机器学习(四) 分类算法--K近邻算法 KNN (上)
一、K近邻算法基础
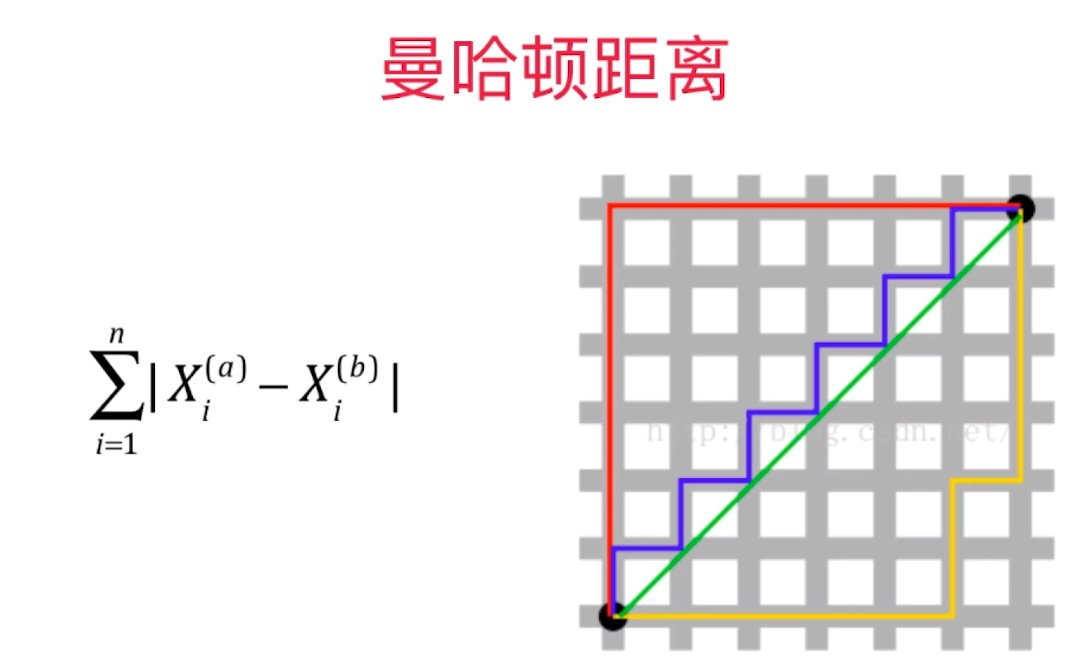
KNN------- K近邻算法--------K-Nearest Neighbors
思想极度简单
应用数学知识少 (近乎为零)
效果好(缺点?)
可以解释机器学习算法使用过程中很多细节问题
更完整的刻画机器学习应用的流程
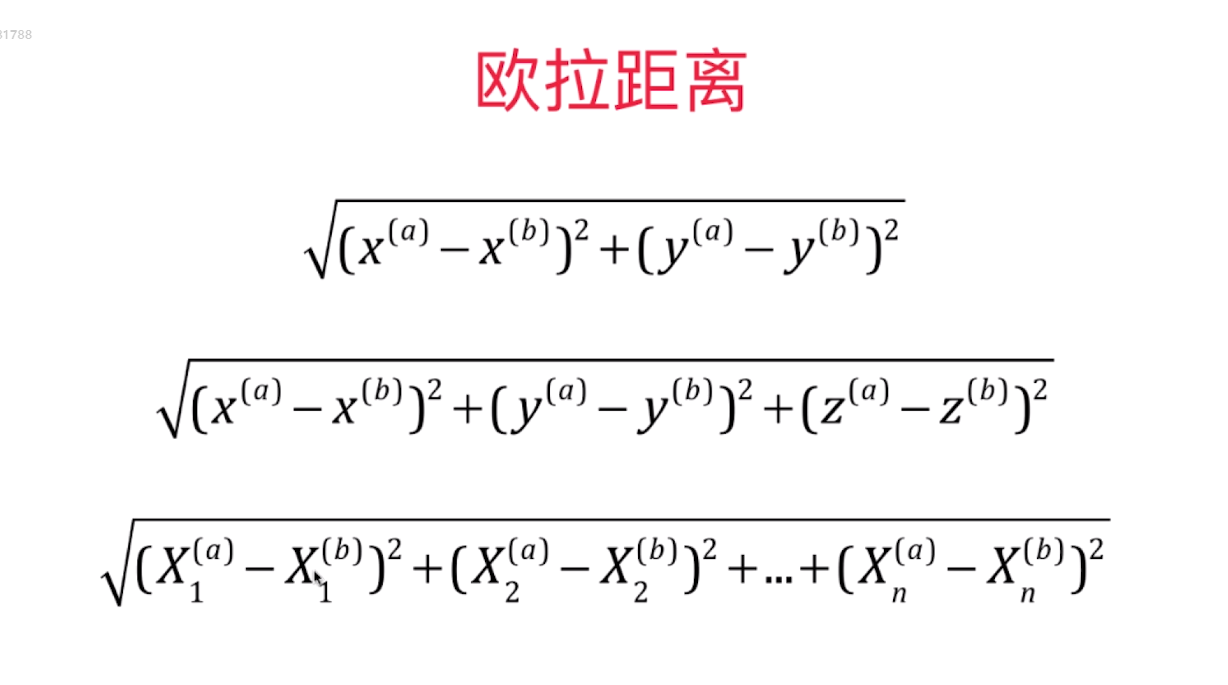
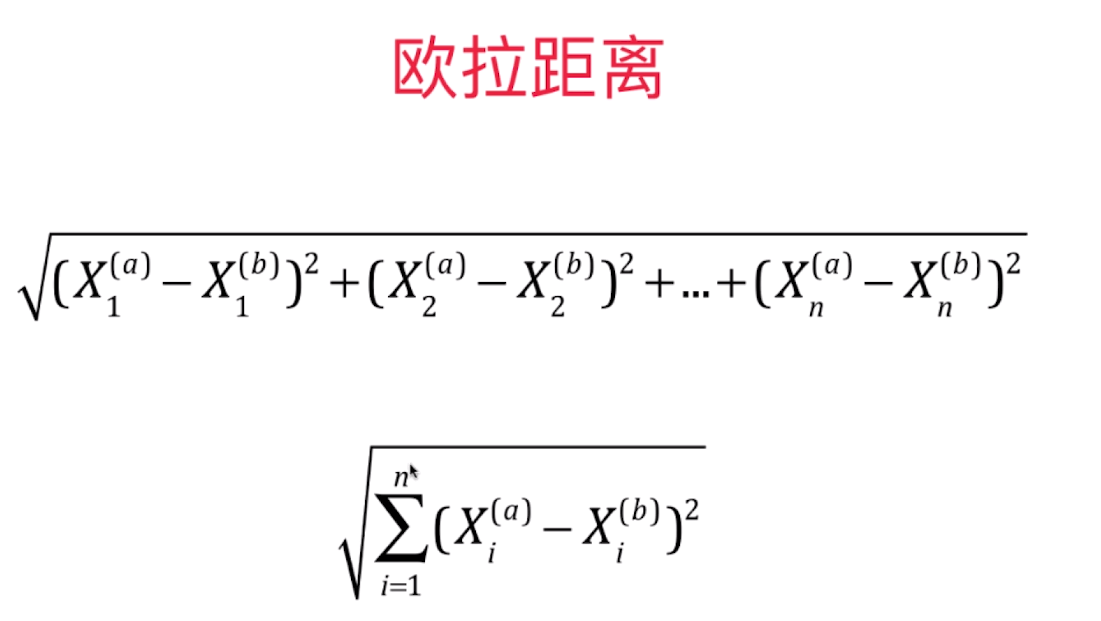
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 实现我们自己的 kNN 创建简单测试用例 raw_data_X = [[3.393533211, 2.331273381], [3.110073483, 1.781539638], [1.343808831, 3.368360954], [3.582294042, 4.679179110], [2.280362439, 2.866990263], [7.423436942, 4.696522875], [5.745051997, 3.533989803], [9.172168622, 2.511101045], [7.792783481, 3.424088941], [7.939820817, 0.791637231] ] raw_data_y = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] X_train = np.array(raw_data_X) y_train = np.array(raw_data_y) X_train array([[ 3.39353321, 2.33127338], [ 3.11007348, 1.78153964], [ 1.34380883, 3.36836095], [ 3.58229404, 4.67917911], [ 2.28036244, 2.86699026], [ 