Vue系列教程(三)之vue-cli脚手架的使用
一、Vue-cli的环境准备
目的:(1)快速管理依赖 (2)确定项目结构
1.安装node.js
Node.js是一个可以让前端运行在服务器上的一个工。
测试node.js是否安装成功:cmd下输入node -v

1 2 | npm config set prefix F:\node\node_globalnpm config set cache F:\node\node_cache |
2. 使用npm安装vue-cli
1 2 3 4 5 6 | npm install -g @vue/cli 3.xnpm install –g vue-cli 2.xnpm: node.js包管理工具install: 安装vue-cli:要安装的工具-g:全局安装 |
3. 配置使用国内源
npm配置国内镜像
1 2 3 | npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.orgnpm config set disturl https://npm.taobao.org/distnpm config set electron_mirror https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/electron/ |
npm查看当前镜像
1 | npm config get registry |
yarn配置国内镜像
1 2 3 | yarn config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.orgyarn config set disturl https://npm.taobao.org/distyarn config set electron_mirror https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/electron/ |
yarn查看当前镜像
1 | yarn get registry |
二、使用vue-cli下载项目骨架搭建项目
- vue create 项目名称
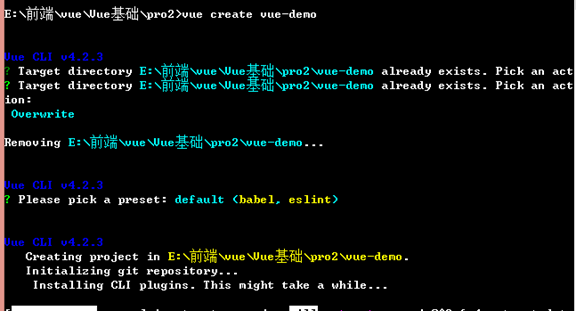
- 安装项目依赖 npm install
注:3.x版本之后创建项目时就会自动安装
-
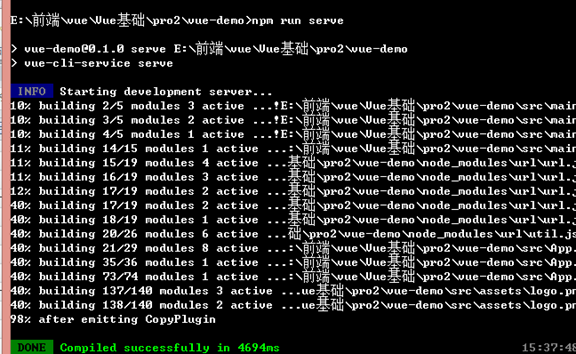
使用开发模式运行项目
npm run dev 2.x
npm run serve 3.x
此时可以在浏览器中:http://localhost:8080 访问首页

三、Vue组件的组成部分
.1. vue文件的组成部分
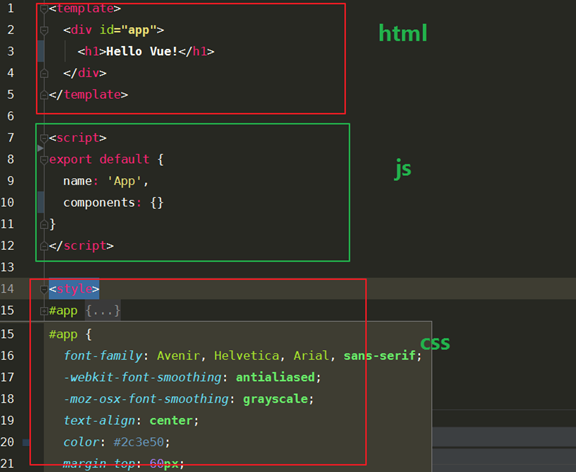
2.在vue组件中使用多个vue组件搭建一个页面
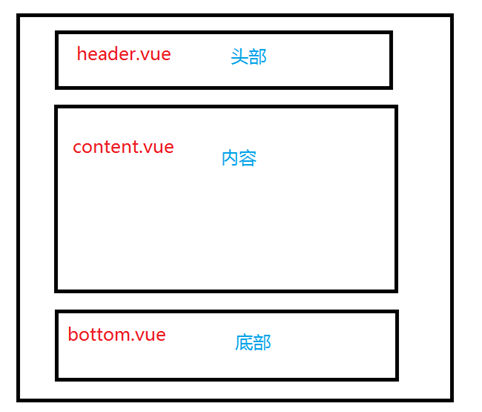
- 全局注册
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'import Header from "./components/Header";import Content from "./components/Content";import Footer from "./components/Footer";Vue.component('MyHeader', Header);Vue.component('MyContent', Content);Vue.component('MyFooter', Footer);Vue.config.productionTip = false;new Vue({ render: h => h(App),}).$mount('#app'); |
- 本地注册
在组件的内部注册另外一个组件,成为一个标签,这个标签只在该组件内部使用,而不能在其他组件内部使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | <template> <div id="app"> <MyHeader></MyHeader> <MyContent></MyContent> <MyFooter></MyFooter> </div></template><script>import Header from "./components/Header";import Content from "./components/Content";import Footer from "./components/Footer"; export default { name: 'App', components: { 'MyHeader': Header, 'MyContent': Content, 'MyFooter': Footer, }}</script> |
四、Vue组件之间的参数传递
- 父传子
App.vue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | <template> <div id="app"> <MyHeader></MyHeader> <MyContent :Mytitle="title"></MyContent> <MyFooter></MyFooter> </div></template> export default { name: 'App', components: { 'MyHeader': Header, 'MyContent': Content, 'MyFooter': Footer, }, data(){ return { title: "Hello Vue!" } }} |
content.vue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <template> <div> <h2>{{Mytitle}}</h2> 商品列表... </div></template><script> export default { name: "Content", props: ['Mytitle',] }</script> |
