[译]ava 设计模式之职责链
(文章翻译自Java Design Pattern: Chain of Responsibility)
职责链模式的主要设计思想是为了构建一连串的处理单元,如果阈值满足的话那么这个单元就来处理这个请求。自从这个链构建以后,如果一个单元不满足,那么就会尝试调用下一个,以此类推。每一个请求会沿着这个链被处理。
职责链模式类图
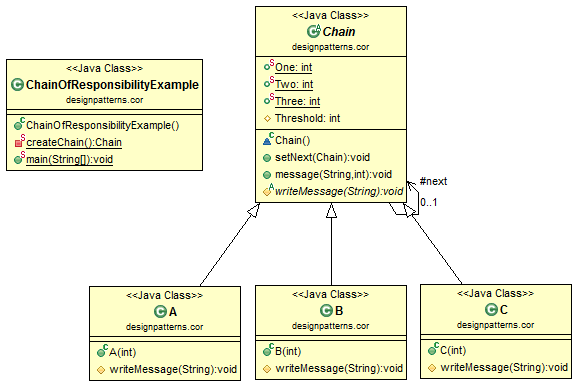
职责链Java 代码
package designpatterns.cor;
abstract class Chain {
public static int One = 1;
public static int Two = 2;
public static int Three = 3;
protected int Threshold;
protected Chain next;
public void setNext(Chain chain) {
next = chain;
}
public void message(String msg, int priority) {
//if the priority is less than Threshold it is handled
if (priority <= Threshold) {
writeMessage(msg);
}
if (next != null) {
next.message(msg, priority);
}
}
abstract protected void writeMessage(String msg);
}
class A extends Chain {
public A(int threshold) {
this.Threshold = threshold;
}
protected void writeMessage(String msg) {
System.out.println("A: " + msg);
}
}
class B extends Chain {
public B(int threshold) {
this.Threshold = threshold;
}
protected void writeMessage(String msg) {
System.out.println("B: " + msg);
}
}
class C extends Chain {
public C(int threshold) {
this.Threshold = threshold;
}
protected void writeMessage(String msg) {
System.out.println("C: " + msg);
}
}
public class ChainOfResponsibilityExample {
private static Chain createChain() {
// Build the chain of responsibility
Chain chain1 = new A(Chain.Three);
Chain chain2 = new B(Chain.Two);
chain1.setNext(chain2);
Chain chain3 = new C(Chain.One);
chain2.setNext(chain3);
return chain1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chain chain = createChain();
chain.message("level 3", Chain.Three);
chain.message("level 2", Chain.Two);
chain.message("level 1", Chain.One);
}
}
在这个例子中,Level1穿过了这个链中的每一个处理单元。
A: level 3
A: level 2
B: level 2
A: level 1
B: level 1
C: level 1

