并发(3) 容器
容器类中提供的ArrayList、HashMap、HashSet不是线程安全的,并发包下提供了类似功能的线程安全的集合。
| 类 | 说明 | 原理 |
| ConcurrentHashMap | ||
| ConcurrentSkipListMap | ||
| ConcurrentSkipListSet | ||
| CopyOnWriteArrayList | ||
| CopyOnWriteArraySet |
队列是一种数据结构,它以一种先进先出的方式管理数据。如果你试图向一个 已经满了的阻塞队列中添加一个元素或者是从一个空的阻塞队列中移除一个元索,将导致线程阻塞。
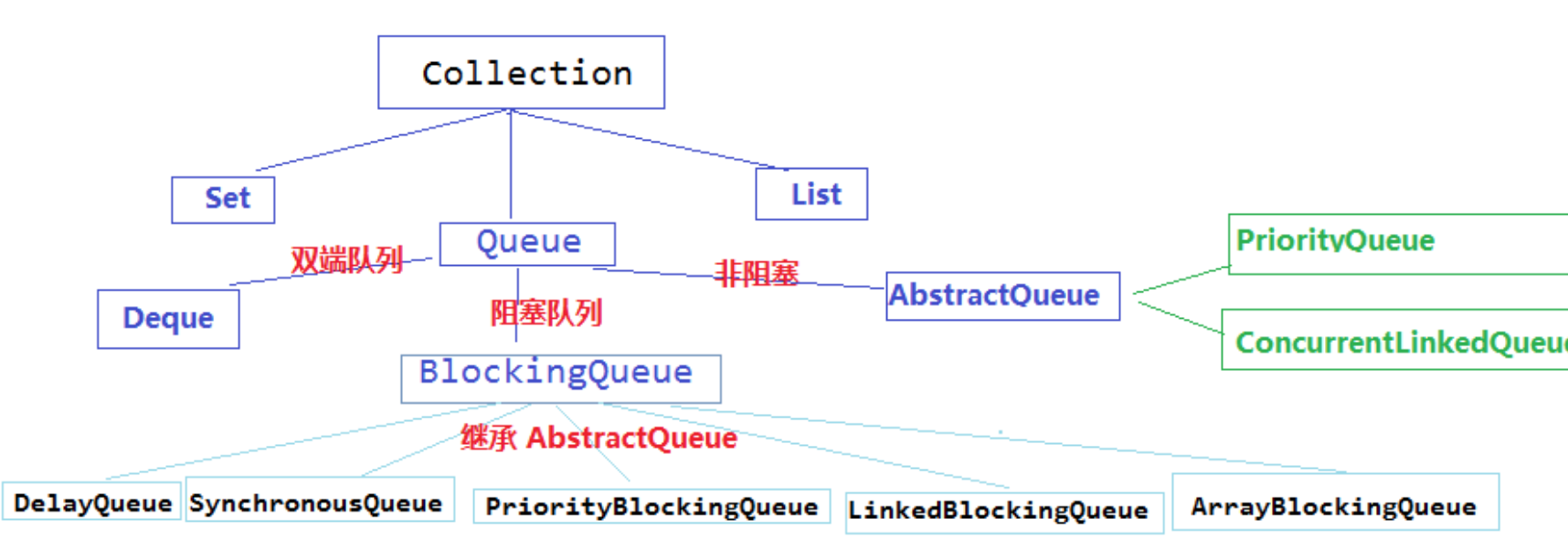
队列操作:
| 方法 | 说明 |
| boolean add(E e) | 添加一个元素到队列中,如果队列已满,则抛出异常 |
| E remove() | 移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常 |
| E element() | 返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常 |
| boolean offer(E e) | 添加一个元素到队列中,如果队列已满,返回false |
| offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 添加一个元素到队列中,等待指定时间,如果队列已满,返回false |
| E poll() | 移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,返回null |
| E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 移除并返回队列头部的元素,等待指定时间,如果队列为空,返回null |
| E peek() | 返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,返回null |
| void put(E e) | 返回队列头部的元素,如果队列已满,阻塞 |
| E take() | 移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空,阻塞 |
数组实现
ArrayBlockingQueue
Qeueu的数组实现,底层使用一个数组实现,数组大小不可变,使用一个count表示当前元素个数,使用putIndex表示当前尾的index,使用takeIndex表示当前头的index,putindex不一定比takeindex大,是在数组连续的循环。使用一个ReentrantLock控制读写并发。使用两个Condition来阻塞数组为空时消费或者数组满时生产的线程,当数组中有数据或者有空间时唤醒。迭代器中使用一个index指向下一个元素位置;

1 public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> 2 implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable { 3 4 //存储数据数组 5 final Object[] items; 6 //头index 7 int takeIndex; 8 //尾index 9 int putIndex; 10 //队列长度 11 int count; 12 //锁 13 final ReentrantLock lock; 14 //非空条件 15 private final Condition notEmpty; 16 //非满条件 17 private final Condition notFull; 18 //初始化 19 public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) { 20 this(capacity, false); 21 } 22 public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) { 23 if (capacity <= 0) 24 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 25 this.items = new Object[capacity]; 26 lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); 27 notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); 28 notFull = lock.newCondition(); 29 } 30 public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair, 31 Collection<? extends E> c) { 32 this(capacity, fair); 33 34 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 35 lock.lock(); // Lock only for visibility, not mutual exclusion 36 try { 37 int i = 0; 38 try { 39 for (E e : c) { 40 checkNotNull(e); 41 items[i++] = e; 42 } 43 } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 44 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 45 } 46 count = i; 47 putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i; 48 } finally { 49 lock.unlock(); 50 } 51 } 52 //新增一个元素 53 public boolean add(E e) { 54 return super.add(e); 55 } 56 57 //新增一个元素 58 public boolean offer(E e) { 59 checkNotNull(e); 60 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 61 lock.lock(); 62 try { 63 //如果已满,返回false,否则添加到队列中 64 if (count == items.length) 65 return false; 66 else { 67 enqueue(e); 68 return true; 69 } 70 } finally { 71 lock.unlock(); 72 } 73 } 74 //新增一个元素 75 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { 76 checkNotNull(e); 77 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 78 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 79 try { 80 //如果已满,等待,否则添加到队列中 81 while (count == items.length) 82 notFull.await(); 83 enqueue(e); 84 } finally { 85 lock.unlock(); 86 } 87 } 88 //添加一个元素 89 private void enqueue(E x) { 90 final Object[] items = this.items; 91 items[putIndex] = x; 92 if (++putIndex == items.length) 93 putIndex = 0; 94 count++; 95 notEmpty.signal(); 96 } 97 //获取头部元素 98 public E poll() { 99 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 100 lock.lock(); 101 try { 102 //如果为空返回null,否则返回头部元素 103 return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue(); 104 } finally { 105 lock.unlock(); 106 } 107 } 108 //获取头部元素 109 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 110 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 111 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 112 try { 113 //如果为空阻塞,否则返回头部元素 114 while (count == 0) 115 notEmpty.await(); 116 return dequeue(); 117 } finally { 118 lock.unlock(); 119 } 120 } 121 //获取头部元素 122 private E dequeue() { 123 // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; 124 // assert items[takeIndex] != null; 125 final Object[] items = this.items; 126 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 127 E x = (E) items[takeIndex]; 128 items[takeIndex] = null; 129 if (++takeIndex == items.length) 130 takeIndex = 0; 131 count--; 132 if (itrs != null) 133 itrs.elementDequeued(); 134 notFull.signal(); 135 return x; 136 } 137 }