通过子组件的props属性,来指明可以接收的参数,父组件通过在标签中写明参数的键值对来传递参数。
props表示一个组件的参数部分,有两种写法:
(1)props:[参数列表]
比如:props:[‘MyProp1’,’MyProp2’]
(2)props:[参数名1:{type:String,required:true,default:”xx”},参数名2:{}]
- 子传父
App.vue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | <template> <div id="app"> <MyHeader></MyHeader> <MyContent :Mytitle="msg" :btnfn="change_msg"></MyContent> <MyFooter></MyFooter> </div></template><script>import Header from "./components/Header";import Content from "./components/Content";import Footer from "./components/Footer"; export default { name: 'App', components: { 'MyHeader': Header, 'MyContent': Content, 'MyFooter': Footer, }, data(){ return { msg: "Hello Vue!" } }, methods:{ change_msg(v){ this.msg = v; } }}</script> |
content.vue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | <template> <div> <h2>{{Mytitle}}</h2> 商品列表... <button type="button" @click="btnfn('hello python')">点我</button> </div></template><script> export default { name: "Content", // props: ['Mytitle',] props:{ 'Mytitle':{ type:String, required: true, default: "xx", }, 'btnfn': { type: Function, } } }</script> |
- 以事件发射的方式子传父
子组件中,使用this.$emit(‘键', ‘值’)
父组件中,在子组件标签中使用@键=”msg=$event”
Content.vue
1 2 3 4 | doClick(){ this.$emit("newName", "hello js"); }} |
App.vue
1 | <MyContent :Mytitle="msg" @newName="msg=$event"></MyContent> |
五、Vue使用Axios
- 安装axios
1 | npm install --save axios vue-axios |
- 在main.js使用axios
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | import Vue from 'vue'import axios from 'axios'import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'Vue.use(VueAxios, axios)或import Vue from 'vue'import axios from 'axios'Vue.prototype.axios = axios |
1. get请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | 方式一 this.axios({ method:'get', url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/register', params:{ "mail": this.mail, "password": this.password, }, }).then(function (response) { console.log(response.data); });方式二 const { data: res, status: status } = await this.axios.get('users/getUserList', { params: this.queryInfo }); if (status !== 200) { return this.$message.error('获取用户列表失败!') } this.userlist = res.data.users; this.total = res.data.total |
2. post请求
发送post请求: 解决axios无法传递data中的参数问题
默认情况下发送axios时请求头中的内容类型为:
Content-Type:application/json;charset=UTF-8
而如果服务端需要的是:
Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
