重学Java设计模式-创建者模式-工厂方法模式
重学Java设计模式-创建者模式-工厂方法模式
内容摘自:重学 Java 设计模式:实战工厂方法模式「多种类型商品不同接口,统一发奖服务搭建场景」 | bugstack 虫洞栈
工厂方法模式介绍#
工厂模式又称工厂方法模式,是一种创建型设计模式,其在父类中提供一个创建对象的方法, 允许子类决定实例化对象的类型。
这种设计模式也是 Java 开发中最常见的一种模式,它的主要意图是定义一个创建对象的接口,让其子类自己决定实例化哪一个工厂类,工厂模式使其创建过程延迟到子类进行。
简单说就是为了提供代码结构的扩展性,屏蔽每一个功能类中的具体实现逻辑。让外部可以更加简单的只是知道调用即可,同时,这也是去掉众多ifelse的方式。当然这可能也有一些缺点,比如需要实现的类非常多,如何去维护,怎样减低开发成本。但这些问题都可以在后续的设计模式结合使用中,逐步降低。
模拟发奖多种商品#
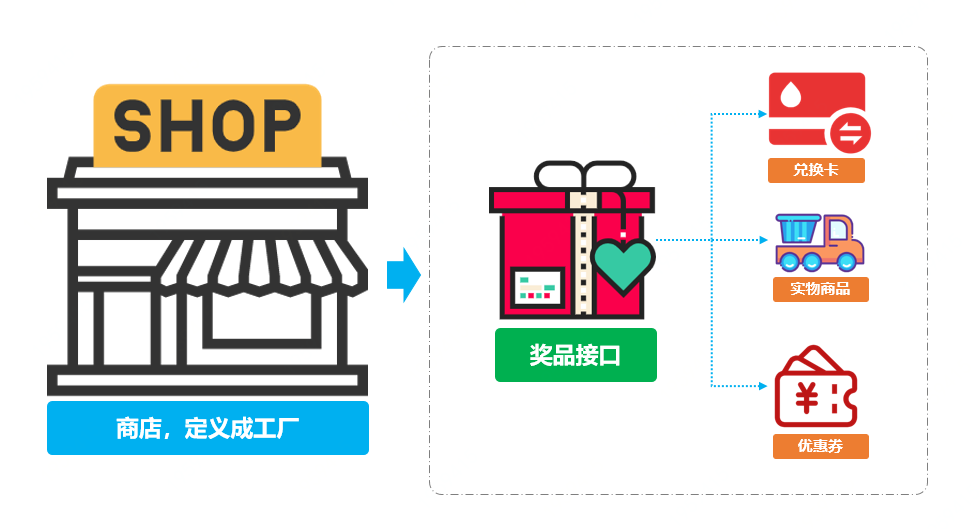
模拟积分兑换中的发放多种类型商品,假如现在我们有如下三种类型的商品接口;
| 序号 | 类型 | 接口 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 优惠券 | CouponResult sendCoupon(String uId, String couponNumber, String uuid) |
| 2 | 实物商品 | Boolean deliverGoods(DeliverReq req) |
| 3 | 第三方爱奇艺兑换卡 | void grantToken(String bindMobileNumber, String cardId) |
从以上接口来看有如下信息:
- 三个接口返回类型不同,有对象类型、布尔类型、还有一个空类型。
- 入参不同,发放优惠券需要仿重、兑换卡需要卡ID、实物商品需要发货位置(对象中含有)。
- 另外可能会随着后续的业务的发展,会新增其他种商品类型。因为你所有的开发需求都是随着业务对市场的拓展而带来的。
工厂模式优化代码#
1. 工程结构#
itstack-demo-design-1-02
└── src
├── main
│ └── java
│ └── org.itstack.demo.design
│ ├── store
│ │ ├── impl
│ │ │ ├── CardCommodityService.java
│ │ │ ├── CouponCommodityService.java
│ │ │ └── GoodsCommodityService.java
│ │ └── ICommodity.java
│ └── StoreFactory.java
└── test
└── java
└── org.itstack.demo.design.test
└── ApiTest.java
2. 代码实现#
2.1 定义发奖接口#
public interface ICommodity {
void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception;
}
- 所有的奖品无论是实物、虚拟还是第三方,都需要通过我们的程序实现此接口进行处理,以保证最终入参出参的统一性。
- 接口的入参包括;
用户ID、奖品ID、业务ID以及扩展字段用于处理发放实物商品时的收获地址。
2.2 实现奖品发放接口#
优惠券
public class CouponCommodityService implements ICommodity {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CouponCommodityService.class);
private CouponService couponService = new CouponService();
public void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception {
CouponResult couponResult = couponService.sendCoupon(uId, commodityId, bizId);
logger.info("请求参数[优惠券] => uId:{} commodityId:{} bizId:{} extMap:{}", uId, commodityId, bizId, JSON.toJSON(extMap));
logger.info("测试结果[优惠券]:{}", JSON.toJSON(couponResult));
if (!"0000".equals(couponResult.getCode())) throw new RuntimeException(couponResult.getInfo());
}
}
实物商品
public class GoodsCommodityService implements ICommodity {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GoodsCommodityService.class);
private GoodsService goodsService = new GoodsService();
public void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception {
DeliverReq deliverReq = new DeliverReq();
deliverReq.setUserName(queryUserName(uId));
deliverReq.setUserPhone(queryUserPhoneNumber(uId));
deliverReq.setSku(commodityId);
deliverReq.setOrderId(bizId);
deliverReq.setConsigneeUserName(extMap.get("consigneeUserName"));
deliverReq.setConsigneeUserPhone(extMap.get("consigneeUserPhone"));
