I2C总线
PHILIPS公司开发的两线式串行总线
GPIO模拟i2c驱动中有自己的一套传输算法。GPIO模拟I2C是要占用CPU资源的,而用I2C芯片是不占CPU资源的
特点
接口线少,控制方式简单,器件封装形式小,通信速率较高
特征
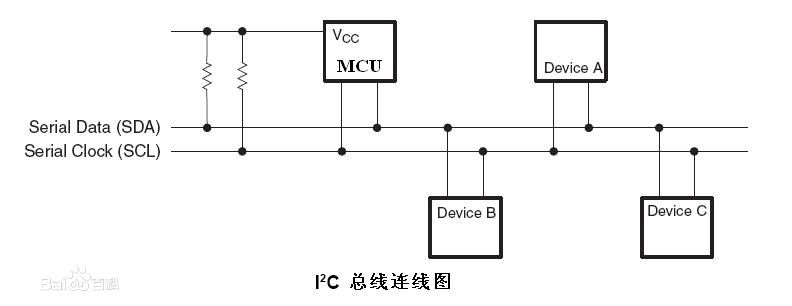
- 一条串行数据线SDA,一条串行时钟线SCL
- 它是一个真正的多主机总线,如果两个或更多主机同时初始化,数据传输可以通过冲突检测和仲裁防止数据被破坏
- 串行的8位双向数据传输位速率在标准模式下可达100kbit/s,快速模式下可达400kbit/s,高速模式下可达3.4Mbit/s
- 连接到相同总线的IC数量只受到总线的最大电容400pF限制
架构
- I2C core框架
提供了核心数据结构的定义和相关接口函数,用来实现I2C适配器。驱动和设备驱动的注册、注销管理
实现在/drivers/i2c目录下的i2c-core.c和i2c-dev.c - I2C总线驱动
定义描述具体I2C总线适配器的i2c_adapter数据结构、实现在具体I2C适配器上的I2C总线通信方法,并由i2c_algorithm数据结构进行描述。 经过I2C总线驱动的的代码,可以为我们控制I2C产生开始位、停止位、读写周期以及从设备的读写、产生ACK等
实现在/drivers/i2c目录下busses文件夹。例如:Linux I2C GPIO总线驱动为i2c_gpio.c;I2C总线算法在/drivers/i2c目录下algos文件夹。例如:Linux I2C GPIO总线驱动算法实现在i2c_algo_bit.c - I2C设备驱动
对具体I2C硬件驱动的实现。I2C 设备驱动通过I2C适配器与CPU通信。其中主要包含i2c_driver和i2c_client数据结构,i2c_driver结构对应一套具体的驱动方法,例如:probe、remove、suspend等,需要自己申明;i2c_client数据结构由内核根据具体的设备注册信息自动生成
实现在/drivers/i2c目录下chips文件夹
设备连接图
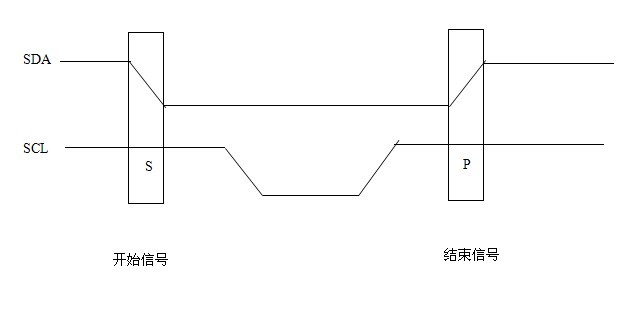
波形图
开始信号:当SCL为高电平时,SDA由高电平向低电平跳变,表示将要开始传输数据
结束信号:当SCL为高电平时,SDA由低电平向高电平跳变,表示结束传输数据
i2c_client
struct i2c_client
{
unsigned short flags; //标志位
unsigned short addr; //设备的地址,低7位为芯片地址
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; //设备的名称,最大为20个字节
struct i2c_adapter *adapter; //依附的适配器i2c_adapter,适配器指明所属的总线
struct i2c_driver *driver; //指向设备对应的驱动程序
struct device dev; //设备结构体
int irq; //设备申请的中断号
struct list_head list; //连接到总线上的所有设备
struct list_head detected; //已经被发现的设备链表
struct completion released; //是否已经释放的完成量
};
地址码
1101000x
读地址:11010001 = 0xd1
写地址:11010000 = 0xd0
设备地址:01101000 = 0x68 //高位补0 地址码
i2c_driver
struct i2c_driver
{
int id; //驱动标识ID
unsigned int class; //驱动的类型
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *); //当检测到适配器时调用的函数
int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *); //卸载适配器时调用的函数
int (*detach_client)(struct i2c_client *) __deprecated; //卸载设备时调用的函数
/*以下是一种新类型驱动需要的函数,这些函数支持IIC设备动态插入和拔出。如果不想支持只实现上面3个。要不实现上面3个。
要么实现下面5个。不能同时定义*/
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *); //新类型设备探测函数
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *); //新类型设备的移除函数
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *); //关闭IIC设备
int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_messge_t mesg); //挂起IIC设备
int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *); //恢复IIC设备
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg); //使用命令使设备完成特殊的功能。类似ioctl()函数
struct devcie_driver driver; //设备驱动结构体
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table; //设备ID表