因此,使用axios的qs内置库中的方法进行内容类型的转换。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | import Qs from 'qs'this.axios({method:'post',url:'http://localhost:8081/regist',transformRequest: [function (data) {return Qs.stringify(data)}],data:{email:this.email}}).then(function (response) {alert(response.data.message)})方式二const { data: res, status: status } = await this.axios.post('users/addOneUser', user_form); if (status !== 200) { this.$message.error('添加用户失败!') } this.$message.success('添加用户成功!') this.UserDialogVisible = false; this.getUserList() |
3.pu
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | const { data: res, status: status } = await this.axios.put('users/updateUser', user_form); if (status !== 200) { this.$message.error('更新用户信息失败!') } // 隐藏添加用户对话框 this.UserDialogVisible = false; this.$message.success('更新用户信息成功!') this.getUserList() |
4.delete
1 2 3 4 5 6 | const { data: res, status: status } = await this.axios.delete('users/deleteUser', { params:{"id": id}, }); if (status !== 200) return this.$message.error('删除用户失败!') this.$message.success('删除用户成功!'); this.getUserList() |
5. axios拦截器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | axios.interceptors.request.use(config => { NProgress.start() config.headers.Authorization = Storage.sessionGet("token"); return config})axios.interceptors.response.use( response => { NProgress.done() if (response.status >= 250 && response.status <= 260) { Storage.sessionRemove('token') // 删除已经失效或过期的token(不删除也可以,因为登录后覆盖) router.replace({path: '/Login'}).catch(err => {err}) } else if (response.data.token) { Storage.sessionSet('token', response.data.token) } return response}) |
六、解决跨域请求问题
1) 什么是跨域?
跨域,指的是浏览器不能执行其他网站的脚本。它是由浏览器的同源策略造成的,是浏览器施加的安全限制。
所谓同源是指,域名,协议,端口均相同,只要有一个不同,就是跨域。不明白没关系,举个栗子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | http://www.123.com/index.html 调用 http://www.123.com/server.php (非跨域)http://www.123.com/index.html 调用 http://www.456.com/server.php (主域名不同:123/456,跨域)http://abc.123.com/index.html 调用 http://def.123.com/server.php (子域名不同:abc/def,跨域)http://www.123.com:8080/index.html 调用 http://www.123.com:8081/server.php (端口不同:8080/8081,跨域)http://www.123.com/index.html 调用 https://www.123.com/server.php (协议不同:http/https,跨域)请注意:localhost和127.0.0.1虽然都指向本机,但也属于跨域。 |
浏览器执行javascript脚本时,会检查这个脚本属于哪个页面,如果不是同源页面,就不会被执行。
2)为何要研究跨域问题?
因为浏览器的同源策略规定某域下的客户端在没明确授权的情况下,不能读写另一个域的资源。而在实际开发中,前后端常常是相互分离的,并且前后端的项目部署也常常不在一个服务器内或者在一个服务器的不同端口下。前端想要获取后端的数据,就必须发起请求,如果不做一些处理,就会受到浏览器同源策略的约束。后端可以收到请求并返回数据,但是前端无法收到数据。
3)为何浏览器会制定同源策略
之所以有同源策略,其中一个重要原因就是对cookie的保护。cookie 中存着sessionID 。黑客一旦获取了sessionID,并且在有效期内,就可以登录。当我们访问了一个恶意网站 如果没有同源策略 那么这个网站就能通过js 访问document.cookie 得到用户关于的各个网站的sessionID 其中可能有银行网站 等等。通过已经建立好的session连接进行攻击,比如CSRF攻击。这里需要服务端配合再举个例子,现在我扮演坏人 我通过一个iframe 加载某宝的登录页面 等傻傻的用户登录我的网站的时候 我就把这个页面弹出 用户一看 阿里唉大公司 肯定安全 就屁颠屁颠的输入了密码 注意 如果没有同源策略 我这个恶意网站就能通过dom操作获取到用户输入的值 从而控制该账户所以同源策略是绝对必要的.还有需要注意的是同源策略无法完全防御CSRF。
4)跨域会阻止什么操作?