deliverReq.setConsigneeUserAddress(extMap.get("consigneeUserAddress"));
Boolean isSuccess = goodsService.deliverGoods(deliverReq);
logger.info("请求参数[优惠券] => uId:{} commodityId:{} bizId:{} extMap:{}", uId, commodityId, bizId, JSON.toJSON(extMap));
logger.info("测试结果[优惠券]:{}", isSuccess);
if (!isSuccess) throw new RuntimeException("实物商品发放失败");
}
private String queryUserName(String uId) {
return "花花";
}
private String queryUserPhoneNumber(String uId) {
return "15200101232";
}
}
第三方兑换卡
public class CardCommodityService implements ICommodity {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CardCommodityService.class);
// 模拟注入
private IQiYiCardService iQiYiCardService = new IQiYiCardService();
public void sendCommodity(String uId, String commodityId, String bizId, Map<String, String> extMap) throws Exception {
String mobile = queryUserMobile(uId);
iQiYiCardService.grantToken(mobile, bizId);
logger.info("请求参数[爱奇艺兑换卡] => uId:{} commodityId:{} bizId:{} extMap:{}", uId, commodityId, bizId, JSON.toJSON(extMap));
logger.info("测试结果[爱奇艺兑换卡]:success");
}
private String queryUserMobile(String uId) {
return "15200101232";
}
}
- 从上面可以看到每一种奖品的实现都包括在自己的类中,新增、修改或者删除都不会影响其他奖品功能的测试,降低回归测试的可能。
- 后续在新增的奖品只需要按照此结构进行填充即可,非常易于维护和扩展。
- 在统一了入参以及出参后,调用方不在需要关心奖品发放的内部逻辑,按照统一的方式即可处理。
2.3 创建商店工厂#
public class StoreFactory {
public ICommodity getCommodityService(Integer commodityType) {
if (null == commodityType) return null;
if (1 == commodityType) return new CouponCommodityService();
if (2 == commodityType) return new GoodsCommodityService();
if (3 == commodityType) return new CardCommodityService();
throw new RuntimeException("不存在的商品服务类型");
}
}
- 这里我们定义了一个商店的工厂类,在里面按照类型实现各种商品的服务。可以非常干净整洁的处理你的代码,后续新增的商品在这里扩展即可。如果你不喜欢
if判断,也可以使用switch或者map配置结构,会让代码更加干净。 - 另外很多代码检查软件和编码要求,不喜欢if语句后面不写扩展,这里是为了更加干净的向你体现逻辑。在实际的业务编码中可以添加括号。
3. 测试验证#
编写测试类:
@Test
public void test_commodity() throws Exception {
StoreFactory storeFactory = new StoreFactory();
// 1. 优惠券
ICommodity commodityService_1 = storeFactory.getCommodityService(1);
commodityService_1.sendCommodity("10001", "EGM1023938910232121323432", "791098764902132", null);
// 2. 实物商品
ICommodity commodityService_2 = storeFactory.getCommodityService(2);
Map<String,String> extMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
extMap.put("consigneeUserName", "谢飞机");
extMap.put("consigneeUserPhone", "15200292123");
extMap.put("consigneeUserAddress", "吉林省.长春市.双阳区.XX街道.檀溪苑小区.#18-2109");
commodityService_2.sendCommodity("10001","9820198721311","1023000020112221113", extMap);
// 3. 第三方兑换卡(爱奇艺)
ICommodity commodityService_3 = storeFactory.getCommodityService(3);
commodityService_3.sendCommodity("10001","AQY1xjkUodl8LO975GdfrYUio",null,null);
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~