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, int kind, struct i2c_board_info *); //自动探测设备的回调函数
const struct i2c_client_address_data *address_data; //设备所在的地址范围
struct list_head clients; //指向驱动支持的设备
};
i2c_adapter
struct i2c_adapter
{
struct module *owner; //模块计数
unsigned int id; //alogorithm的类型,定义于i2c_id.h中
unsigned int class; //允许探测的驱动类型
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; //指向适配器的驱动程序
void *algo_data; //指向适配器的私有数据,根据不同的情况使用方法不同
int (*client_register)(struct i2c_client *); //设备client注册时调用
int (*client_unregister(struct i2c_client *); //设备client注销时调用
u8 level;
struct mutex bus_lock; //对总线进行操作时,将获得总线锁
struct mutex clist_lock; //链表操作的互斥锁
int timeout; //超时
int retries; //重试次数
struct device dev; //指向适配器的设备结构体
int nr;
struct list_head clients; //连接总线上的设备的链表
char name[48]; //适配器名称
struct completion dev_released; //用于同步的完成量
};
i2c_algorithm
struct i2c_algorithm
{
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msg, int num);
//传输函数指针,指向实现IIC总线通信协议的函数,用来确定适配器支持那些传输类型
int (*smbus_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr, unsigned short flags, char read_write, u8 command, int size,
union i2c_smbus_data *data); /*smbus方式传输函数指针,指向实现SMBus总线通信协议的函数。
SMBus和IIC之间可以通过软件方式兼容,所以这里提供了一个函数,但是一般都赋值为NULL*/
u32 (*functionality)(struct i2c_adapter *); //返回适配器支持的功能
};
i2c_msg
struct i2c_msg
{
__u16 addr; //IIC设备地址。这个字段说明一个适配器在获得总线控制权后,可以与多个IIC设备进行交互
__u16 flags; //消息类型标志
__u16 len; //消息字节长度
__u8 *buf; //指向消息数据的缓冲区
};
i2c_adapter 与 i2c_algorithm
i2c_adapter 对应于物理上的一个适配器,而 i2c_algorithm 对应一套通信方法。一个 I2C 适配器需要 i2c_algorithm 中提供的通信函数来控制适配器上产生特定的访问周期。缺少 i2c_algorithm 的 i2c_adapter 什么也做不了,因此 i2c_adapter 中包含其使用的 i2c_algorithm 的指针
i2c_algorithm 中的关键函数 master_xfer() 用于产生 I2C 访问周期需要的信号,以 i2c_msg为单位
i2c_driver 与 i2c_client
i2c_driver 对应一套驱动方法,是纯粹的用于辅助作用的数据结构,它不对应于任何的物理实体。 i2c_client 对应于真实的物理设备,每个 I2C 设备都需要一个 i2c_client 来描述。 i2c_client 一般被包含在 i2c 字符设备的私有信息结构体中
i2c_driver 与 i2c_client 发生关联的时刻在 i2c_driver 的 attach_adapter() 函数被运行时。 attach_adapter() 会探测物理设备,当确定一个 client 存在时,把该 client 使用的 i2c_client 数据结构的 adapter 指针指向对应的 i2c_adapter
driver 指针指向该 i2c_driver ,并会调用 i2c_adapter 的 client_register() 函数。相反的过程发生在 i2c_driver 的 detach_client() 函数被调用的时候
i2c_adpater 与 i2c_client
i2c_adpater 与 i2c_client 的关系与 I2C 硬件体系中适配器和设备的关系一致,即 i2c_client 依附于 i2c_adpater 。由于一个适配器上可以连接多个 I2C 设备,所以一个 i2c_adpater 也可以被多个 i2c_client 依附, i2c_adpater 中包括依附于它的 i2c_client 的链表
SMBus
SMBus 是 I2C 的子集
- i2c_smbus_read_byte
从设备读取一个字节(不定义位置偏移,使用以前发起的命令的偏移)。意义不大,无基地址 - i2c_smbus_write_byte
从设备写入一个字节(使用以前发起的命令的偏移) - i2c_smbus_write_quick
