Flask初识
Flask是一个Python编写的Web 微框架,让我们可以使用Python语言快速实现一个网站或Web服务。
一、安装Flask模块
pip install flask
二、运行第一个Flask程序
打开一个Python文件,输入下面的内容并运行该文件。然后访问localhost:5000/index,我们应当可以看到浏览器上输出了Hello World
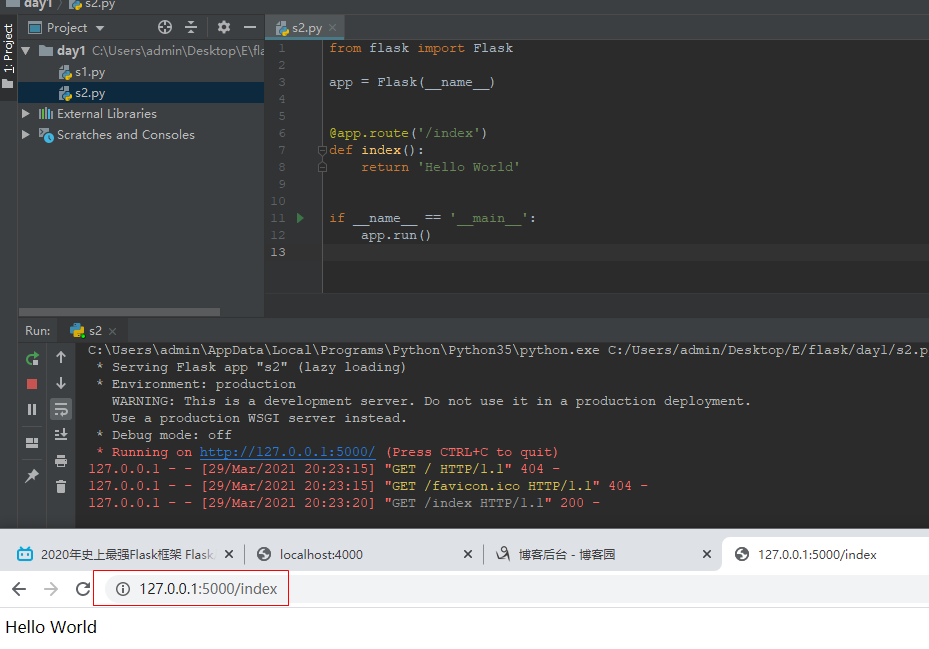
from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/index') def index(): return 'Hello World' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
三、调试模式
Flask内置了调试模式,可以自动重载代码并显示调试信息。这需要我们开启调试模式:FLASK_DEBUG=1,然后再次运行程序,会看到有这样的输出。这时候如果再次修改代码,会发现这次Flask会自动重启。
* Restarting with stat
* Debugger is active!
* Debugger PIN: 157-063-180
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
四、Flask快速使用示例:用户登录
app.py:
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect, session app = Flask(__name__) app.secret_key = '1121' # 对session进行加密 USER_DICT = { '1': {'name': '大军', 'age': 18}, '2': {'name': '大志', 'age': 25}, '3': {'name': '梅凯', 'age': 10}, '4': {'name': '院长', 'age': 69} } @app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST']) def index(): if request.method == 'GET': return render_template('login.html')
# request.form获取POST传过来的数据 usr = request.form.get('usr') pwd = request.form.get('pwd') if usr == 'ZGS' and pwd == '1121': # 用户信息放入session session['usr_info'] = usr return redirect('/home') else: return render_template('login.html', msg='用户名或密码错误') # return render_template('login.html', **{'msg:'用户名或密码错误'}) @app.route('/home') def home(): usr_info = session.get('usr_info') if not usr_info: return redirect('/login') return render_template('index.html', usr_dict=USER_DICT) @app.route('/logout') def logout(): del session['usr_info'] return redirect('/login') @app.route('/detail') def detail(): usr_info = session.get('usr_info') if not usr_info: return redirect('/login') uid = request.args.get('uid') info = USER_DICT.get(uid) return render_template('detail.html', info=info) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
login.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-cn"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>休息系统,用户登录</title> </head> <body> <h1>登录</h1> <form method="post"> <input type="text" name="usr"> <input type="password" name="pwd"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> {{msg}} </form> </body> </html>
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-cn"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <ul> {% for k,v in usr_dict.items()%} <li> {{v.name}} <a href="/detail?uid={{k}}">查看详细</a></li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html>
detail.html:
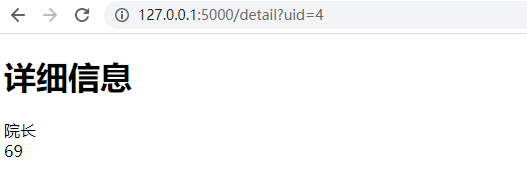
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-cn"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>详细信息</title> </head> <body> <h1>详细信息</h1> <div>{{info.name}}</div> <div>{{info.age}}</div> </body> </html>
页面效果:
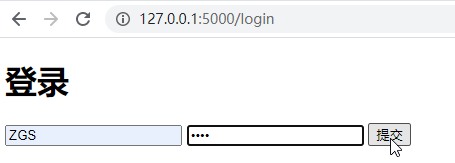
输入用户名密码,点击登录:
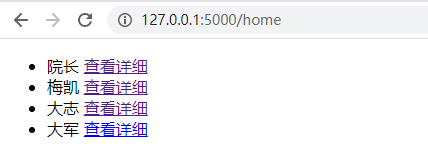
点击查看详情:
五、各参数解释
1、路由:
路由通过使用Flask的app.route装饰器来设置
2、URL:
在Web程序中常常需要获取某个页面的URL,在Flask中需要使用url_for('方法名')来构造对应方法的URL
3、HTTP方法:
需要处理具体的HTTP方法,在Flask中使用route装饰器的method参数设置
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST']) def index(): if request.method == 'GET': return render_template('login.html')
4、静态文件:
Web程序中常常需要处理静态文件,在Flask中需要使用url_for函数并指定static端点名和文件名。在下面的例子中,实际的文件应放在static/文件夹下。
url_for('static', filename='style.css')
5、生成模板
Flask默认使用Jinja2作为模板,模板文件需要放在templates文件夹下。使用 Jinja 模板,只需要使用render_template函数并传入模板文件名和参数名。
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect, session app = Flask(__name__) USER_DICT = { '1': {'name': '大军', 'age': 18}, '2': {'name': '大志', 'age': 25}, '3': {'name': '梅凯', 'age': 10}, '4': {'name': '院长', 'age': 69} } @app.route('/home') def home(): usr_info = session.get('usr_info') if not usr_info: return redirect('/login') return render_template('index.html', usr_dict=USER_DICT)
相应模板:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-cn"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <ul> {% for k,v in usr_dict.items()%} <li> {{v.name}} <a href="/detail?uid={{k}}">查看详细</a></li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html>
页面访问:

6、Request 对象
Request 对象是一个全局对象,利用它的属性和方法,我们可以方便的获取从页面传递过来的参数。
method属性会返回HTTP方法的类似,例如post和get。
form属性是一个字典,如果数据是POST类型的表单,就可以从form属性中获取:request.form.get('usr')。如果数据是由GET方法传送过来的,可以使用args属性获取:request.args.get(uid)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号