浏览器是从两个方面去做这个同源策略的,一是针对接口的请求,二是针对Dom的查询
5)多种跨域方法
跨域可以大概分为两种目的
前后端分离时,前端为了获取后端数据而跨域
为不同域下的前端页面通信而跨域
为前后端分离而跨域
ü Cross Origin Resource Share (CORS)
CORS是一个跨域资源共享方案,为了解决跨域问题,通过增加一系列请求头和响应头,规范安全地进行跨站数据传输。CORS背后的基本思想是使用自定义的HTTP头部允许浏览器和服务器相互了解对方,从而决定请求或响应成功与否.通过过滤器在response中返回头部,使服务器和浏览器可互通。
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:指定授权访问的域
Access-Control-Allow-Methods:授权请求的方法(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE,OPTIONS等)
适合设置单一的(或全部)授权访问域,所有配置都是固定的,特简单。也没根据请求的类型做不同的处理

func Cors() gin.HandlerFunc { return func(c *gin.Context) { method := c.Request.Method c.Header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*") c.Header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type,AccessToken,X-CSRF-Token, Authorization, Token") c.Header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST, GET, OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE,UPDATE") //服务器支持的所有跨域请求的方 c.Header("Access-Control-Expose-Headers", "Content-Length, Access-Control-Allow-Origin, Access-Control-Allow-Headers, Content-Type") c.Header("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true") //放行所有OPTIONS方法 if method == "OPTIONS" { c.AbortWithStatus(http.StatusNoContent) } // 处理请求 c.Next() } } func main() { r := gin.Default() r.Use(Cors(),) r.GET("/register", RegisterHandler) _ = r.Run(":8000") }
- JSONP 跨域
JSONP是前端解决跨域最实用的方法
原理就是html中 的link,href,src属性都是不受跨域影响的,link可以调用远程的css文件,href可以链接到随便的url上,图片的src可以随意引用图片,script的src属性可以随意引入不同源的js文件。JSONP既是利用了<srcipt>,那么就只能支持GET请求。其他请求无法实现
- nginx 反向代理实现跨域
七、Vue路由
路由器的功能:在数据通信时选择通信的路线。
在vue中的路由,能够在一个vue组件中实现其他组件的相互切换。也就是说,可以通过路由模块,创建路由表,将制定的组件显示在路由视图中。
1.安装路由模块
1 | npm install vue-router –s |
2.设计路由界面
3. 创建静态路由表
router.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import Home from "./components/Home";import Products from "./components/Products";export const routes = [ { path: "/Home", component: Home, }, { path: "/Products", component: Products, }]; |
4.在mian.js中使用路由模块以及注册路由表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'import VueRouter from 'vue-router'import {routes} from "./router";Vue.config.productionTip = false;Vue.use(VueRouter); // 使用路由模块// 创建一个VueRouter模块实例const router = new VueRouter({ routes: routes});new Vue({ router, render: h => h(App),}).$mount('#app'); |
5.创建路由链接和路由视图4.在mian.js中使用路由模块以及注册路由表
App.vue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <template> <div id="app"> <div> <span> <router-link to="/Home">首页</router-link> </span> <span> <router-link to="/Products">商品列表</router-link> </span> </div> <router-view></router-view> </div></template> |
6.路由之间的参数传递
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | 1. 设参 { path: "/Products/:id", component: Products, }2. 传参<router-link to="/Products/1">最新商品</router-link>3.接参this.$route.params.iddata(){ return { id: this.$route.params.id } }, |
7.路由之间跳转的方式
1)通过html中的路由<router-link to=”/Home”>首页</router-link>
2)通过js实现路由的跳转 this.$router.push("/Home").catch(err => {err});;
补充:组件样式表的作用范围
如果vue组件中的style标签没有带上scoped标签,那么这个style的样式将会作用在整个页面中,如果加上scoped标签,则样式只会作用在当前组件中。
8.嵌套路由(子路由)
路由显示的组件内部,又嵌套者路由,成为子路由。
1,嵌套路由表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | export default new Router({ routes: [ { path: "/Login", name: "Login", component: Login, }, { path: "/Backend", name: "Backend", component: Backend, children: [ { path: "/ProductList", name: "ProductList", component: ProductList, }, { path: "/ProductInfo", name: "ProductInfo", component: ProductInfo, }, ] } ]}); |