7.42343694, 4.69652288], [ 5.745052 , 3.5339898 ], [ 9.17216862, 2.51110105], [ 7.79278348, 3.42408894], [ 7.93982082, 0.79163723]]) y_train array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])

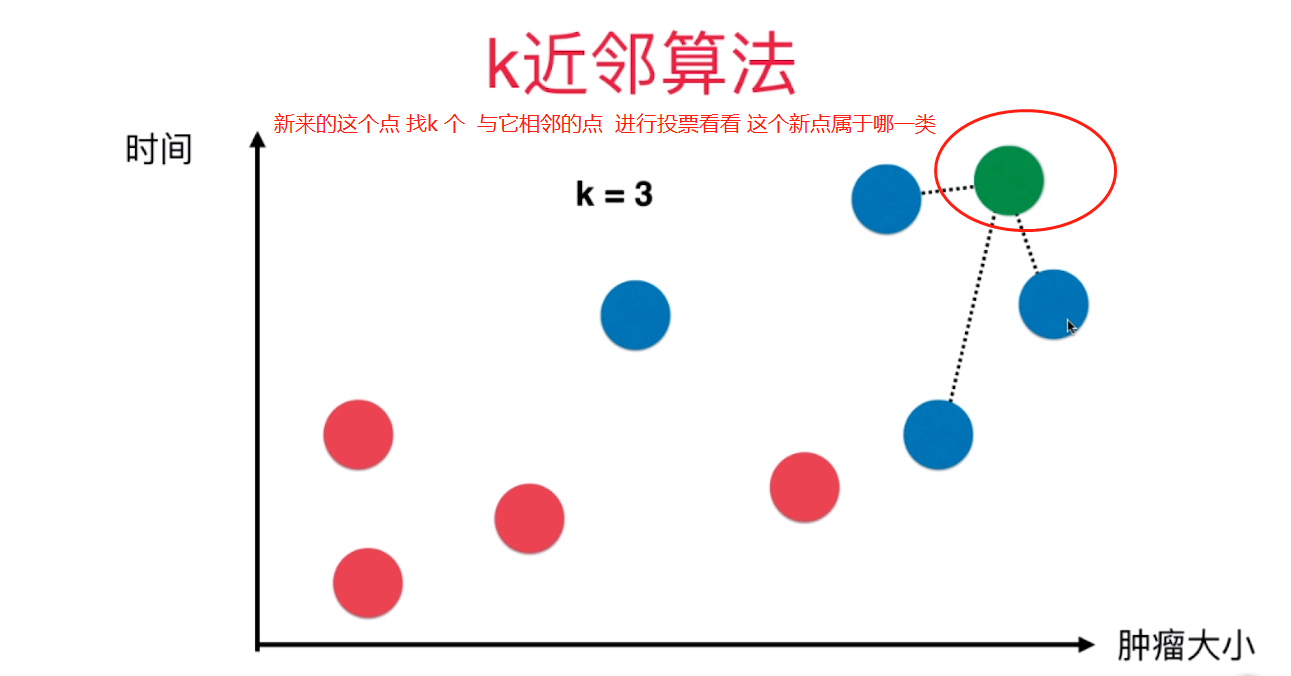
kNN的过程
from math import sqrt distances = [] for x_train in X_train: d = sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2)) distances.append(d) distances [4.812566907609877, 5.229270827235305, 6.749798999160064, 4.6986266144110695, 5.83460014556857, 1.4900114024329525, 2.354574897431513, 1.3761132675144652, 0.3064319992975, 2.5786840957478887] distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2)) for x_train in X_train] distances [4.812566907609877, 5.229270827235305, 6.749798999160064, 4.6986266144110695, 5.83460014556857, 1.4900114024329525, 2.354574897431513, 1.3761132675144652, 0.3064319992975, 2.5786840957478887] np.argsort(distances) array([8, 7, 5, 6, 9, 3, 