深入理解Spring系列之十二:@Transactional是如何工作的
首先从tx:annotation-driven/说起。配置了tx:annotation-driven/,就必定有对应的标签解析器类,查看NamespaceHandler接口的实现类,可以看到一个TxNamespaceHandler,它注册了AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser对annotation-driven元素进行解析。
public class TxNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static final String TRANSACTION_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE = "transaction-manager";
static final String DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME = "transactionManager";
public TxNamespaceHandler() {
}
static String getTransactionManagerName(Element element) {
return element.hasAttribute("transaction-manager") ? element.getAttribute("transaction-manager") : "transactionManager";
}
public void init() {
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("advice", new TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser());
// <tx:annotation-driven/> 标签解析器
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser());
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("jta-transaction-manager", new JtaTransactionManagerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
进入AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser类,重点看parse方法。
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
this.registerTransactionalEventListenerFactory(parserContext);
String mode = element.getAttribute("mode");
if ("aspectj".equals(mode)) {
this.registerTransactionAspect(element, parserContext);
} else {
AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser.AopAutoProxyConfigurer.configureAutoProxyCreator(element, parserContext);
}
return null;
}
从代码中可以看出,如果<tx:annotation-driven/>中没有配置mode参数,则默认使用代理模式进行后续处理;如果配置了mode=aspectj,则使用aspectj代码织入模式进行后续处理。
本篇分析使用代理模式的代码,进入AopAutoProxyConfigurer.configureAutoProxyCreator方法。
public static void configureAutoProxyCreator(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 重点代码
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
String txAdvisorBeanName = "org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor";
if (!parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName)) {
Object eleSource = parserContext.extractSource(element);
RootBeanDefinition sourceDef = new RootBeanDefinition("org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource");
sourceDef.setSource(eleSource);
sourceDef.setRole(2);
String sourceName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(sourceDef);
RootBeanDefinition interceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(TransactionInterceptor.class);
interceptorDef.setSource(eleSource);
interceptorDef.setRole(2);
AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser.registerTransactionManager(element, interceptorDef);
interceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
String interceptorName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(interceptorDef);
RootBeanDefinition advisorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor.class);
advisorDef.setSource(eleSource);
advisorDef.setRole(2);
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("transactionAttributeSource", new RuntimeBeanReference(sourceName));
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("adviceBeanName", interceptorName);
if (element.hasAttribute("order")) {
advisorDef.getPropertyValues().add("order", element.getAttribute("order"));
}
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(txAdvisorBeanName, advisorDef);
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), eleSource);
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(sourceDef, sourceName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(interceptorDef, interceptorName));
compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(advisorDef, txAdvisorBeanName));
parserContext.registerComponent(compositeDef);
}
}
上面的代码中标出了一行核心代码,容易被忽略。进入 AopNamespaceUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary 方法。
public static void registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
// 重点代码
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}
重点关注上面标出的代码,进入AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法。
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
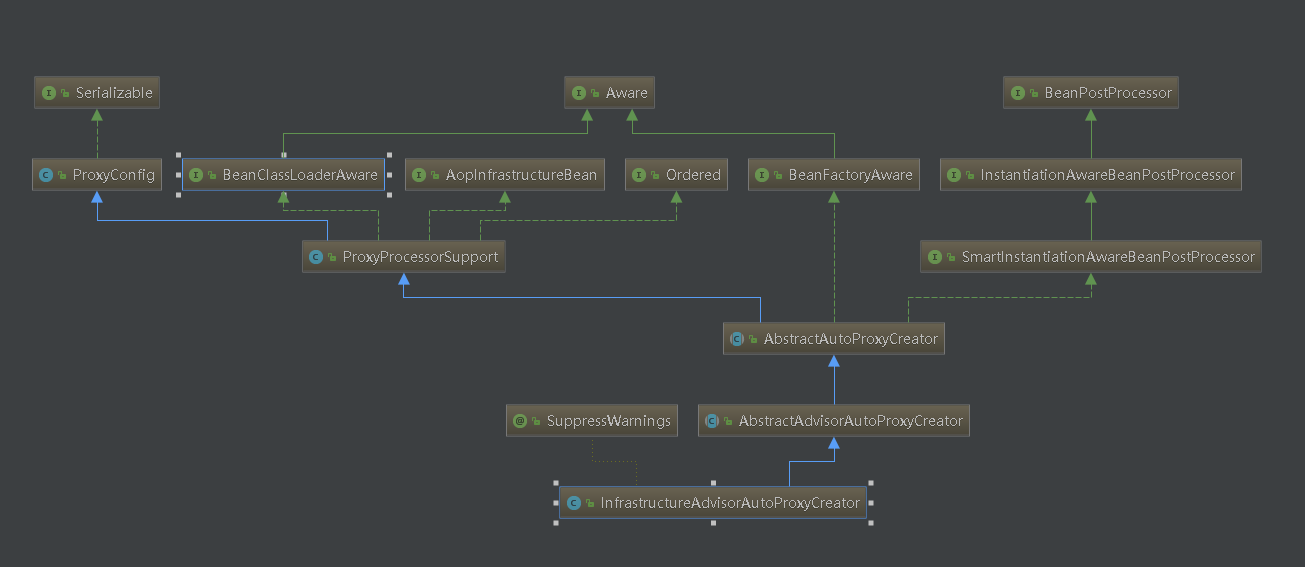
上面中的代码向Spring容器中注册了一个InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类。可能会疑问为什么要注册这个类,有什么作用?
查看InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类继承关系。
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
// 重点代码: 是创建代理对象的核心方法
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
其中 wrapIfNecessary 方法 是创建代理对象的核心方法。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//重点代码:获取事务属性切面
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 重点代码: 创建一个AOP代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法会遍历容器中所有的切面,查找与当前实例化bean匹配的切面,这里就是获取事务属性切面,查找@Transactional注解及其属性值,具体实现比较复杂,这里暂不深入分析,最终会得到 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 实例,然后根据得到的切面进入createProxy方法,创建一个AOP代理。
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//重点代码
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
进入ProxyFactory.getProxy方法。
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 重点代码:进入 createAopProxy() 方法
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
createAopProxy方法决定使用JDK还是Cglib创建代理。createAopProxy方法代码如下:
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
// 重点代码: 进入 createAopProxy 方法
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
可以看出默认是使用JDK动态代理创建代理,如果目标类是接口,则使用JDK动态代理,否则使用Cglib。这里分析使用JDK动态代理的方式,进入JdkDynamicAopProxy.getProxy方法。
@Override
public Object getProxy() {
return getProxy(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
@Override
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
//重点代码
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
可以看到很熟悉的创建代理的代码Proxy.newProxyInstance。这里要注意的是,newProxyInstance方法的最后一个参数是JdkDynamicAopProxy类本身,也就是说在对目标类进行调用的时候,会进入JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法。这里只关注JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法的重点代码。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation invocation;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
// Get the interception chain for this method.
// 重点代码
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
// 重点代码
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// 重点代码
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}

