DRF认证源码、频率、过滤、自定义异常类、Response
DRF认证源码、频率、过滤、自定义异常类、Response
1.认证功能
有的接口必须登录才可以访问 ,其实就是判断登录状态
写一个类继承BaseAuthentication, 重写authenticate方法
全局使用 和局部使用
由于python是鸭子类型 ,认证类 不需要显示的继承BaseAuthentication 只要他重写了authenticate方法 就可以 #但是为了约束最好是继承 方法里是逻辑判断,返回一个当前登录对象,和auth 不满足 抛异常AuthenticationFailed 或者APIException 但是为了规范 用AuthenticationFailed 他里面其实也继承了APIException
1.1认证源码
#APIView的self都是视图类的对象 差找不到再去父类找
1.APIView ----里面的dispatch ----self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.perform_authentication(request) 认证
self.check_permissions(request) 权限
self.check_throttles(request) 频率
2.perform_authentication这个方法里只有request.user 这个request 是drf的request封装后的request 去Request类中找user这个属性或者方法
3.@property 类封装成属性 可以直接调用 ; @property setter 写入用
4.发现user 是方法封装成属性 里面进行了反射和上下文管理器 然后执行了self._authenticate() 目前这个self是Request类的对象在这里面找_authenticate方法
5._authenticate方法 :for authenticator in self.authenticators: 这个authenticators是在哪来的 在上面发现self.authenticators = authenticators or ()
然后__init__里面authenticators=None 可以初始化类时候传入
6.类初始化
Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), #这时候传进来的 这个self是继承APIView产生的对象
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
)
7.去找get_authenticators方法
#列表生成式
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]
#发现authentication_classes 如果对象里面定义了 那么他存放的是类 取出一个类()执行 生成对象 现在对象中找authentication_classes如果没有去父类APIView找
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
#发现是从配置文件中获取
8.所以Request类产生对象时候传入的 authenticators=self.get_authenticators()
是类产生的一个个对象
9.一直到了第五步里面的authenticators是对象 循环他 就是一个个对象 拿到了认证类的对象
10.里面调用了对象.authenticate方法 接受返回值
11.判断返回值是否为None 目前的self是Request类产生的对象,这个是封装后的request
12. 因为在dispatch request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
这个request是Request产生的对象 ,所以request.user可以取到值 在十一步赋值了
2.频率
2.1频率简介
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
#BaseThrottle里面有
1) AnonRateThrottle
限制所有匿名未认证用户,使用IP区分用户。
使用DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES['anon'] 来设置频次
2)UserRateThrottle
限制认证用户,使用User id 来区分。
使用DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES['user'] 来设置频次
3)ScopedRateThrottle
限制用户对于每个视图的访问频次,使用ip或user id。
2.2频率使用
#频率 限制ip一分钟只能访问三次
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle
class MyThrottling(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'ip_1_3'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
#返回什么就以什么做限制,返回的是客户端ip地址
return request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
全局配置 settings
#全局配置频率
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': ['app01.auth.MyThrottling'],
# Throttling
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'ip_1_3': '3/m', #key:对应频率scope属性的值 value:一分钟访问三次 3/m
},
局部配置>>>视图类配置
throttle_classes = [MyThrottling]
3.过滤
3.1过滤简介
对于列表数据可能需要根据字段进行过滤,我们可以通过添加django-fitlter扩展来增强支持。
3.2过滤使用
安装django-filter
pip install django-filter
3.2.1全局配置

REST_FRAMEWORK 加入全局配置 k/v形式 value:是一个元组所以加逗号
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
...
