_type 查询类型 SIMPLE 简单查询 PRIMARY 最外层查询 SUBQUERY 映射为子查询 DERIVED 子查询 UNION 联合 UNION RESULT 使用联合的结果 ... table 正在访问的表名 type 查询时的访问方式,性能:all < index < range < index_merge < ref_or_null < ref < eq_ref < system/const ALL 全表扫描,对于数据表从头到尾找一遍 select * from tb1; 特别的:如果有limit限制,则找到之后就不在继续向下扫描 select * from tb1 where email = 'seven@live.com' select * from tb1 where email = 'seven@live.com' limit 1; 虽然上述两个语句都会进行全表扫描,第二句使用了limit,则找到一个后就不再继续扫描。 INDEX 全索引扫描,对索引从头到尾找一遍 select nid from tb1; RANGE 对索引列进行范围查找 select * from tb1 where name < 'alex'; PS: between and in > >= < <= 操作 注意:!= 和 > 符号 INDEX_MERGE 合并索引,使用多个单列索引搜索 select * from tb1 where name = 'alex' or nid in (11,22,33); REF 根据索引查找一个或多个值 select * from tb1 where name = 'seven'; EQ_REF 连接时使用primary key 或 unique类型 select tb2.nid,tb1.name from tb2 left join tb1 on tb2.nid = tb1.nid; CONST 常量 表最多有一个匹配行,因为仅有一行,在这行的列值可被优化器剩余部分认为是常数,const表很快,因为它们只读取一次。 select nid from tb1 where nid = 2 ; SYSTEM 系统 表仅有一行(=系统表)。这是const联接类型的一个特例。 select * from (select nid from tb1 where nid = 1) as A; possible_keys 可能使用的索引 key 真实使用的 key_len MySQL中使用索引字节长度 rows mysql估计为了找到所需的行而要读取的行数 ------ 只是预估值 extra 该列包含MySQL解决查询的详细信息 “Using index” 此值表示mysql将使用覆盖索引,以避免访问表。不要把覆盖索引和index访问类型弄混了。 “Using where” 这意味着mysql服务器将在存储引擎检索行后再进行过滤,许多where条件里涉及索引中的列,当(并且如果)它读取索引时,就能被存储引擎检验,因此不是所有带where子句的查询都会显示“Using where”。有时“Using where”的出现就是一个暗示:查询可受益于不同的索引。 “Using temporary” 这意味着mysql在对查询结果排序时会使用一个临时表。 “Using filesort” 这意味着mysql会对结果使用一个外部索引排序,而不是按索引次序从表里读取行。mysql有两种文件排序算法,这两种排序方式都可以在内存或者磁盘上完成,explain不会告诉你mysql将使用哪一种文件排序,也不会告诉你排序会在内存里还是磁盘上完成。 “Range checked for each record(index map: N)” 这个意味着没有好用的索引,新的索引将在联接的每一行上重新估算,N是显示在possible_keys列中索引的位图,并且是冗余的。
 mysql常用语法命令及函数
mysql常用语法命令及函数1 #创建数据库# create database 数据库名; 2 #查看数据库# show databases; 3 4 #选择数据库# use 数据库名; 5 6 #删除数据库# drop database 数据库名; 7 8 9 10 #创建表# create table 表名(属性名1 数据类型 ,属性名2 数据类型。。。。); 11 12 #查看表结构# desc 表名; 13 14 #查看建表语言# show create table 表名; 15 16 #表中新增字段# alter table 表名 add( 属性名1 数据类型,属性名2 数据类型.....); 17 18 #在表的第一个位置增加字段# alter table 表名 add 属性名 数据类型 first; 19 20 #在指定字段后面增加字段# alter table 表名 add 新增属性名 数据类型 after 属性名; 21 22 #删除表中字段# alter table 表名 drop 属性名; 23 24 #删除表# drop table 表名; 25 26 27 28 #修改表名# alter table 旧表名 rename 新表名; 或alter table 旧表名 rename to 新表名; 29 30 #修改表中字段的数据类型# alter table 表名 modify 需要修改的属性名 想要修改成的数据类型; 31 32 #修改表中字段名称 alter table 表名 change 旧属性名 新属性名 旧数据类型; 33 34 #修改表中字段名称和数据类型 alter table 表名 change 旧属性名 新属性名 新数据类型; 35 36 #修改表中字段为头字段# alter table 表名 modify 属性名 数据类型 first; 37 38 #修改字段1为顺序,在字段2后面# alter table 表名 modify 属性名1 数据类型 after 属性名2; 39 40 41 42 #插入数据记录# insert into 表名(字段1,字段2,.....或不写) values(一条数据),(一条数据); 43 44 #插入查询结果# insert into 要插入表表名 (插入表中字段1,插入表中字段2,.....) select (查询表中字段1,查询表中字段2......) from 要查询表表名 查询语句; 45 46 #更新数据记录# update 表名 set 字段1=新值, 字段2=新值.........where 查询语句; 47 48 #删除数据记录# delete from表名 where 查询语句; 49 50 #查询部分数据记录# select 字段1,字段2。。。。 from 要查询的表; 51 52 #避免重复查询# select distinct 字段1,字段2。。。。 from 要查询的表; 53 54 #为查询结果起别名# select 字段1 as或不写 别名1,字段2 as或不写 别名2。。。。 