LinkedBlockingQueue
Qeueu的列表实现,底层使用一个单向链表实现。大小可变也可以设定大小。使用一个节点作为头节点,不存储数据;使用一个节点作为尾节点,存储数据,使用两个ReentrantLock分别控制读写锁,头节点不存储数据也是避免读写并发冲突,count使用了原子变量也是为了避免读写冲突。
因为使用了读写锁,所以吞吐量要比ArrayBlockingQueue好。对内存和GC的影响会大于ArrayBlockingQueue。

1 public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> 2 implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable { 3 private static final long serialVersionUID = -6903933977591709194L; 4 //链表节点 5 static class Node<E> { 6 E item; 7 8 /** 9 * One of: 10 * - the real successor Node 11 * - this Node, meaning the successor is head.next 12 * - null, meaning there is no successor (this is the last node) 13 */ 14 Node<E> next; 15 16 Node(E x) { item = x; } 17 } 18 //队列容量 19 private final int capacity; 20 //队列元素个数 21 private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(); 22 //头节点 23 transient Node<E> head; 24 //尾节点 25 private transient Node<E> last; 26 //取数据锁 27 private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock(); 28 29 private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition(); 30 //存数据锁 31 private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock(); 32 33 private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition(); 34 35 public LinkedBlockingQueue() { 36 this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); 37 } 38 39 public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) { 40 if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 41 this.capacity = capacity; 42 last = head = new Node<E>(null); 43 } 44 //存放元素 45 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { 46 if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 47 int c = -1; 48 Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); 49 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; 50 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 51 putLock.lockInterruptibly(); 52 try { 53 //如果到达容量,则等待 54 while (count.get() == capacity) { 55 notFull.await(); 56 } 57 enqueue(node); 58 c = count.getAndIncrement(); 59 if (c + 1 < capacity) 60 notFull.signal(); 61 } finally { 62 putLock.unlock(); 63 } 64 if (c == 0) 65 signalNotEmpty(); 66 } 67 68 //存放元素 69 public boolean offer(E e) { 70 if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 71 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 72 if (count.get() == capacity) 73 return false; 74 int c = -1; 75 Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); 76 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; 77 putLock.lock(); 78 try { 79 //如果到达容量,返回false 80 if (count.get() < capacity) { 81 enqueue(node); 82 c = count.getAndIncrement(); 83 if (c + 1 < capacity) 84 notFull.signal(); 85 } 86 } finally { 87 putLock.unlock(); 88 } 89 if (c == 0) 90 signalNotEmpty(); 91 return c >= 0; 92 } 93 private void enqueue(Node<E> node) { 94 // assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); 95 // assert last.next == null; 96 last = last.next = node; 97 } 98 //获取元素 99 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 100 E x; 101 int c = -1; 102 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 103 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; 104 takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); 105 try { 106 //如果队列为空,则等待 107 while (count.get() == 0) { 108 notEmpty.await(); 109 } 110 x = dequeue(); 111 c = count.getAndDecrement(); 112 if (c > 1) 113 notEmpty.signal(); 114 } finally { 115 takeLock.unlock(); 116 } 117 if (c == capacity) 118 signalNotFull(); 119 return x; 120 } 121 //获取元素 122 public E poll() { 123 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 124 if (count.get() == 0) 125 return null; 126 E x = null; 127 int c = -1; 128 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; 129 takeLock.lock(); 130 try { 131 //如果队列为空,返回null 132 if (count.get() > 0) { 133 x = dequeue(); 134 c = count.getAndDecrement(); 135 if (c > 1) 