'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS': ('django_filters.rest_framework.DjangoFilterBackend',)
}
3.2.2使用
class Book1(ListAPIView):
#必须指定queryset和serializer_class
queryset = models.Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
#这句话是配置类以什么过滤条件
filter_fields = ('title',)
注意 因为继承了ListAPIView所以路由正常写
路由
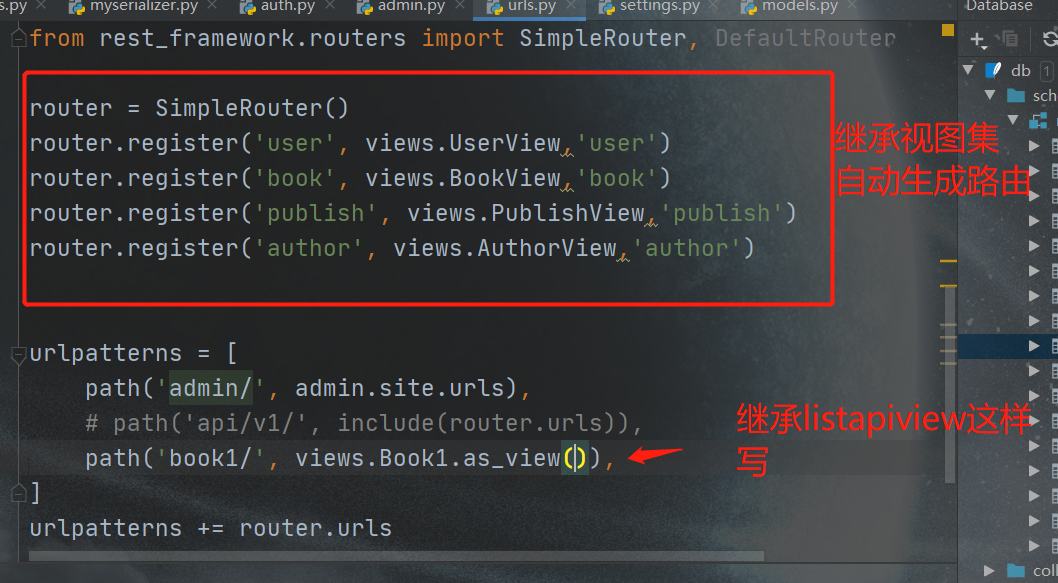
全部数据

过滤数据
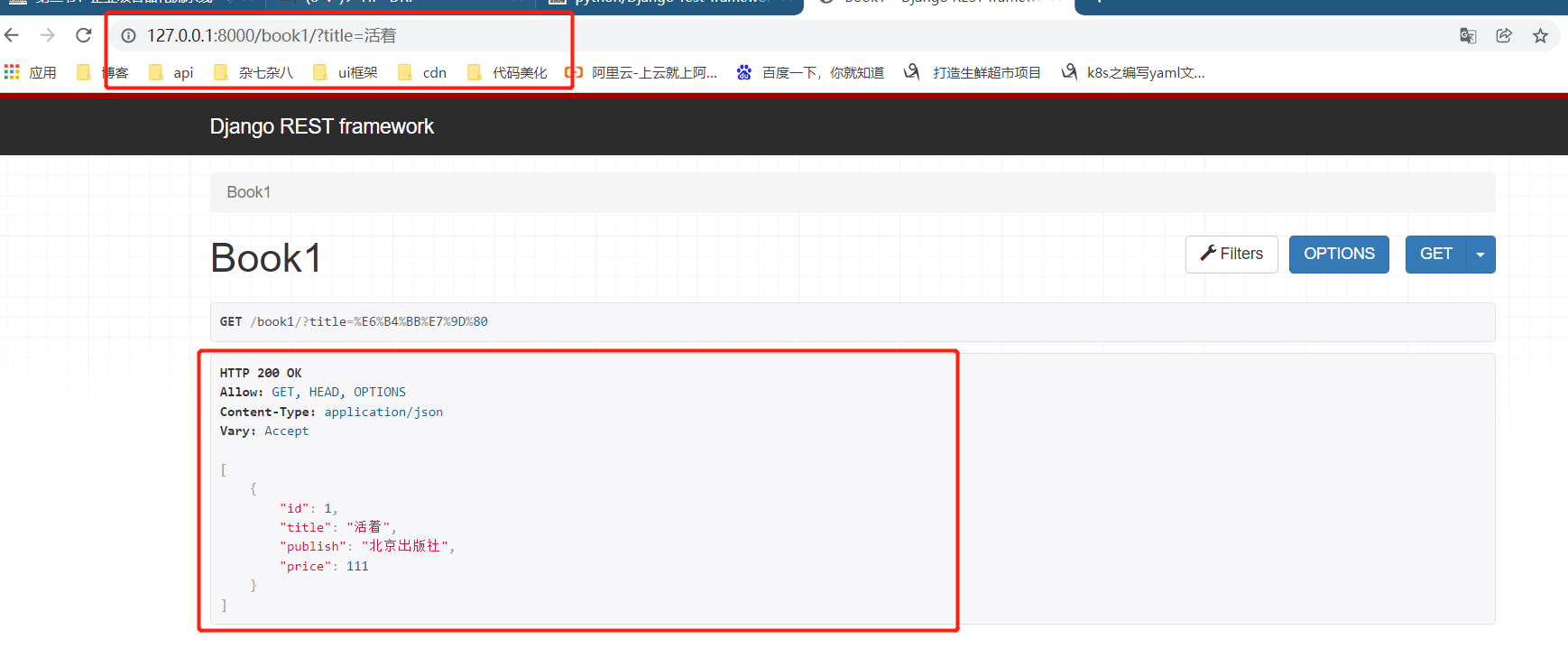
3.2.3使用方法2
# 方式二:使用内置的过滤类(可以自己写,使用第三方)
filter_backends=[SearchFilter,] ## 过滤类:可以自己写,也可以用内置,使用第三方
# SearchFilter类中通过反射获取的字段
search_fields=['name','publish'] # 按那个字段过滤,可以模糊匹配
# http://127.0.0.1:8000/book/?search=条件 并且支持模糊匹配
4.排序
4.1概念
对于列表数据,REST framework提供了OrderingFilter过滤器来帮助我们快速指明数据按照指定字段进行排序。
使用方法:
在类视图中设置filter_backends,使用rest_framework.filters.OrderingFilter过滤器,REST framework会在请求的查询字符串参数中检查是否包含了ordering参数,如果包含了ordering参数,则按照ordering参数指明的排序字段对数据集进行排序。
前端可以传递的ordering参数的可选字段值需要在ordering_fields中指明。
4.2配置
from rest_framework.generics import ListAPIView
from students.models import Student
from .serializers import StudentModelSerializer
from django_filters.rest_framework import DjangoFilterBackend
class Student3ListView(ListAPIView):
queryset = Student.objects.all()
serializer_class = StudentModelSerializer
filter_fields = ('age', 'sex')
# 因为局部配置会覆盖全局配置,所以需要重新把过滤组件核心类再次声明,
# 否则过滤功能会失效
filter_backends = [OrderingFilter,DjangoFilterBackend]
ordering_fields = ('id', 'age')
