Spring Boot入门系列(九)如何实现异步执行任务
前面介绍了Spring Boot 如何整合定时任务,不清楚的朋友可以看看之前的文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangweizhong/category/1657780.html。
今天主要讲解Spring Boot中的另外一个任务:异步任务。所谓异步任务,其实就是异步执行程序,有些时候遇到一些耗时的的任务,如果一直卡等待,肯定会影响其他程序的执行,所以就让这些程序需要以异步的方式去执行。那么下面就来介绍Spring Boot 如何实现异步任务。
一、使用注解@EnableAsync 开启异步调用方法
在application启动类中,加上@EnableAsync注解,Spring Boot 会自动扫描异步任务。
package com.weiz;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
@SpringBootApplication
//扫描 mybatis mapper 包路径
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.weiz.mapper")
//扫描 所有需要的包, 包含一些自用的工具类包 所在的路径
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.weiz","org.n3r.idworker"})
//开启定时任务
@EnableScheduling
//开启异步调用方法
@EnableAsync
public class SpringBootStarterApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootStarterApplication.class, args);
}
}
二、创建异步执行类,定义@Component及@Async组件
创建com.weiz.tasks包,在tasks包里增加AsyncTask 异步任务类,加上@Component 注解,然后在需要异步执行的方法前面加上@Async注解,这样Spring Boot容器扫描到相关异步方法之后,调用时就会将这些方法异步执行。
package com.weiz.tasks; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class AsyncTask { @Async public Future<Boolean> doTask11() throws Exception { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(1000); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("任务1耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"); return new AsyncResult<>(true); } @Async public Future<Boolean> doTask22() throws Exception { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(700); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("任务2耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"); return new AsyncResult<>(true); } @Async public Future<Boolean> doTask33() throws Exception { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Thread.sleep(600); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("任务3耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"); return new AsyncResult<>(true); } }
说明:@Async 加上这个注解,就表示该方法是异步执行方法。
三、调用
创建一个DoTask调用类,我们看看这几个方法,是怎么执行的:
package com.weiz.tasks; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("tasks") public class DoTask { @Autowired private AsyncTask asyncTask; @RequestMapping("test1") public String test1() throws Exception { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Future<Boolean> a = asyncTask.doTask11(); Future<Boolean> b = asyncTask.doTask22(); Future<Boolean> c = asyncTask.doTask33(); while (!a.isDone() || !b.isDone() || !c.isDone()) { if (a.isDone() && b.isDone() && c.isDone()) { break; } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); String times = "任务全部完成,总耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒"; System.out.println(times); return times; } }
四、测试
启动程序之后,在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/tasks/test1 。
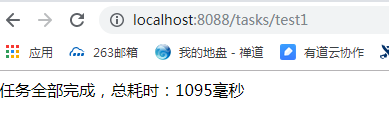
从这个总耗时可以看出,三个方法确实是异步执行的。耗时接近时间最长的doTask11方法。
最后
以上,就把Spring Boot 创建异步任务的方法简单介绍完了,是不是特别简单。
这个系列课程的完整源码,也会提供给大家。大家关注我的微信公众号(架构师精进),回复:springboot源码。获取这个系列课程的完整源码。
作者:章为忠
如有问题,可以微信:18618243664 联系我,非常感谢。
关注我的微信公众号,获取相关的 源代码及视频资料。







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
2015-03-26 记录一次阻塞引发的系统超时