android--------自定义控件 之 ViewGroup
前面几篇讲了自定义控件的组合控件,地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangqie/p/8985612.html
今天这篇博文主要来说说 自定义控件的 ViewGroup。
什么是ViewGroup?
ViewGroup是一种容器。它包含零个或以上的View及子View
ViewGroup有什么作用?
ViewGroup内部可以用来存放多个View控件,并且根据自身的测量模式,来测量View子控件,并且决定View子控件的位置。这在下面会逐步讲解它是怎么测量及决定子控件大小和位置的。
自定义控件
public class FlowLayoutb extends ViewGroup { private int horizontolSpacing; private int verticalSpacing; public FlowLayoutb(Context context) { super(context); init(context); } public FlowLayoutb(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) { super(context, attrs, defStyle); init(context); } private Line currentline;// 当前的行 private int useWidth = 0;// 当前行使用的宽度 private List<Line> mLines = new ArrayList<Line>(); private int width; public FlowLayoutb(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); init(context); } private void init(Context context) { horizontolSpacing = Util.dip2px(13, context); verticalSpacing = Util.dip2px(13, context); } // 测量 当前控件Flowlayout // 父类是有义务测量每个子View的 @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { mLines.clear(); currentline = null; useWidth = 0; /** * 获得此ViewGroup上级容器为其推荐的宽和高,以及计算模式 */ int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); // 计算出所有的childView的宽和高 measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight(); int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - getPaddingBottom() - getPaddingTop(); // 获取到宽和高 int childeWidthMode; int childeHeightMode; // 为了测量每个子View 需要指定每个子View测量规则 childeWidthMode = widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : widthMode; childeHeightMode = heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : heightMode; int childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childeWidthMode, width); int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childeHeightMode, height); currentline = new Line();// 创建了第一行 for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); // 测量每个子View child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); useWidth += measuredWidth;// 让当前行加上使用的长度 if (useWidth <= width) { currentline.addChild(child);//这时候证明当前的子View是可以放进当前的行里,放进去 useWidth += horizontolSpacing; } else { //换行 newLine(child); } } if (!mLines.contains(currentline)) { mLines.add(currentline);// 添加最后一行 } int totalheight = 0; for (Line line : mLines) { totalheight += line.getHeight(); } totalheight += verticalSpacing * (mLines.size() - 1) + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(); System.out.println(totalheight); setMeasuredDimension(width + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(), resolveSize(totalheight, heightMeasureSpec)); } private void newLine(View child) { mLines.add(currentline);// 记录之前的行 currentline = new Line();// 创建新的一行 currentline.addChild(child); useWidth = currentline.lineWidth; } private class Line { int height = 0; //当前行的高度 int lineWidth = 0; private List<View> children = new ArrayList<View>(); /** * 添加一个子View * * @param child */ public void addChild(View child) { children.add(child); if (child.getMeasuredHeight() > height) { height = child.getMeasuredHeight(); } lineWidth += child.getMeasuredWidth(); } public int getHeight() { return height; } /** * 返回子View的数量 * * @return */ public int getChildCount() { return children.size(); } public void layout(int l, int t) { lineWidth += horizontolSpacing * (children.size() - 1); int surplusChild = 0; int surplus = width - lineWidth; if (surplus > 0 && children.size() > 0) { surplusChild = surplus / children.size(); } for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) { View child = children.get(i); child.layout(l, t, l + child.getMeasuredWidth() + surplusChild, t + child.getMeasuredHeight()); l += child.getMeasuredWidth() + surplusChild; l += horizontolSpacing; } } } // 分配每个子View的位置 @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { l += getPaddingLeft(); t += getPaddingTop(); for (int i = 0; i < mLines.size(); i++) { Line line = mLines.get(i); line.layout(l, t); //交给每一行去分配 t += line.getHeight() + verticalSpacing; } } }
自定义ViewGroup的步骤:
- 继承ViewGroup,覆盖构造方法
- 重写onMeasure方法测量子控件和自身宽高
- 实现onLayout方法摆放子控件
效果图:
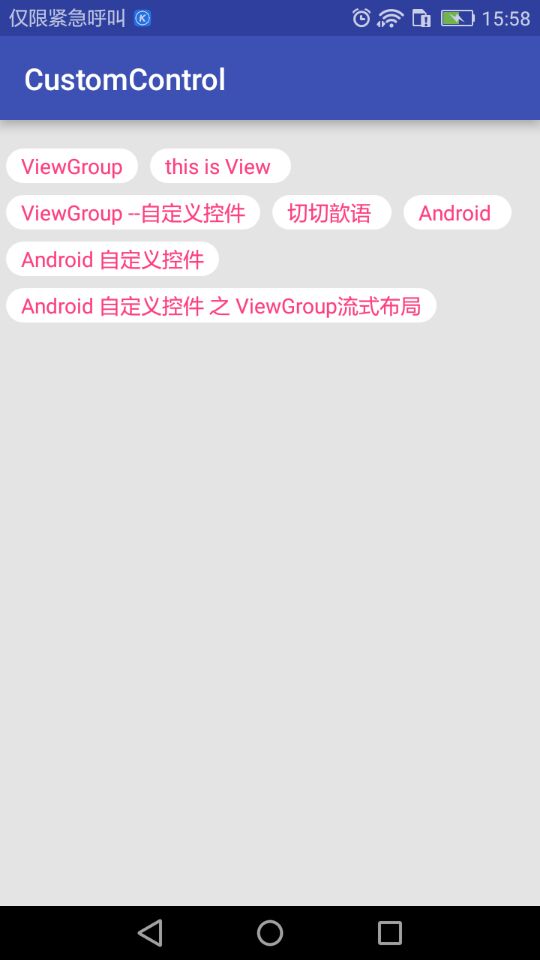

源码地址:https://github.com/DickyQie/android-custom-control
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/shineflowers/article/details/48055879
https://blog.csdn.net/zxt0601/article/details/50533658
https://blog.csdn.net/shakespeare001/article/details/51089453