from 要查询的表; 55 56 #设置显示格式数据查询# select concat(字段1,‘提示语句’,字段2。。。。) from 要查询的表; 57 58 #where条件查询# select * from 表名 where 字段=值; 59 60 #between and 关键字范围查询# select * from 表名 where 字段 between 值1 and 值2; 61 62 #between and 关键字不再范围内查询# select * from 表名 where 字段 not between 值1 and 值2 ; 63 64 #带null关键字空查询# select * from 表名 where 字段 is not null; 或 select * from 表名 where 字段 is not null; 65 66 #带in关键字的集合查询# select 字段1 ,字段2.。。。。。from 表名 where 字段n in(值1,指2。。。。。); 67 68 #带like关键字的模糊查询# select * from 表名 where 字段 like ‘字段串%’ ; 或select * from 表名 where 字段 like ‘字段串_’ ; 或 select * from 表名 where not 字段 like ‘字段串_’ ; 69 70 #排序数据查询# select * from 表名 order by 依照排序的字段名 asc(升序) 或 desc (降序); 71 72 #多字段排序# select * from 表名 order by 字段1 asc ,字段2 desc 。。。。; 73 74 #带limit关键字的限制查询数量# select * from 表名 where limit 开始条数位置 ,显示条数; 75 76 #分组数据查询# select * from 表名 group by 字段; #随机显示出每个分组的一条数据,一般讲分组与统计合起来使用才有意义# 77 78 #带having的分组限定查询# select * from 表名 group by 字段 having 条件; 79 80 81 #inner join on内连接# select * from 表1 inner join 表2 on 条件; 82 83 #自连接# select e.字段 as 别名1,f.字段 as 别名2.。。。。from 表名 as e inner join 表 as f on 条件; 84 85 #from多表连接# select * from 表1 , 表 2 。。。 where 条件; 86 87 #左外连接# select * from 表1 left join 表2 on 条件; 88 89 #右外连接# select * from 表1 right join 表2 on 条件; 90 91 #允许重复值的合并查询# select * from 表1 union all 表2 on 条件; 92 93 #不含重复值的合并查询# select * from 表1 union 表2 on 条件; 94 95 #where型子查询# select * from 表名 where (字段1,字段2)=(select 字段1, 字段2 from 表名 where 。。。。); 96 97 #in关键字的子查询# select * from 表名 where 字段 in (select 。。。。查询语句); 98 99 #any关键字的子查询# select * from 表名 where 字段 >=any (select 。。。。查询语句); 100 101 #all关键字的子查询# select * from 表名 where 字段 <= all(select 。。。。查询语句); 102 103 #exists关键字的子查询# select * from 表名 where not exists (select 。。。。查询语句); 104 105 #regexp正则表达式运算符# select ‘chshs’ rehexp ‘c.’ ; 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 #计数函数# count(); 113 114 #求平均函数# avg(); 115 116 #求和函数# sum(); 117 118 #取最大函数# max(); 119 120 #取最小函数# min(); 121 122 #取绝对值# abs(); 123 124 #取大于x的最大整数# cell(x); 125 126 #取小于x的最大整数# floor(x); 127 128 #取数值x的四舍五入后有y为小数# round(x,y); 129 130 #直接截取x为有y位的小数# truncate(x,y); 131 132 #返回0~1之间的一个随机数#rand(); 133 134 #获取第n组返回相同值得随机数# rand(n); 135 136 137 #对字符串进行加密# password(); 138 139 #字符串连接函数# concat(字符串1,字符串2.。。); 140 141 #带分隔符字符串合并# concat(分隔符,字符串1,字符串2.。。。); 142 143 #返回在字符串str2。。。中与str1相匹配的字符串位置# find_in_set(‘str1’,‘str2,str3.。。。。’); 144 145 #返回字符串str1第一次出现位置# field(‘str1’,‘str2’,‘str3’。。。。); 146 147 #返回子字符串str在字符串str1中匹配开始的位置# locate(str,str1);或 position(str in str1); 或 instr(str1 ,str); 148 149 #返回第n'个字符串# elt(n,str1,str2.。。