0, 1, 4, 2]) nearest = np.argsort(distances) k = 6 topK_y = [y_train[neighbor] for neighbor in nearest[:k]] topK_y [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0] from collections import Counter votes = Counter(topK_y) votes Counter({0: 1, 1: 5}) votes.most_common(1) [(1, 5)] predict_y = votes.most_common(1)[0][0] predict_y 1
二、scikit-learn 中的机器学习算法封装
KNN/KNNN.py
import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter class KNNClassifier: def __init__(self, k): """初始化kNN分类器""" assert k >= 1, "k must be valid" self.k = k self._X_train = None self._y_train = None def fit(self, X_train, y_train): """根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器""" assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \ "the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train" assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0], \ "the size of X_train must be at least k." self._X_train = X_train self._y_train = y_train return self def predict(self, X_predict): """给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量""" assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None, \ "must fit before predict!" assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1], \ "the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict] return np.array(y_predict) def _predict(self, x): """给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值""" assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1], \ "the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2)) for x_train in self._X_train] nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]] votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] def __repr__(self): return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
kNN_function/KNN.py
import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter def kNN_classify(k, X_train, y_train, x): assert 1 <= k <= X_train.shape[0], "k must be valid" assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \ "the size of X_train must equal to the size of y_train" assert X_train.shape[1] == x.shape[0], \ "the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2)) for x_train in X_train] nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [y_train[i] for i in nearest[:k]] votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0]

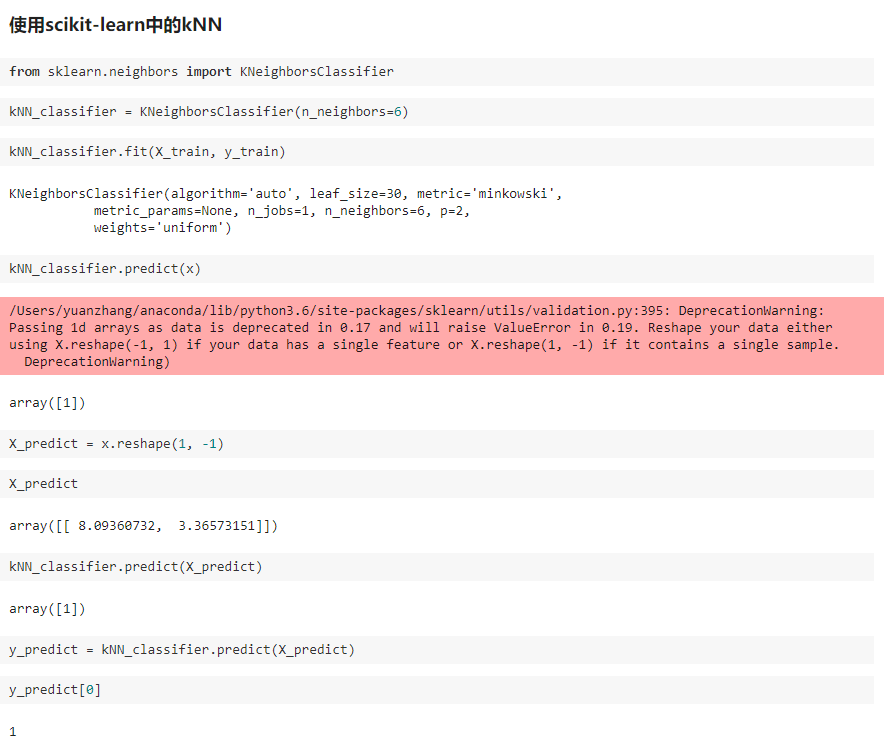
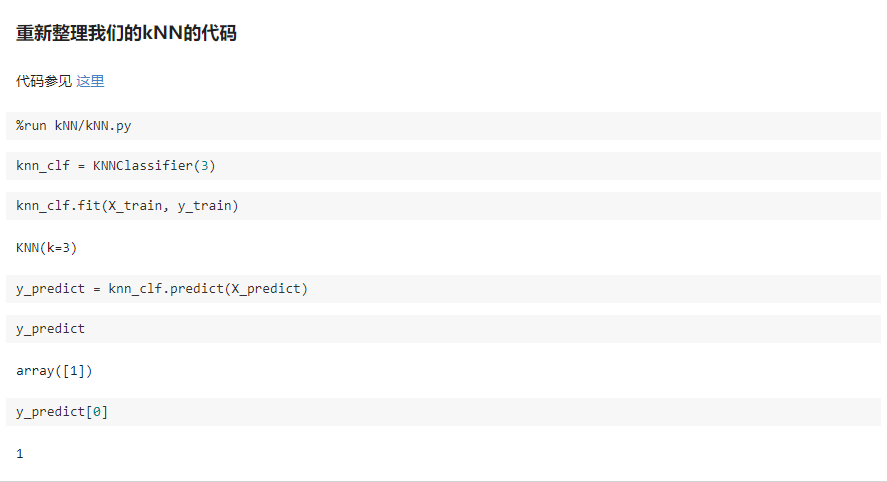
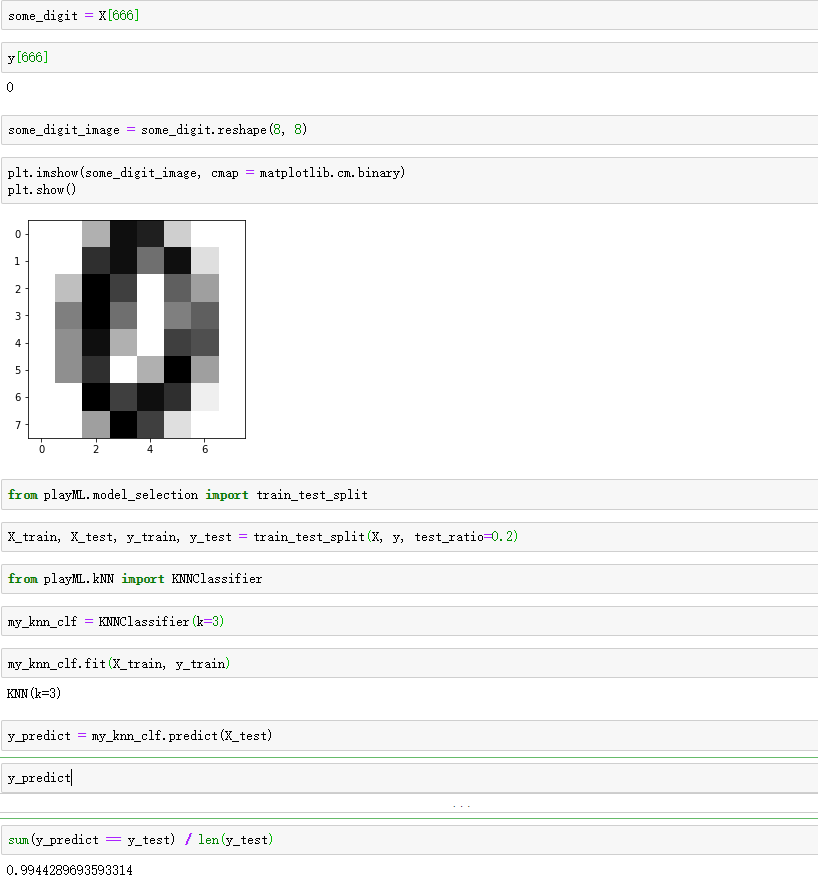
三、训练数据集、测试数据集
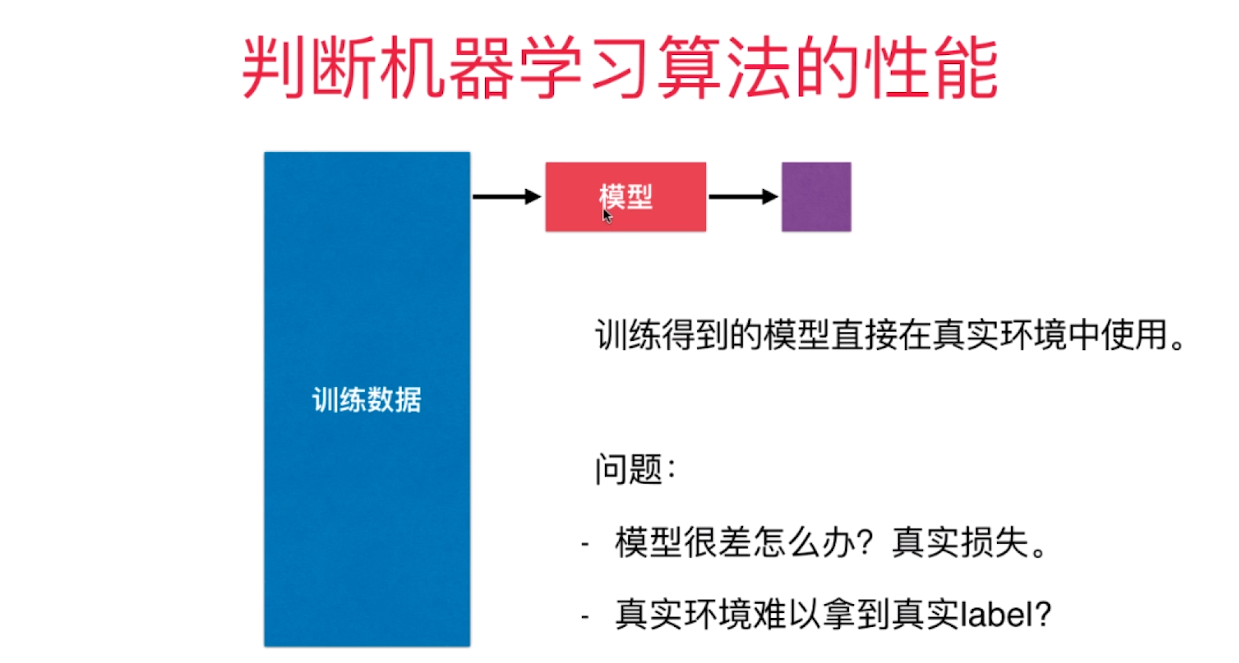
判断机器学习算法的性能
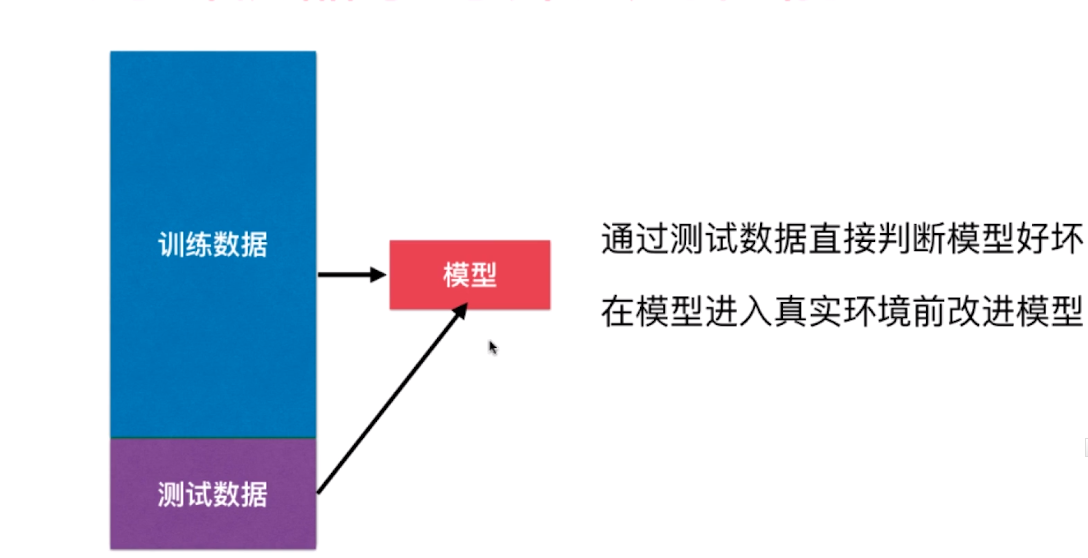
playML/KNN.py
import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter class KNNClassifier: def __init__(self, k): """初始化kNN分类器""" assert k >= 1, "k must be valid" self.k = k self._X_train = None self._y_train = None def