# 127.0.0.1:8000/books/?ordering=-age
# -id 表示针对id字段进行倒序排序
# id 表示针对id字段进行升序排序
5.分页
5.1配置
#分页
from rest_framework.generics import ListAPIView
#内置三种分页方式
from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination,LimitOffsetPagination,CursorPagination
#自定义分页
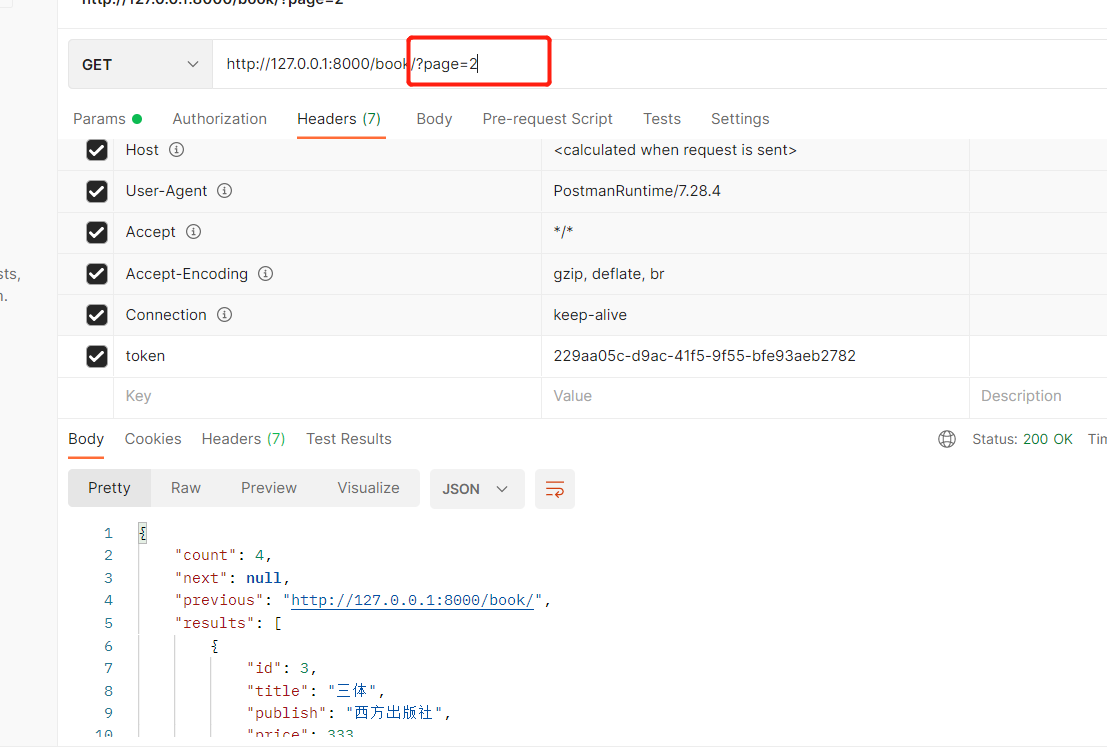
class MyPageNumberPagination(PageNumberPagination):
##http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/books1/?aaa=1&size=10 前端查询数据格式
page_size = 2 #每页数目
page_query_param = 'page' #前端发送的页数关键字名,默认为”page”
page_size_query_param='size' #前端发送的每页数目关键字名,默认为None 每页显示条数
max_page_size=10 #前端最多能设置的每页数量
# 自定义分页2
class MyLimitOffsetPagination(LimitOffsetPagination):
# limit:取几条数据 offset从第几个数据开始取 不算自己
#http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/books1/?limit=5&offset=2 前端数据格式
default_limit = 3 #每页显示几条数据
limit_query_param = 'limit' #开始数据
offset_query_param = 'offset' #多少数据
max_limit = None #限制最大取多少个数据
# 自定义分页3 效率高 因为上面的两个分页从最开始开始走 数据量很大推荐使用这个
#缺陷 只能取上一页下一页
class MyCursorPagination(CursorPagination):
cursor_query_param = 'cursor' #每一页查询的key
page_size = 2 #每页显示的条数
ordering = 'id' #排序字段
5.2使用
class BookView(ListAPIView):
queryset = models.Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = ser.BookModelSerialzer
#配置分页 也可以自定义类继承PageNumberPagination 下面指定时候指定自己的类
pagination_class = MyPageNumberPagination #MyLimitOffsetPagination MyCursorPagination
6.异常处理

settings里面配置
自定义异常类路径
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'app01.auth.my_exception_handler',