backend.vue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | <template> <el-container style="height: 500px; border: 1px solid #eee"> <el-aside width="200px" style="background-color: rgb(238, 241, 246)"> <el-menu :default-openeds="['1', '3']"> <el-submenu index="1"> <template slot="title"><i class="el-icon-message"></i>商品管理</template> <el-menu-item-group> <el-menu-item index="1-1"><router-link to="/ProductList">商品列表</router-link></el-menu-item> <el-menu-item index="1-2"><router-link to="/ProductInfo">商品信息</router-link></el-menu-item> </el-menu-item-group> </el-submenu> </el-menu> </el-aside> <el-container> <el-header style="text-align: right; font-size: 12px"> <el-dropdown> <i class="el-icon-setting" style="margin-right: 15px"></i> <el-dropdown-menu slot="dropdown"> <el-dropdown-item><a href="#">查看</a></el-dropdown-item> <el-dropdown-item><a href="#">新增</a></el-dropdown-item> <el-dropdown-item><a href="/#/Login">退出</a></el-dropdown-item> </el-dropdown-menu> </el-dropdown> <span>王小虎</span> </el-header> <el-main> <router-view></router-view> </el-main> </el-container> </el-container></template> |
说明:
(1)在<el-main>元素中配置了<router-view>用于展示嵌套路由
(2)主要使用 <router-link to=”路由”>展示嵌套路由内容
9.路由重定向
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | export default new Router({ routes: [ { path: "/Login", name: "Login", component: Login, }, { path: "/Logout", redirect: "/Login", },]}) |
10 参数传递
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | 1.使用路径匹配的方式1)修改路由配置{path: '/user/profile/:id', name:'UserProfile', component: UserProfile}2)传递参数(1)router-link<router-link :to="{name: 'UserProfile', params: {id: 1}}">个人信息</router-link>说明:此时我们将 to 改为了 :to ,是为了将这一属性当成对象使用,注意 router-link 中的 name 属性名称一定要和 路由中的 name 属性名称 匹配,因为这样 Vue 才能找到对应的路由路径;(2)js代码方式this.$router.push({ name: 'UserProfile', params: {id: 1}});3)接收参数{{ $route.params.id }} 2.使用props方式1)修改路由配置{path: '/user/profile/:id', name:'UserProfile', component: UserProfile, props: true}说明:主要增加了 props: true 属性2)传递参数同上3)接收参数export default {props: ['id'],name: "UserProfile"}模板中{{id}} |
11.路由钩子
路由钩子函数
beforeRouteEnter :在进入路由前执行
beforeRouteLeave :在离开路由前执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | export default {props: ['id'],name: "UserProfile",beforeRouteEnter: (to, from, next) => {console.log("准备进入个人信息页");next();},beforeRouteLeave: (to, from, next) => {console.log("准备离开个人信息页");next();}} |
参数说明:
-
to :路由将要跳转的路径信息
-
from :路径跳转前的路径信息
-
next :路由的控制参数
-
next() 跳入下一个页面
-
next('/path') 改变路由的跳转方向,使其跳到另一个路由
-
next(false) 返回原来的页面
-
next((vm)=>{}) 仅在 beforeRouteEnter 中可用,vm 是组件实例
生命周期执行顺序
准备进入个人信息页
-
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:17 beforeCreate
-
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:21 created
-
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:24 beforeMount
-
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:30 mounted
-
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:13 准备离开个人信息页
-
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:39 beforeDestory
-
ProductInfo.vue?ca1b:42 destory
路由文件示例

import Vue from "vue"; import Router from "vue-router" import store from "../store" // 路由懒加载 const Login = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Login_Home_Welcome_ResetPwd" */ '../view/Login.vue') const Home = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Login_Home_Welcome_ResetPwd" */ '../view/Home.vue') const Welcome = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Login_Home_Welcome_ResetPwd" */ '../view/personal/Welcome.vue') const ResetPwd = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Login_Home_Welcome_ResetOwd" */ '../view/personal/ResetPwd.vue') const Users = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Users" */ '../view/users/User.vue') const Roles = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Auth" */ '../view/authority/Roles.vue') const Menus = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Auth" */ '../view/authority/Menus.vue') const API = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Auth" */ '../view/authority/API.vue') const BaseList = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "System" */ '../view/system/Base.vue') const ClassList = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "System" */ '../view/system/Class.vue') const Course = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "System" */ '../view/system/Course.vue') const StudentList = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Students" */ '../view/student/StudentList.vue') const StudentInfo = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Students" */ '../view/student/StudentInfo.vue') const StuActivity = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Students" */ '../view/student/StuActivity.vue') const Research = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Students" */ '../view/student/Research.vue') const Grants = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Students" */ '../view/student/Grants.vue') const Rewards = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Students" */ '../view/student/Rewards.vue') const Jobs = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Students" */ '../view/student/Jobs.vue') // const ScoreImport = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Scores" */ '../view/score/ScoreImport.vue') const UploadExcel = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Scores" */ '../view/score/upload-excel.vue') const ScoreList = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Scores" */ '../view/score/ScoreList.vue') const ScoreSummary = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Scores" */ '../view/score/ScoreSummary.vue') const ScoreFilter = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Scores" */ '../view/score/ScoreFilter.vue') const Archives = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Party" */ '../view/party/Archives.vue') const PartyFilter = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Party" */ '../view/party/partyFilter.vue') const Messages = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Message" */ '../view/message/Messages.vue') const Notices = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Message" */ '../view/message/Notices.vue') const Tasks = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Message" */ '../view/message/Tasks.vue') const Error = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "Error" */ '../view/404.vue') // 注册路由 Vue.use(Router); // 配置路由 const router = new Router({ // mode: "history", routes: [ { path: "/", redirect: "/home"}, { path: "/Login", component: Login}, { path: "/home", component: Home, redirect: "/welcome", children: [ {path: "/welcome", component: Welcome}, {path: "/reset_pwd", component: ResetPwd}, {path: "/users", component: Users, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "用户列表"}}, {path: "/roles", component: Roles, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "角色列表"}}, {path: "/menus", component: Menus, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "菜单列表"}}, {path: "/api", component: API, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "API列表"}}, {path: "/base", component: BaseList, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "基础配置"}}, {path: "/class", component: ClassList, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "班级列表"}}, {path: "/course", component: Course, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "课程管理"}}, {path: "/students", component: StudentList, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "学生列表"}}, {path: "/studentInfo/:id",name: "studentInfo", component: StudentInfo, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "学生信息"}}, {path: "/stuActivity", component: StuActivity, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "学生活动"}}, {path: "/stuResearch", component: Research, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "科研管理"}}, {path: "/rewards", component: Rewards, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "获奖经历"}}, {path: "/grants", component: Grants, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "助学金"}}, {path: "/jobs", component: Jobs, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "学生就业"}}, // {path: "/scoreImport", component: ScoreImport, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "成绩导入"}}, {path: "/scoreImport", component: UploadExcel, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "成绩导入"}}, {path: "/scoreList", component: ScoreList, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "成绩列表"}}, {path: "/scoreSummary", component: ScoreSummary, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "成绩汇总"}}, {path: "/scoreFilter", component: ScoreFilter, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "成绩筛选"}}, {path: "/archives", component: Archives, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "政治档案"}}, {path: "/partyFilter", component: PartyFilter, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "党员筛选"}}, {path: "/messages", component: Messages, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "消息列表"}}, {path: "/notices", component: Notices, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "通知列表"}}, {path: "/tasks", component: Tasks, meta: {requireAuth: true, title: "任务列表"}}, {path: "/404", component: Error} ] }, { path: "*", redirect: "/404"}, ] }); router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { if (to.path === "/Login") return next() if (to.meta.requireAuth){ if (!store.getters.menu_path_map.hasOwnProperty(to.path) ) { if (!store.getters.menu_path_map.hasOwnProperty("/" + to.name)) { return next('/404') } } } const tokenStr = window.sessionStorage.getItem("token"); if (!tokenStr) return next("/Login") next() }) export default router

import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import router from "./router"; import store from "./store"; import axios from "axios" import VueAxios from "vue-axios" import Storage from "./plugins/storage" import "./assets/fonts/iconfont.css" import "element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css" import "./assets/css/global.css" import ElementUI from "element-ui" // 添加进度条效果 import NProgress from 'nprogress' import 'nprogress/nprogress.css' // 简单配置 NProgress.inc(0.2) NProgress.configure({ easing: 'ease', speed: 500, showSpinner: false, trickle: false }) // 配置请求根路径 axios.defaults.baseURL = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1" axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' axios.interceptors.request.use(config => { NProgress.start() config.headers.Authorization = Storage.sessionGet("token"); return config }) axios.interceptors.response.use( response => { NProgress.done() if (response.status >= 250 && response.status <= 260) { Storage.sessionRemove('token') // 删除已经失效或过期的token(不删除也可以,因为登录后覆盖) router.replace({path: '/Login'}).catch(err => {err}) } else if (response.data.token) { Storage.sessionSet('token', response.data.token) } return response }) Vue.filter("datetimeFormat", function(time){ let oldDate = new Date(time) let year = oldDate.getFullYear(); let month = oldDate.getMonth()+1; let day = oldDate.getDate(); let hour = oldDate.getHours(); let minute = oldDate.getMinutes(); let second = oldDate.getSeconds(); return year+"-"+month+"-"+day+" "+hour+":"+minute+":"+second; }) Vue.filter("dateFormat", function(time){ if (time == '0001-01-01T00:00:00Z') return '' let oldDate = new Date(time) let year = oldDate.getFullYear(); let month = oldDate.getMonth()+1; let day = oldDate.getDate(); let hour = oldDate.getHours(); let minute = oldDate.getMinutes(); let second = oldDate.getSeconds(); return year+"-"+month+"-"+day }) Vue.config.productionTip = false Vue.prototype.domain = "http://127.0.0.1:8000" Vue.prototype.storage = Storage Vue.use(VueAxios, axios) Vue.use(ElementUI) new Vue({ router, store, render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app')







【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 现代计算机视觉入门之:什么是图片特征编码
· .NET 9 new features-C#13新的锁类型和语义
· Linux系统下SQL Server数据库镜像配置全流程详解
· 现代计算机视觉入门之:什么是视频
· 你所不知道的 C/C++ 宏知识
· 不到万不得已,千万不要去外包
· C# WebAPI 插件热插拔(持续更新中)
· 会议真的有必要吗?我们产品开发9年了,但从来没开过会
· 【译】我们最喜欢的2024年的 Visual Studio 新功能
· 如何打造一个高并发系统?
2019-05-09 Python调用aiohttp