fit(self, X_train, y_train): """根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器""" assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \ "the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train" assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0], \ "the size of X_train must be at least k." self._X_train = X_train self._y_train = y_train return self def predict(self, X_predict): """给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量""" assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None, \ "must fit before predict!" assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1], \ "the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict] return np.array(y_predict) def _predict(self, x): """给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值""" assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1], \ "the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2)) for x_train in self._X_train] nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]] votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] def __repr__(self): return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
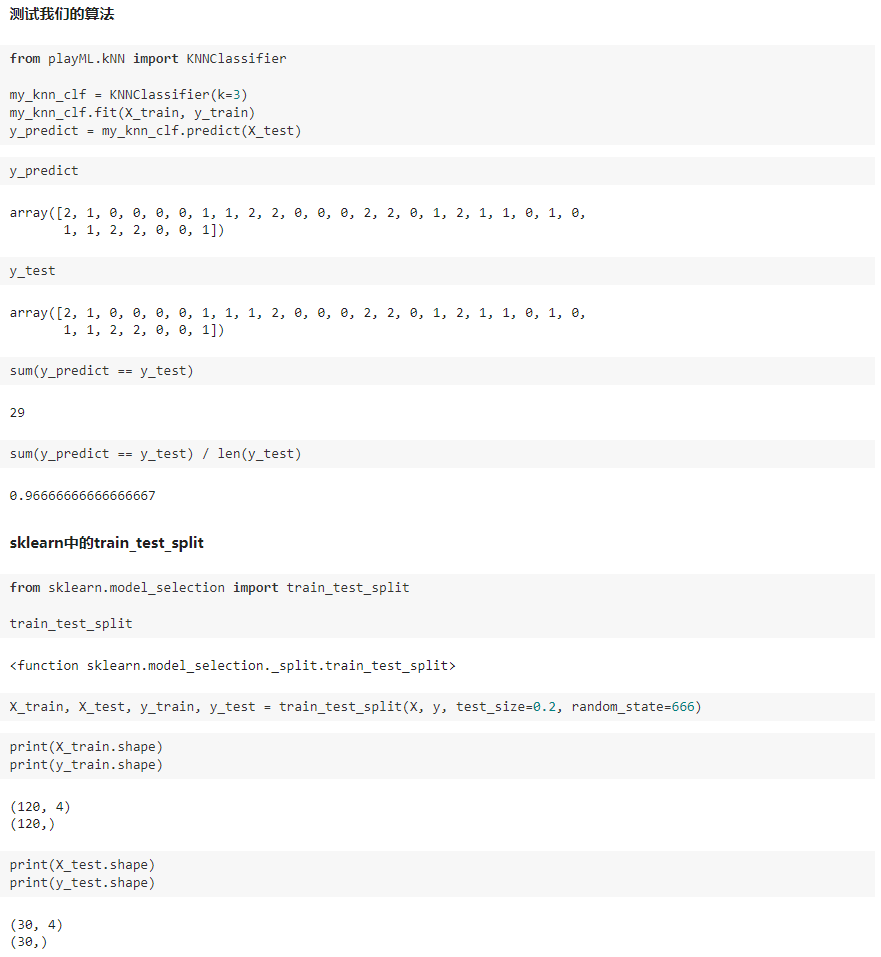
playML/model_selection.py
import numpy as np def train_test_split(X, y, test_ratio=0.2, seed=None): """将数据 X 和 y 按照test_ratio分割成X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test""" assert X.shape[0] == y.shape[0], \ "the size of X must be equal to the size of y" assert 0.0 <= test_ratio <= 1.0, \ "test_ration must be valid" if seed: np.random.seed(seed) shuffled_indexes = np.random.permutation(len(X)) test_size = int(len(X) * test_ratio) test_indexes = shuffled_indexes[:test_size] train_indexes = shuffled_indexes[test_size:] X_train = X[train_indexes] y_train = y[train_indexes] X_test = X[test_indexes] y_test = y[test_indexes] return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