向设备发送一个比特 - i2c_smbus_read_byte_data
从设备指定偏移处读取一个字节。第一个msg用来传送读的基地址,第二个msg用来读取数据 - i2c_smbus_write_byte_data
向设备指定偏移处写入一个字节。传送两个msg - i2c_smbus_read_word_data
从设备指定偏移处读取二个字节 - i2c_smbus_write_word_data
向设备指定偏移处写入二个字节 - i2c_smbus_read_block_data
从设备指定偏移处读取一块数据 - i2c_smbus_write_block_data
向设备指定偏移处写入一块数据(<= 32 字节)
上面的一系列函数最终都是调用的i2c_smbus_xfer()函数
/**
* i2c_smbus_xfer - execute SMBus protocol operations
* @adapter: Handle to I2C bus
* @addr: Address of SMBus slave on that bus
* @flags: I2C_CLIENT_* flags (usually zero or I2C_CLIENT_PEC)
* @read_write: I2C_SMBUS_READ or I2C_SMBUS_WRITE
* @command: Byte interpreted by slave, for protocols which use such bytes
* @protocol: SMBus protocol operation to execute, such as I2C_SMBUS_PROC_CALL
* @data: Data to be read or written
*
* This executes an SMBus protocol operation, and returns a negative
* errno code else zero on success.
*/
s32 i2c_smbus_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adapter, u16 addr, unsigned short flags,
char read_write, u8 command, int protocol,
union i2c_smbus_data *data)
{
unsigned long orig_jiffies;
int try;
s32 res;
/* If enabled, the following two tracepoints are conditional on
* read_write and protocol.
*/
trace_smbus_write(adapter, addr, flags, read_write,
command, protocol, data);
trace_smbus_read(adapter, addr, flags, read_write,
command, protocol);
flags &= I2C_M_TEN | I2C_CLIENT_PEC | I2C_CLIENT_SCCB;
if (adapter->algo->smbus_xfer) {
i2c_lock_adapter(adapter);
/* Retry automatically on arbitration loss */
orig_jiffies = jiffies;
for (res = 0, try = 0; try <= adapter->retries; try++) {
res = adapter->algo->smbus_xfer(adapter, addr, flags,
read_write, command,
protocol, data);
if (res != -EAGAIN)
break;
if (time_after(jiffies,
orig_jiffies + adapter->timeout))
break;
}
i2c_unlock_adapter(adapter);
if (res != -EOPNOTSUPP || !adapter->algo->master_xfer)
goto trace;
/*
* Fall back to i2c_smbus_xfer_emulated if the adapter doesn't
* implement native support for the SMBus operation.
*/
}
res = i2c_smbus_xfer_emulated(adapter, addr, flags, read_write,
command, protocol, data);
trace:
/* If enabled, the reply tracepoint is conditional on read_write. */
trace_smbus_reply(adapter, addr, flags, read_write,
command, protocol, data);
trace_smbus_result(adapter, addr, flags, read_write,
command, protocol, res);
return res;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_smbus_xfer);
首先在判断主控制器是否支持smbus_xfer传输,但是通常i2c主控制器都是不支持的,所以直接调用i2c_smbus_xfer_emulated()函数





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!