136 notEmpty.signal(); 137 } 138 } finally { 139 takeLock.unlock(); 140 } 141 if (c == capacity) 142 signalNotFull(); 143 return x; 144 } 145 private E dequeue() { 146 // assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); 147 // assert head.item == null; 148 Node<E> h = head; 149 Node<E> first = h.next; 150 h.next = h; // help GC 151 head = first; 152 E x = first.item; 153 first.item = null; 154 return x; 155 } 156 //获取元素 157 public E peek() { 158 if (count.get() == 0) 159 return null; 160 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; 161 takeLock.lock(); 162 try { 163 Node<E> first = head.next; 164 if (first == null) 165 return null; 166 else 167 return first.item; 168 } finally { 169 takeLock.unlock(); 170 } 171 } 172 }
SynchronousQueue
PriorityBlockingQueue
优先级队列,按照自定义的优先级顺序进行读取。底层使用一个数组实现二叉堆。大小可变且无边界。
DelayQueue
延时队列,底层使用一个PriorityQueue实现,使用一个ReentrantLock控制并发。其实就是在每次往优先级队列中添加元素,然后以元素的delay/过期值作为排序的因素,以此来达到先过期的元素会拍在队首,每次从队列里取出来都是最先要过期的元素

1 public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E> 2 implements BlockingQueue<E> { 3 4 private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 5 private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>(); 6 private Thread leader = null; 7 private final Condition available = lock.newCondition(); 8 9 public DelayQueue() {} 10 //向队列中添加元素,因为是无边界队列,所以不会抛异常 11 public boolean add(E e) { 12 return offer(e); 13 } 14 //向队列中添加元素 15 public boolean offer(E e) { 16 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 17 lock.lock(); 18 try { 19 q.offer(e); 20 if (q.peek() == e) { 21 leader = null; 22 available.signal(); 23 } 24 return true; 25 } finally { 26 lock.unlock(); 27 } 28 } 29 //向队列中添加元素,因为是无边界队列,所以不会阻塞 30 public void put(E e) { 31 offer(e); 32 } 33 //从队列总获取数据 34 public E poll() { 35 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 36 lock.lock(); 37 try { 38 E first = q.peek(); 39 if (first == null || first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS) > 0) 40 return null; 41 else 42 return q.poll(); 43 } finally { 44 lock.unlock(); 45 } 46 } 47 //从队列总获取数据,如果队列为空,则阻塞 48 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 49 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 50 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 51 try { 52 for (;;) { 53 E first = q.peek(); 54 if (first == null) 55 available.await(); 56 else { 57 long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS); 58 if (delay <= 0) 59 return q.poll(); 60 first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting 61 if (leader != null) 62 available.await(); 63 else { 64 Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread(); 65 leader = thisThread; 66 try { 67 available.awaitNanos(delay); 68 } finally { 69 if (leader == thisThread) 70 leader = null; 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 } finally { 76 if (leader == null && q.peek() != null) 77 available.signal(); 78 lock.unlock(); 79 } 80 } 81 82 public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { 83 long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); 84 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 85 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 86 try { 87 for (;;) { 88 E first = q.peek(); 89 if (first == null) { 90 if (nanos <= 0) 91 return null; 92 else 93 nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos); 94 } else { 95 long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS); 96 if (delay <= 0) 97 return q.poll(); 98 if (nanos <= 0) 99 return null; 100 first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting 101 if (nanos < delay || leader != null) 102 nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos); 103 else { 104 Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread(); 105 leader = thisThread; 106 try { 107 long timeLeft = available.awaitNanos(delay); 108 nanos -= delay - timeLeft; 109 } finally { 110 if (leader == thisThread) 111 leader = null; 112 } 113 } 114 } 115 } 116 } finally { 117 if (leader == null && q.peek() != null) 118 available.signal(); 119 lock.unlock(); 120 } 121 } 122 // 123 public E peek() { 124 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 125 lock.lock(); 126 try { 127 return q.peek(); 128 } finally { 129 lock.unlock(); 130 } 131 } 132 133 134 }