# 因为旧的exception_handler里面执行了一部分代码 需要这一部分 所以导入执行
from rest_framework.views import exception_handler
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import status
#自定义异常类
def my_exception_handler(exc, context):
#print(exc) #是一个对象,异常对象
#print(context) #哪个view的那个函数的错误
# exception_handler 有两种返回情况 一种是Response对象,一种是None 我们只需要处理None的情况
# 因为如果是Response 他已经处理过了 ,但是处理的不太符合期望 所以
response = exception_handler(exc, context)
#如果返回值response为None 取反 true 执行自己的异常处理
#重点 这里要记日志,方便以后查找错误
if not response:
#data错误信息 status错误状态码
return Response(data={'status': 999, 'msg': str(exc)}, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
else:
return Response(data={'status': 888, 'msg': response.data.get('detail')}, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
自定义异常:统一错误返回,记日志
7.自定义Response对象
from rest_framework.response import Response
#自定义Response
class APIResponse(Response):
def __init__(self,code=100,msg='成功',data=None,status=None,headers=None,**kwargs):
dic={'code':code,'msg':msg}
if data:
dic={'code':code,'msg':msg,'data':data}
dic.update(kwargs)
#屌用Response的__init__方法 传入data等
super().__init__(data=dic, status=status,headers=headers)
#视图类
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from app01.auth import APIResponse
class Book2(APIView):
authentication_classes = [] # 局部配置
permission_classes = []
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return APIResponse(token='asdasd')