playML/__init__.py



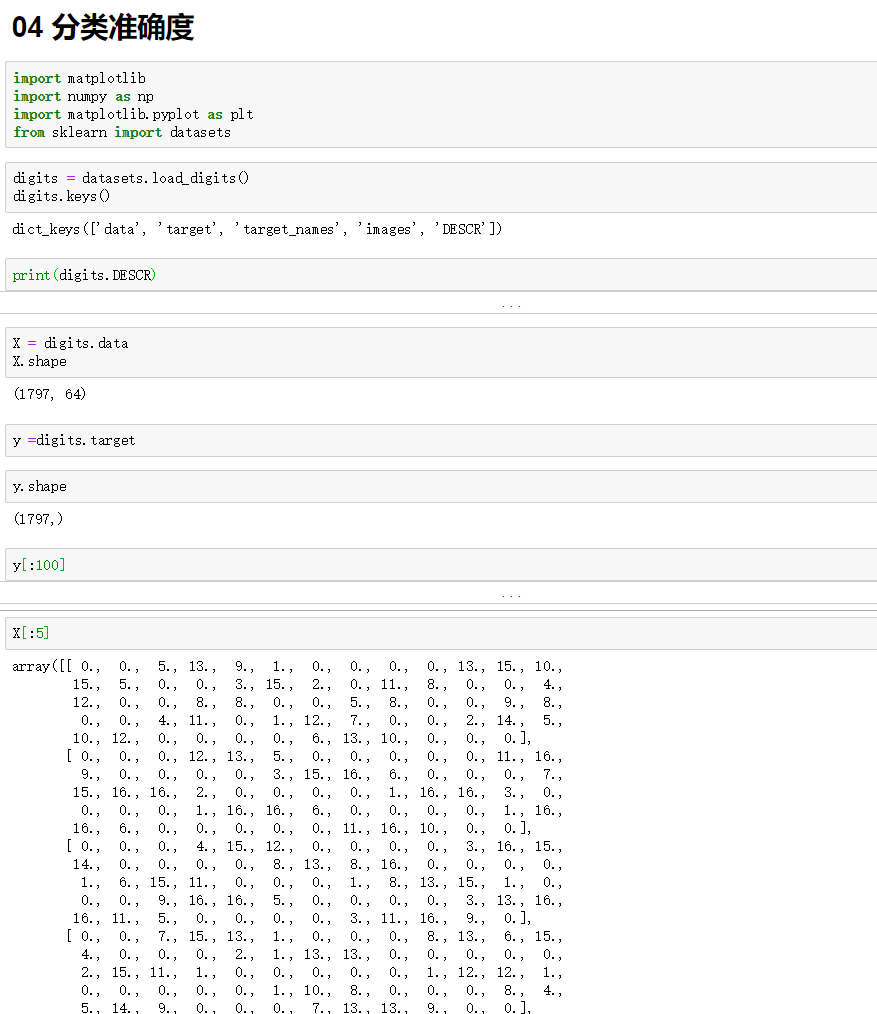
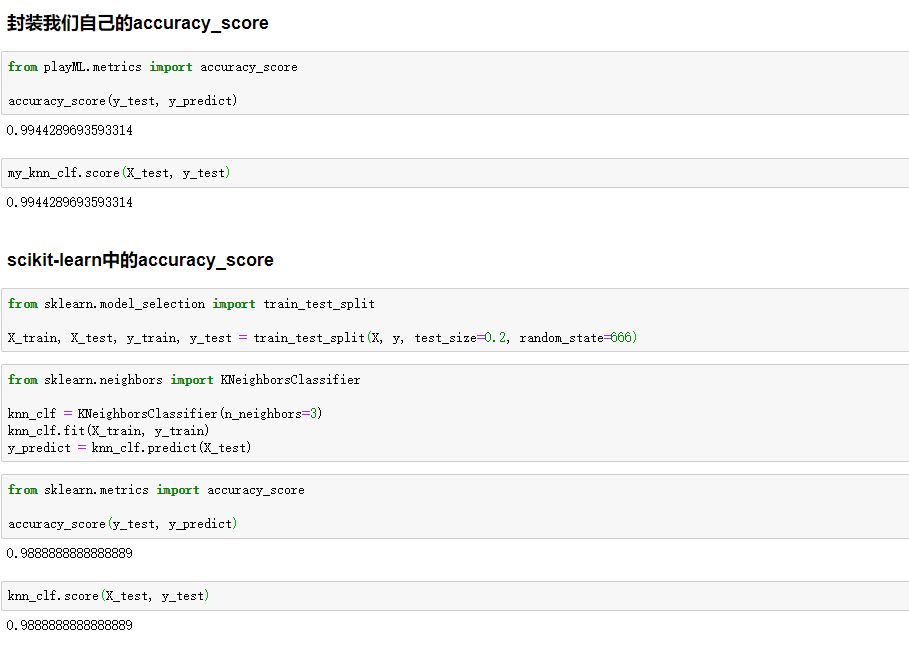
四、分类的准确度
playML/metrics.py
import numpy as np def accuracy_score(y_true, y_predict): '''计算y_true和y_predict之间的准确率''' assert y_true.shape[0] == y_predict.shape[0], \ "the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict" return sum(y_true == y_predict) / len(y_true)
model_selection.py-->KNNClassifier 类 里面添加 这样一个方法
from .metrics import accuracy_score def score(self, X_test, y_test): """根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度""" y_predict = self.predict(X_test) return accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
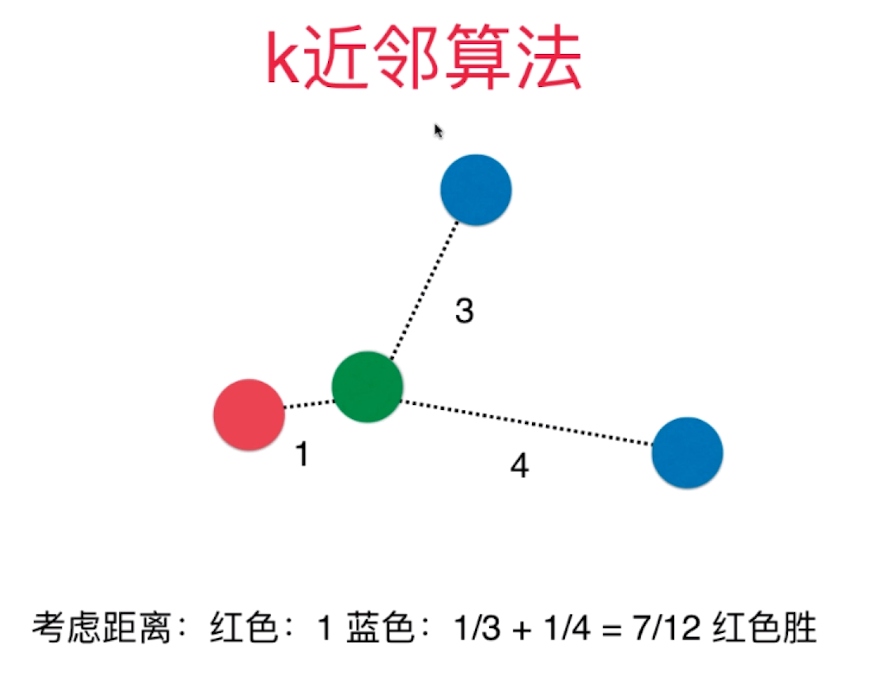
五、超参数
超参数:在算法运行前需要决定的参数
模型参数:算法过程中学习的参数
KNN算法没有模型参数
KNN算法中的 K 是 典型的 超参数
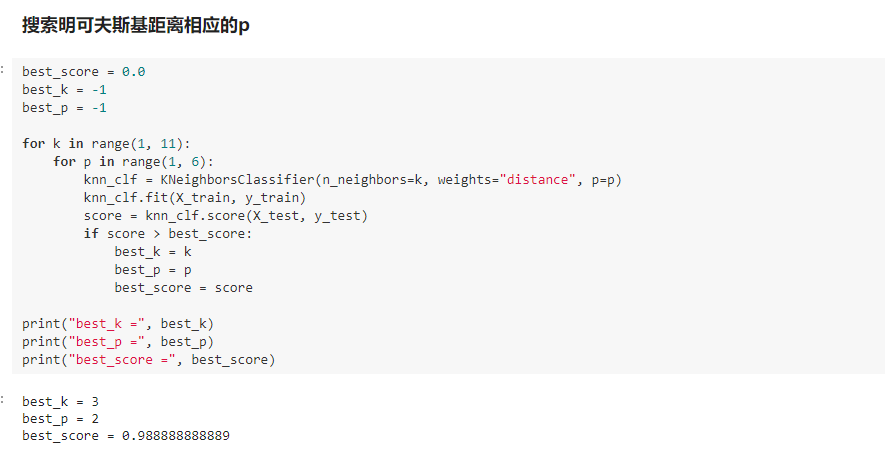
寻找好的超参数:
领域知识、经验数值、实验搜索





我写的文章只是我自己对bobo老师讲课内容的理解和整理,也只是我自己的弊见。bobo老师的课 是慕课网出品的。欢迎大家一起学习。
我曾拾到过一束光,日落时还给了夕阳。




