java 多线程 Thread.join子线程结束父线程再运行;join(long):等待超时毫秒数
Join的使用
目的:当子线程运行结束后,父线程才能再继续运行
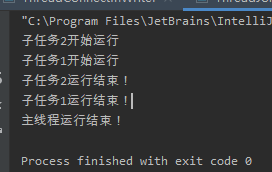
/** * @ClassName ThreadJoinExample * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/24. */ public class ThreadJoinExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Runnable r = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { String tName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); try { System.out.println(tName + "开始运行"); Thread.sleep(4000); System.out.println(tName +"运行结束!"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; Thread thread = new Thread(r,"子任务1"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(r,"子任务2"); thread.start(); thread2.start(); thread.join(); //子线程阻塞主线程,待子线程运行结束 thread2.join(); //子线程阻塞主线程,待子线程运行结束 Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("主线程运行结束!"); } }
不能interrupt中断一个有join()子线程的父线程
/** * @ClassName ThreadInterruptJoinThread * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/24. */ public class ThreadInterruptJoinThread { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread("parent"){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(getName() + "开始运行"); Thread thread1 = new Thread("child"){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(getName() + "开始运行"); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(getName() + "运行结束"); } }; thread1.start(); //thread1.join(); try { thread1.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(getName() + "运行结束"); } }; thread.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); thread.interrupt(); thread.join(); System.out.println("主线程运行结束"); } }
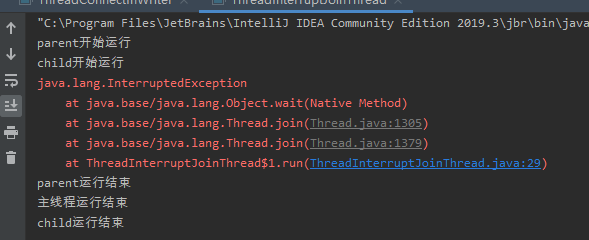
如上代码执行结果:join的child子线程还没结束,父线程就被interrupt中断,会导致父线程异常,且不再等待子线程child运行结束。
join(long):等待指定时间不结束就不等待了
/** * @ClassName ThreadJoinTime * @projectName: object1 * @author: Zhangmingda * @description: XXX * date: 2021/4/24. */ public class ThreadJoinTime { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread("child"){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("子线程开始运行"); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("子线程运行结束"); } }; thread.start(); thread.join(1000); System.out.println("主线程代码运行结束"); } }
posted on 2021-04-24 21:53 zhangmingda 阅读(212) 评论(0) 收藏 举报

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号