python(六):python的四种配置文件
参考:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/PBLiKCNivXdTH5Fufou3UA
1. ini
.ini 文件是Initialization File的缩写,即初始化文件,是windows的系统配置文件所采用的存储格式,统管windows的各项配置。
1.1 ini文件的定义
.ini 文件通常由节(Section)、键(key)和值(value)组成。具体形式如下:
; 关于mysql的一个小配置
; db.ini
[mysql]
host = 127.0.0.1
port = 3306
user = root
password = 123456
database = test
1.2 python读取ini文件
使用python内置的 configparser 标准库进行解析ini文件。
read()读取文件内容items()获取指定节的所有键值对
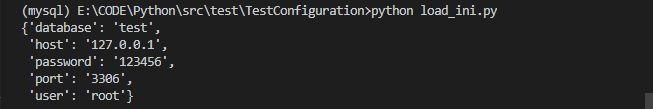
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
* @Author : bpf
* @Date : 2020-10-14 22:11:06
* @Description : 读取ini文件
* @LastEditTime : 2020-10-14 22:41:53
'''
from configparser import ConfigParser
from pprint import pprint
import mysql.connector as MySQL
ini_file = "E:\\CODE\\Python\\src\\test\\TestConfiguration\\db.ini"
db_name = "mysql"
cfg = ConfigParser()
# 读取文件内容
cfg.read(ini_file)
# cfg.items()返回list,元素为tuple
db_cfg = dict(cfg.items(db_name))
# 打印参数
pprint(db_cfg)
# 连接数据库
con = MySQL.connect(**db_cfg)
con.close()
2. json
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation,) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
2.1 json文件的定义
语法格式:
简单小示例:
{
"mysql": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3306,
"user": "root",
"password": "123456",
"database": "test"
}
}
2.2 python读取json文件
使用python内置的 json 标准库进行解析ini文件。
load()从json文件中读取json格式数据loads()将字符串类型数据转化为json格式数据dump()将json格式数据保存到文件dumps()将json格式数据保存为字符串类型
'''
* @Author : bpf
* @Date : 2020-10-14 22:39:44
* @Description : 读取json文件
* @LastEditTime : 2020-10-14 23:17:48
'''
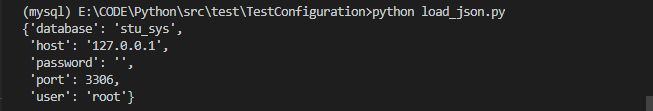
import json
from pprint import pprint
import mysql.connector as MySQL
json_file = "E:\\CODE\\Python\\src\\test\\TestConfiguration\\db.json"
db_name = "mysql"
with open(json_file) as f:
cfg = json.load(f)[db_name]
pprint(cfg)
con = MySQL.connect(**cfg)
con.close()
import pandas as pd import json excel_table = pd.read_excel("all_0723.xlsx", sheet_name="data") """句子""" sentence = excel_table["句子"] """句子标签""" label = excel_table["句子标签"] """语义类别""" semantic_cls = excel_table["语义类别"] """语义编号""" semantic_code = excel_table["语义编号"] label_to_code = {} code_to_label = {} for s,l,c,code in zip(sentence, label, semantic_cls, semantic_code): if str(c) != "nan": label_to_code[l] = (c, code) code_to_label[code] = (c, l) with open("label_to_code.json", "w", encoding="utf8") as f: json.dump(label_to_code, f, ensure_ascii=False) with open("code_to_label.json", "w", encoding="utf8") as f: json.dump(code_to_label, f, ensure_ascii=False) with open("label_to_code.json", "r", encoding="utf8") as f: a = json.load(f) print(a)
3. toml
TOML 是 Github 联合创始人 Tom Preston-Werner 所提出的一种配置文件格式,是一种旨在成为一个小规模、易于使用的语义化的配置文件格式,它被设计为可以无二义性的转换为一个哈希表。
3.1 定义toml文件
语法:
TOML的语法广泛地由key = "value"、[节名]、#注释构成。
支持以下数据类型:字符串、整形、浮点型、布尔型、日期时间、数组和图表。
# db.toml
[mysql]
[mysql.config]
host = "127.0.0.1"
user = "root"
port = 3306
password = "123456"
database = "test"
[mysql.parameters]
pool_size = 5
charset = "utf8"
[mysql.fields]
course_cols = ["cno", "cname", "ccredit", "cdept"]
3.2 python读取toml文件
使用外部库 toml 解析toml文件。
安装:
pip install toml
语法:CSDN
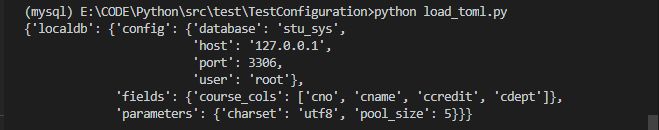
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
* @Author : bpf
* @Date : 2020-10-14 23:24:05
* @Description : 读取toml文件
* @LastEditTime : 2020-10-14 23:31:07
'''
import toml
from pprint import pprint
import mysql.connector as MySQL
toml_file = "E:\\CODE\\Python\\src\\test\\TestConfiguration\\db.toml"
cfg = toml.load(toml_file)
pprint(cfg)
conn = MySQL.connect(**cfg["mysql"]['config'])
conn.close()
4. yaml
YAML(YAML Ain't a Markup Language", YAML不是一种标记语言) 格式是目前较为流行的一种配置文件,它早在 2001 由一个名为 Clark Evans 的人提出;同时它也是目前被广泛使用的配置文件类型。
4.1 定义yaml文件
语法:
# db.yaml
mysql:
config:
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 3306
user: "root"
password: ""
database: "stu_sys"
parameters:
pool_size: 5
charset: "utf8"
fileds:
course_cols:
- cno
- cname
- ccredit
- cdept
4.2 python读取yaml文件
使用外部库 pyyaml 解析toml文件。
安装:
pip install pyyaml
语法:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
* @Author : bpf
* @Date : 2020-10-14 23:34:37
* @Description : 读取yaml文件
* @LastEditTime : 2020-10-14 23:39:58
'''
import yaml
from pprint import pprint
import mysql.connector as MySQL
yaml_file = "E:\\CODE\\Python\\src\\test\\TestConfiguration\\db.yaml"
with open(yaml_file, 'r') as f:
cfg = yaml.safe_load(f)
pprint(cfg)
conn = MySQL.connect(**cfg['mysql']['config'])
conn.close()






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