Python 第五十七章 Django 视图函数
视图
HTTPRequest对象就是咱们的视图函数的参数request
# print(request) #<WSGIRequest: GET '/home/'>
# # print(dir(request))
#
# print(request.path) #/home/ 纯路径
# print(request.path_info) #/home/ 纯路径
# print(request.get_full_path()) #/home/?a=1&b=2 全路径(不包含ip地址和端口)
# print(request.META) #请求头相关数据,是一个字典
# print(request.method) #GET
# print(request.GET)
# print(request.POST)
# print(request.body) 能够拿到请求数据部分的数据(post,get没有)
HTTPResponse对象
HTTPResponse('字符串')
render(request,'xx.html')
redirect 重定向#用法 redirect(路径) 示例:redirect('/index/')
FBV和CBV 视图(视图函数和视图类)
类视图 CBV
views.py
from django.views import View
class LoginView(View):
# def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# print('xx请求来啦!!!!')
# ret = super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
# print('请求处理的逻辑已经结束啦!!!')
# return ret
def get(self,request): #处理get请求直接定义get方法,不需要自己判断请求方法了,源码中用dispatch方法中使用了反射来处理的
print('小小小小')
return render(request,'login.html')
def post(self,request):
print(request.POST)
return HttpResponse('登录成功')
View 源码
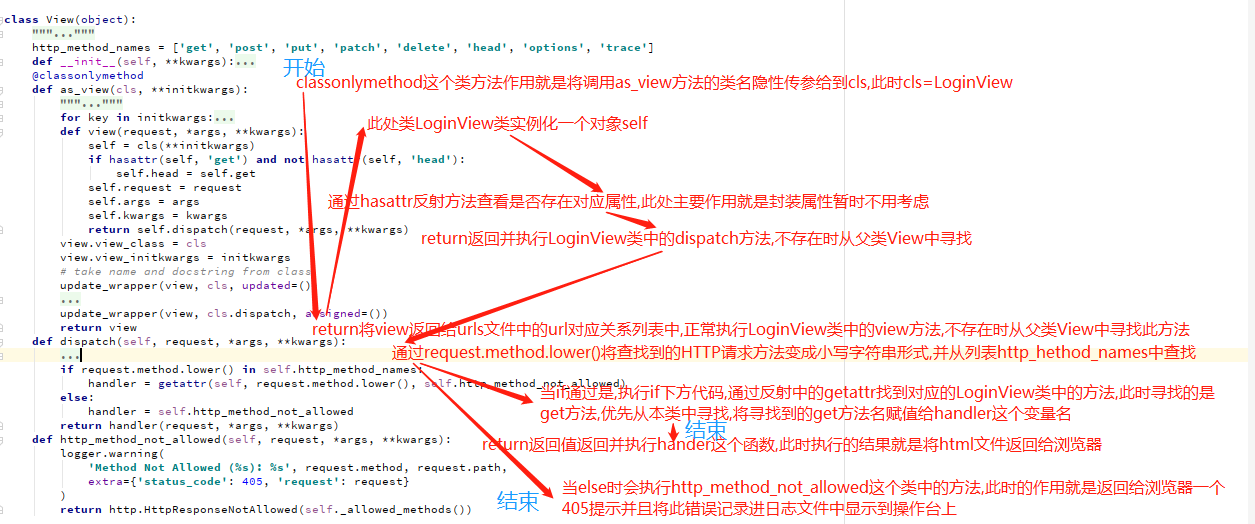
执行步骤:
1.类名去调用as_view方法
2.as_view返回一个view方法名
3.urls执行view方法
4.执行到view方法self = cls(**initkwargs)#实例化一个对象cls对应的就是 LoginView视图类
5. 继续往下执行return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)#这时self是LoginView视图类的实例化对象 去LoginView类中去寻找dispatch方法
6.LoginView视图类没有找到去对应的父类View去寻找
dispatch方法
7.找到http_method_names对应属性里面有各类方法
8.请求的方法名在这个属性中继续往下执行反射
9.利用反射去寻找对应的方法
#注意
getattr 第二个参数找不到就执行第三个参数 执行第三个方法直接报错返回 日志打印405
父类view
class View(object):
http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace']
@classonlymethod
def as_view(cls, **initkwargs):
for key in initkwargs:
if key in cls.http_method_names:
raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a "
"keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that."