strn); 150 #截取指定位置和长度的字符串# substring(str,num,length); 或 mid(str,num,length); 151 #将字符串str从第x位置开始,y个字符长的字串替换为字符串str2# insert(str , x ,y,str2); 152 #将字符变为小写# lower(str);或 lcase(str) 153 #将字符变为大写# upper(str);或 ucase(str) 154 #获取字符串长度# length(str); 155 #获取字符数函数# char_length(str); 156 #返回字符串str中最左边的x个字符# left(str,x); 157 #返回字符串str中最右边的x个字符# right(str,x); 158 #使用字符串pad对字符串str最左边进行填充,知道长度为n个字符长度# lpad(str,n,pad); 159 #使用字符串pad对字符串str最右边进行填充,知道长度为n个字符长度# rpad(str,n,pad); 160 #去掉字符串str左边的空格# ltrim(str); 161 #去掉字符串str右边的空格# rtrim(str); 162 #返回字符串str重复x次的结果# repeat(str,x); 163 #使用字符串b代替字符串str中的所有字符串a# replace(str,a,b); 164 #比较字符串str1和str2# strcmp(str1,str2); 165 #去掉字符串str行头和行尾的空格# trim(str); 166 #返回字符串str中从x位置起y个长度的字符串# substring(str,x,y); 167 #获取当前日期# curdate(); 或 current_date(); 168 #获取当前时间# curtime(); 或 current_time(); 169 #获取当前日期和时间# now();或 current_timestamp() 或 localtime() 或 systemdate(); 170 #获取日期date的UNIX时间戳# unix_timestamp(date); 171 #获取unix时间戳的日期值# from_unixtime(); 172 #返回日期date为一年中的第几周# week(date); 或 weekofyear(time); 173 #返回日期的英文周几# dayname(time); 174 #返回日期和时间中周几(1:周日,2:周一)# dayofweek(); 175 #返回日期和时间中周几(0:周一,1:周二)# weekday(); 176 #返回年中第几天# dayofyear(time); 177 #返回月中第几天# dayofmonth(time); 178 #返回日期date的年份# year(date); 179 #返回时间time的小时值# hour(time); 180 #返回时间time的分钟值# minute(time); 181 #返回时间time的月份值# monthname(date); 或 month(time) 182 #截取日期中的各部分值# extrcat(年或月或日或时或分或秒 from time); 183 #计算date1与date2之间相隔天数# datediff(date1,date2); 184 #计算date加上n天后的日期# adddate(date,n); 185 #计算date减去n天后的日期# subdate(date,n); 186 #计算time加上n秒后的时间# adddate(time,n); 187 #计算time减去n秒后的时间# subdate(time,n); 188 #返回数据库版本号# version(); 189 #返回当前数据库名# database(); 190 #返回当前用户# user(); 191 #将IP地址转化为数字# inet_aton(ip); 192 #将数字转化为IP地址# inet_ntoa(x); 193 #创建一个持续时间为time的名为name的锁# cet_loct(name,time); 194 #为名为name的锁解锁# release_loct(name); 195 #将表达式重复执行count次# benchmark(count,表达式); 196 #将x变为type形式# convert(x,type); 197 #设置字段的非空约束# create table 表名 (属性名 数据类型 not null); 198 #设置字段的默认值# create table 表名 (属性名 数据类型 default 默认值); 199 #设置字段的唯一约束# create table 表名(属性名 数据类型 unique ); 200 #设置字段的唯一约束并未约束命名# create table 表名(属性名1 数据类型 , 属性名2 数据类型 .......... constraint 约束名 unique (属性名1,属性名2......)); 201 #设置单字段为主键约束# create table 表名(属性名1 数据类型 primary key....); 202 #设置多字段为主键约束# create table 表名(属性名1 数据类型 , 属性名2 数据类型........constraint 约束名 primary key (属性名1,属性名2......)); 203 #设置字段自动增加值# create table 表名 (属性名 数据类型 auto_increment.........); 204 #设置外键约束# create table 表名 (属性名1 数据类型 , 属性名2 数据类型........ constraint 外键约束名 foreing key (外键属性名1) references 表名 (主键属性名2)); 205 #创建普通索引# create table 表名(属性名 数据类型 ,属性名 数据类型..... index或 key 索引名(可省略)(属性名 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc); 206 #在已存在表创建普通索引# create index 索引名 on 表名 ( 属性名 (长度或不写) asc或desc或不写); 或 207 alter table 表名 add index或key 索引名(属性名 (长度或不写) asc或desc或不写); 208 #创建唯一索引# create table 表名(属性名 数据类型 ,属性名 数据类型..... unique index或 key 索引名(可省略)(属性名 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc); 209 #在已存在表创建唯一索引# create unique index 索引名 on 表名 ( 属性名 (长度或不写) asc或desc或不写); 或 210 alter table 表名 add unique index或key 索引名(属性名 (长度或不写) asc或desc或不写); 211 #创建全文索引# create table 表名(属性名 数据类型 ,属性名 数据类型..... fulltext index或 key 索引名(可省略)(属性名 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc); 212 #在已存在表创建全文索引# create fulltext index 索引名 on 表名 ( 属性名 (长度或不写) asc或desc或不写); 或 213 alter table 表名 add fulltext