POJ3414—Pots(bfs加回溯)
http://poj.org/problem?id=3414
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |||
| Total Submissions: 9996 | Accepted: 4198 | Special Judge | ||
Description
You are given two pots, having the volume of A and B liters respectively. The following operations can be performed:
- FILL(i) fill the pot i (1 ≤ i ≤ 2) from the tap;
- DROP(i) empty the pot i to the drain;
- POUR(i,j) pour from pot i to pot j; after this operation either the pot j is full (and there may be some water left in the pot i), or the pot i is empty (and all its contents have been moved to the pot j).
Write a program to find the shortest possible sequence of these operations that will yield exactly C liters of water in one of the pots.
Input
On the first and only line are the numbers A, B, and C. These are all integers in the range from 1 to 100 and C≤max(A,B).
Output
The first line of the output must contain the length of the sequence of operations K. The following K lines must each describe one operation. If there are several sequences of minimal length, output any one of them. If the desired result can’t be achieved, the first and only line of the file must contain the word ‘impossible’.
Sample Input
3 5 4
Sample Output
6 FILL(2) POUR(2,1) DROP(1) POUR(2,1) FILL(2) POUR(2,1)
题目大意:
给出了两个瓶子的容量A,B, 以及一个目标水量C,
对A、B可以有如下操作:
FILL(i) fill the pot i (1 ≤ i ≤ 2) from the tap;
DROP(i) empty the pot i to the drain;
POUR(i,j) pour from pot i to pot j; after this operation either the pot j is full (and there may be some water left in the pot i), or the pot i is empty (and all its contents have been moved to the pot j).
问经过哪几个操作后能使得任意一个瓶子的残余水量为C。
若不可能得到则输出impossible
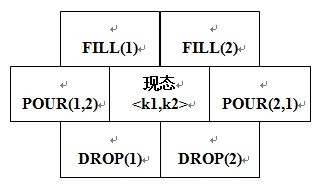
解题思路:
6入口的bfs
把两个两个桶的某个同一时间的状态看做一个整体,视为初态
可对初态进行六种操作,即FILL(1),FILL(2),DROP(1),DROP(2),POUR(1,2),POUR(2,1)
这6种操作在我的程序中分别用一个整数进行记录;
1z0: 清空z瓶子
2z0: 装满z瓶子
3xy: 从x瓶倒向y瓶
(x,y,z∈{1,2})
这样在输出操作时就能根据数字的特点 进行选择性输出 了
最后我简单说说各种操作的数学表达式:
设1瓶的容量为v1,残余水量为k1, 2瓶的容量为v2,残余水量为 k2
那么 fill(1) 相当于 k1=v1 fill(2)相当于k2=v2 drop(1)相当于k1=0 drop(2)相当于k2=0
对于Pour(1,2),若k1+k2<=v2,则 k2=k1+k2 , k1=0 (有先后顺序)
否则k1=k1+k2-v2 , k2=v2 (有先后顺序)
Pour(2,1)亦同理
利用pre[i]数组来存储当前节点的父节点的位置信息。
之前不会回溯,感到这题无从下手,之后要多做这种题。
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; int a,b,c,s,e; int v[101][101]; struct node { int x,y,ans,d,d1; }q[100001],t,f; int pre[100001],p[100001]; void FILI(int xx,int yy,int zz,int i,int ff) { if(i==0) { f.x=a; f.y=yy; if(v[f.x][f.y]==0) { f.ans=zz+1; f.d=1; f.d1=0; q[e]=f; pre[e]=ff; e++; v[f.x][f.y]=1; } } else if(i==1) { f.x=xx; f.y=b; if(v[f.x][f.y]==0) { f.ans=zz+1; f.d=0; f.d1=1; q[e]=f; pre[e]=ff; e++; v[f.x][f.y]=1; } } } void POUR(int xx,int yy,int zz,int i,int ff) { if(i==2) { f.x=0; f.y=yy; if(v[f.x][f.y]==0) { f.ans=zz+1; f.d=2; f.d1=0; q[e]=f; pre[e]=ff; e++; v[f.x][f.y]=1; } } else if(i==3) { f.x=xx; f.y=0; if(v[f.x][f.y]==0) { f.ans=zz+1; f.d=0; f.d1=2; q[e]=f; pre[e]=ff; e++; v[f.x][f.y]=1; } } } void D(int xx,int yy,int zz,int i,int ff) { if(i==4) { if(xx+yy>=a) { f.x=a; f.y=yy+xx-a; } else { f.x=xx+yy; f.y=0; } if(v[f.x][f.y]==0) { f.ans=zz+1; f.d=3; f.d1=0; q[e]=f; pre[e]=ff; e++; v[f.x][f.y]=1; } } else if(i==5) { if(xx+yy>=b) { f.y=b; f.x=xx+yy-b; } else { f.y=xx+yy; f.x=0; } if(v[f.x][f.y]==0) { f.ans=zz+1; f.d=0; f.d1=3; q[e]=f; pre[e]=ff; e++; v[f.x][f.y]=1; } } } void print(int s) { int ss=0; for(int i=s;i!=-1;i=pre[i]) { p[ss++]=i; } for(int i=ss-1;i>=0;i--) { if(q[p[i]].d==1||q[p[i]].d1==1) { if(q[p[i]].d==1) { printf("FILL(1)\n"); } else printf("FILL(2)\n"); } else if(q[p[i]].d==2||q[p[i]].d1==2) { if(q[p[i]].d==2) { printf("DROP(1)\n"); } else printf("DROP(2)\n"); } else if(q[p[i]].d==3||q[p[i]].d1==3) { if(q[p[i]].d==3) { printf("POUR(2,1)\n"); } else printf("POUR(1,2)\n"); } } } void BFS() { e=0; s=0; memset(pre,-1,sizeof(pre)); memset(v,0,sizeof(v)); v[0][0]=1; t.x=0; t.y=0; t.ans=0; t.d=0; t.d1=0; q[e++]=t; while(s<e) { t=q[s++]; if(t.x==c||t.y==c) { printf("%d\n",t.ans); print(s-1); return ; } for(int i=0;i<6;i++) { if(i==0) FILI(t.x,t.y,t.ans,i,s-1); else if(i==1) FILI(t.x,t.y,t.ans,i,s-1); else if(i==2) POUR(t.x,t.y,t.ans,i,s-1); else if(i==3) POUR(t.x,t.y,t.ans,i,s-1); else if(i==4) D(t.x,t.y,t.ans,i,s-1); else if(i==5) D(t.x,t.y,t.ans,i,s-1); } } printf ("impossible\n"); } int main() { while(scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)!=EOF) { BFS(); } return 0; }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 张高兴的大模型开发实战:(一)使用 Selenium 进行网页爬虫
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构