% (key, cls.__name__))
if not hasattr(cls, key):
raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r. as_view "
"only accepts arguments that are already "
"attributes of the class." % (cls.__name__, key))
2.#as_view里面有一个view方法
def view(request, *args, **kwargs):
self = cls(**initkwargs)
3.#实例化cls方法(就是LoginView视图类) 拿到自己类的对象
if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'):
self.head = self.get
self.request = request
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
4.#执行到这发现 类调用一个方法 去试图类(LoginView)寻找dispatch方法,没有这个方法就去继承的父类去寻找 执行
view.view_class = cls
view.view_initkwargs = initkwargs
update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=())
update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=())
return view 1.#返回一个view方法
"""
dispatch方法
"""
```````````````````````````````````````
5.找到dispatch方法执行
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
#request.method.lower()取得请求对应的方法 方法名都是大写的所以需要小写对应
urls.py路由写法
url(r'^login/', views.LoginView.as_view()),
视图加装饰器
视图函数
def wrapper(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
print(11111)
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
print(22222)
return ret
return inner
@wrapper
def index(request):
print('xxxxx')
return HttpResponse('indexxxxxxxxx')
视图类
from django.utils.decorator import method_decorator
@method_decorator(wrapper,name='get') # 方式3
class LoginView(View):
# @method_decorator(wrapper) #方式2
# def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# print('xx请求来啦!!!!')
#
# ret = super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
#
# print('请求处理的逻辑已经结束啦!!!')
# return ret
# @method_decorator(wrapper) #方式1
def get(self,request):
print('小小小小')
return render(request,'login.html')
def post(self,request):
print(request.POST)
return HttpResponse('登录成功')
模板渲染
{{ 变量 }} {% 逻辑 %} -- 标签
万能的点
<h1>91李业网</h1>
<h2>{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>{{ d1.items }}</h2>
<h2>我是"{{ l1.1 }}"</h2>
<h2>{{ num }}</h2>
<h2>{{ obj.p }}</h2> #如果调用的方法需要传参,sorry用不了
过滤器(内置)
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/clschao/articles/10414811.html
标签
for循环标签
循环列表等
{% for person in person_list %}
<p>{{ person.name }}</p> <!--凡是变量都要用两个大括号括起来-->
{% endfor %}
循环字典
{% for key,val in dic.items %}
<p>{{ key }}:{{ val }}</p>
{% endfor %}
empty
{% for person in person_list %}
<p>{{ person.name }}</p> <!--凡是变量都要用两个大括号括起来-->
{% empty %}
<p>没有找到东西!</p>
{% endfor %}
forloop.counter 当前循环的索引值(从1开始),forloop是循环器,通过点来使用功能
forloop.counter0 当前循环的索引值(从0开始)
forloop.revcounter 当前循环的倒序索引值(从1开始)
forloop.revcounter0 当前循环的倒序索引值(从0开始)
forloop.first 当前循环是不是第一次循环(布尔值)
forloop.last 当前循环是不是最后一次循环(布尔值)
forloop.parentloop 本层循环的外层循环的对象,再通过上面的几个属性来显示外层循环的计数等
示例:
{% for i in d2 %}
{% for k,v in d1.items %}
<li>{{ forloop.counter }}-- {{ forloop.parentloop.counter }} === {{ k }} -- {{ v }}</li>
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
if判断标签
{% if num > 100 or num < 0 %}
<p>无效</p> <!--不满足条件,不会生成这个标签-->
{% elif num > 80 and num < 100 %}
<p>优秀</p>
{% else %} <!--也是在if标签结构里面的-->
<p>凑活吧</p>
{% endif %}
if语句支持 and 、or、==、>、<、!=、<=、>=、in、not in、is、is not判断,注意条件两边都有空格。
with
方法1
{% with total=business.employees.count %} #注意等号两边不能有空格
{{ total }} <!--只能在with语句体内用-->
{% endwith %}
方法2
{% with business.employees.count as total %}
{{ total }}
{% endwith %}