index或key 索引名(属性名 (长度或不写) asc或desc或不写); 214 #创建多列索引# create table 表名(属性名 数据类型 ,属性名 数据类型..... index或 key 索引名(可省略)(属性名1 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc ,属性名2 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc.........); 215 #在已存在表创建多列索引# create index 索引名 on 表名 (属性名1 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc ,属性名2 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc.........); 或 216 alter table 表名 add index或key 索引名(属性名1 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc ,属性名2 (长度(可省略)) asc或desc.........);; 217 #查看索引是否用到# explain select * from 表名 where .......; 218 #删除索引# drop index 索引名 on 表名; 219 #创建视图# create view 视图名 as 查询语句; 220 #查看视图详细信息# show table status from 数据库名 like '视图名'; 或 show table status 221 #查看视图定义信息# show create view 视图名; 222 #查看视图设计信息# desc 视图名; 223 #通过系统表查看视图信息# use information_schema ; select * from views where table_name='视图名'\G; 224 #删除视图# drop view 视图名; 225 #修改视图# create or replace view 视图名 as 查询语句; 或 alter view 视图名 as 查询语句 ; 226 #创建触发器# create trigger 触发器名 before或after 触发条件(delete、insert、update) on 触发条件的操作表表名 for each row 触发语句; 227 #创建含多条语句的触发器# delimiter $$ create trigger 触发器名 before或after 触发条件(delete、insert、update) on 触发条件的操作表表名 for each row begin 触发语句1; 触发语句2;......;end $$ delimiter; 228 #查看触发器# show triggers\G 229 #通过查看系统表查看触发器信息# use information_schema; select * from triggers\G 230 #删除触发器# drop trigger 触发器名字 231 #查看错误信息# show warnings; 232 #查看支持的存储引擎# show engines; 或 show variables like 'have%'; 233 #查看默认存储引擎# show variables like 'storage_engine% '; 234 #查看MySQL的帮助文档目录列表# help contents; 235 #查看数据类型# help data types; 236 #显示当前年月日# select curdate(); 237 #显示当前年月日和时间# select now(); 238 #显示当前时间# select time(now()); 239 #显示当前年月日# select year (now()) ; 240 #创建存储过程# create procedure 存储过程名字 (存储过程参数:输入/输出类型,参数名,参数类型) 存储过程特性或不写 存储过程的语句; 241 #创建函数过程# create function 函数名字 (函数的参数:参数名,参数类型) 函数特性或不写 函数过程语句; 242 #查看存储过程# show procedure status like '存储过程名' \G 或 use information_schema; select * from routines where specific_name='存储过程名'\G 243 #查看函数过程# show function status like '函数过程' \G或 use information_schema; select * from routines where specific_name='函数过程名'\G 244 #查看存储过程定义信息# show create procedure 存储过程名\G 245 #查看函数过程定义信息# show crate function 函数名\G 246 #删除存储过程# drop procedure 存储过程名\G 247 # 删除函数# drop function 函数名\G 248 #创建普通用户账户# create user 用户名 identified by ‘密码’; 249 #创建带权限的普通用户账户# grant 权限参数:select、create、drop等 on 库.表(权限范围) to 用户名 identified by ‘密码’; 250 #更改超级用户root的密码# set password=password(“新密码”); 251 #利用root用户修改带权限的普通用户密码# grant 权限参数:select、create、drop等 on 库.表(权限范围) to 用户名 identified by ‘新密码’; 252 #利用root用户修改普通用户密码#set password for 用户名=password(“新密码”); 253 #普通用户更改自身密码#set password=password(“新密码”); 254 #删除普通用户# drop user 用户名; 或 delete from user where user=“用户名”; 255 #对普通用户进行授权# grant 权限参数:select、create、drop等 on 库.表(权限范围) to 用户名; 256 #收回权限# revoke 权限参数:select、create、drop等 on 库.表(权限范围) from 用户名; 257 #收回所有权限# revoke all privileges,grant option from 用户名;






